PROPERTY STUDENT NOTES COPY
advertisement

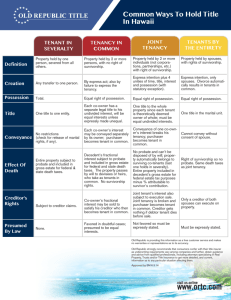
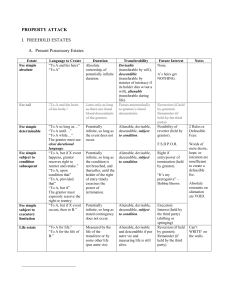
REAL & INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY Mr. Valanzano Business Law What is property? __________ – something that is _________ or ________, which is subject to _________ and a ________________________ Example: ◦ If you own ______ and a _______, the legal rights you have are: To _________, _______, and enjoy it Dispose of (by ______ or _____), consume, or ______ it Give it away by ________ after death _________ your property to a __________ ____________ of Property _______ Property – also called __________; ______ and anything __________________ to the land _______ Property – goods that are _______ or ________ and the ________ to use those goods ________________ Property – something a person ________; also known as _________ property ◦ Examples: ___________, patents, ____________, servicemarks, ______________ Intellectual Property Copyright – ______________________________________ ◦ Owner has right to _________, sell, _______, or display the work. ◦ Examples: books, paintings, music ◦ _______________ – the unauthorized copying, sale, display, or performance of the work _____________ – a _____________________ that identifies a __________ of a particular manufacturer or merchant ◦ Must be ________________________________ the product ◦ _______________ – a unique word, mark, or symbol that identifies a service instead of a product ________ – the grant of the exclusive right to make, use, and sell a ________________________ product or process ◦ Something no one has ever thought of the product or process before ◦ The product or process can _____________________ ________________ – commercially valuable information that the owner attempts to keep a secret Features of Intellectual Property What is protected? Registration required? Duration Examples Prescription drugs; processes to make industrial chemicals Books, poems, songs, paintings, photographs Logos, emblems, catchphrases, slogans How is property acquired? By ___________ – property may be acquired and transferred, or bought and sold, by contract By __________ – to create a valid gift, the donor must do 2 things: ___________________________________________________ By ____________ – the right of an owner of property to an increase in that property By __________________ – personal property rights can be acquired by original production By ________ – lost (________________) property becomes owned by the finder if not claimed within ____ days; mislaid (________________ ________________) property is required to be returned to owner By _____________ – taking possession of personal property that belongs to no one else By _______________ – real and personal property can be acquired by inheritance through a valid will; if no will is left, the state determines how to divide property among surviving relatives ___________ of Ownership An owner of property is not permitted to use that property in an ___________ or ____________ manner that ______________. Federal, state, and local governments may adopt laws to protect the public __________________ _________________, which may limit ownership and freedom of use. Examples: ◦ ________________________________________ __________________ ◦ _______________________________________ ◦ ________________________________________ __________________ Forms of Ownership _________________________ – exists when someone owns property by themselves ______________ – when two or more people have ownership rights in the same property ◦ _______________________ – no co-owner can exclude another co-owner from any physical portion of the property ◦ ______________________ – allows any co-owner to require the division of the property among the co-owners Types of Co-ownership: ◦ ______________________ – the equal co-ownership of the same property with the right of survivorship (if one owner dies, their claim is divided equally among remaining tenants) ◦ ________________ – shares may be unequal and there is no right of survivorship (if a co-owner dies, their share is passed to any heirs) ◦ _______________________ – form of co-ownership limited to married couples and has the right of survivorship; shares are equal and may not be sold without the other’s consent ◦ _______________________ – all property acquired by a married couple during their marriage is evenly owned by both people Features of Co-Ownership May any number co-own? Tenancy in Common Joint Tenancy Tenancy by the Entireties Community Property Must shares be equal? Is consent of co-owners required for sale? Right of survivorship Is marriage required? Can a will replace survivorship? Quick Review Answer the following questions on your handout: ◦ 1) A unique word, protected by federal law, that identifies a business’s product is called a(n) _________________. ◦ 2) True or False: Copyrights held by authors are