Understanding Weather - Smyrna Middle School
advertisement

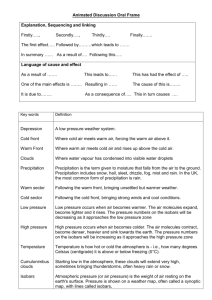
Understanding Weather Carin Miranda Smyrna Middle School Winter 2013 Water in the Air • Evaporation is when water changes from a liquid to a gas. • When air reaches its dew point relative humidity is at 100% Clouds • Nimbostratus clouds will bring light to heavy continuous rainy weather. • Cumulonimbus clouds are large thunderstorm clouds that produce precipitation. • Altocumulus clouds are puffy mid-level clouds. • Cirrus clouds are high clouds made of ice crystals. Precipitation • Sleet-Starts as rain then freezes in the air. • Snow-Water vapor changes directly into a solid because of cold temperatures. • Hail-Forms when precipitation is sent back up into the clouds many times. Air Masses • • • • • • • • Continental polar (cP) dry and cold Maritime polar (mP) wet and cold Continental tropical (cT) dry and warm Maritime tropical (mT) wet and warm C=dry P=cold M=wet t-=warm Fronts • Warm front-warm air moves over cold air and replaces it. • Stationary front-Not moving. Brings many days of cloudy, wet weather. • Cold front-cold air mass displaces a warm air mass. • Occluded front-warm air mass is caught between two cold air masses and is forced to rise. Lots of precipitation. Meteorology • Images of weather systems on television come from weather satellites. • From a weather map you can tell the locations of cold and warm fronts. • The lines connecting points of equal pressure on weather maps are called isobars. • Isobars help meteorologists by showing areas of high and low pressure. Vocabulary • • • • • • Humidity Air mass Front Barometric pressure Meteorologist Psychrometer Vocabulary 2 • • • • • • Thermometer Barometer Anemometer Rain Gauge Wind Vane Wind Vocabulary 3 • • • • • • Hygrometer Weather Relative Humidity Condensation Cloud Precipitation