protected by federal law for the life of the author plus 50 years past their death. ◦ 3) Property that is intentionally placed somewhere but then forgotten is: A) Lost B) Missing C) Mislaid D) Vanished ◦ 4) When there is only one owner of property, they are said to own in ___________. A) Joint tenancy B) Intestate C) Severalty D) Custody ◦ True or False: The co-ownership forms of community property and tenancy by the entireties requires that the coowners be married. _________________ Real property includes: ◦ ________ ◦ Things _________________ to the land ◦ Certain ________ to use the land of others Besides the land itself, the owner has rights to the ____________________________ of that land. When personal property is permanently attached to realty it is called a _________. ◦ ______________ – personal property attached to realty by ________________ Transfer of Ownership Ownership of realty is usually acquired by _____________________. When an ________ is transferred from grantor to grantee by ______, it is called a ________________. ◦ ______________ – someone’s property and any legal rights associated with that property Deed – _______________________________________________ _________________ – giving real property to the government and is effective only if the government accepts the property ________________ – the power of the government to take private property for public use in exchange for fair market value ________ – a legal right in another’s property given as security for the performance of a ____________________ Realty may also be transferred through a _____. If owner(s) die without a will, their property will be distributed according to state statutes. ◦ Intestate – ___________________________________ __________ Realty _________ – an agreement in which one party receives _____________________ of another’s real property in exchange for _______ Rent – ___________________________ ____________________________ A lease creates a relationship between the person conveying possession of realty (_____________) and the person receiving possession (_____________). Leasehold Estates Leasehold Estate – ___________________ _________________________________ Types of leasehold estates: ◦ _______________ – the lease is for a renewable period of time with rent due at stated intervals ◦ _______________ – when a lease is for a definite period of time; could be months or years ◦ _______________________ – when a tenant remains in possession after a lease has expired ◦ ______________ – if a party possesses land with the owner’s permission but without an agreement as to the term of lease or amount of rent ________ Rights and Duties Tenant’s rights: ◦ __________ of the property starting at _______in the ______ agreement and be _______ of all other persons ◦ ______ of the leased property in the ______________ by the lease ◦ __________ the lease or ________ the premises ◦ Landlords generally do not have a right to enter the leased property for inspection unless this right is given in the lease ◦ _____________ – when the landlord blocks the tenant from possession of all the real property Tenant’s duties: ◦ ________________ ◦ _________________________ ◦ __________________________________________ _________________ __________ Rights and Duties Landlord’s rights: ◦ ___________________ agreed upon in lease ◦ Take ____________ and/or _______ the tenant if they ______ to pay the rent ◦ Regain possession of the ____________ and any ________ added at the end of the lease Landlord’s duties: ◦ ____________________________ ◦ ____________________________ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Exposed wires, roof leaks, screens on outside doors and windows, private bathrooms in each unit, ceilings and walls must be smooth, free of loose plaster, and be easily cleanable Responsible for others in ________________________ ___________________________ Comply with the _______________________ _________________________________________ Quick Review Answer the following questions on your handout: ◦ 1) True or False: Land is the only component of real estate. ◦ 2) True or False: An estate is a particular bundle of legal rights in real property. ◦ 3) Which type of lease does not have an ending date indentified in it? A) Periodic tenancy B) Tenancy for years C) Tenancy at sufferance D) Tenancy at will ◦ 4) In a tenancy, the right of possession is owned by the _______________. ◦ 5) The landlord is responsible for all repairs for: A) Common areas B) The tenant’s premises C) Both A & B D) Neither A & B Property and Casualty Insurance __________________ – the general type of insurance intended to indemnify for harm to the insured’s personal or real property brought about by perils such as fire, theft, or severe weather ◦ Indemnify – ____________________________________ ◦ Beneficiary – ___________________________________ ____________________ – the type of insurance that indemnifies for losses resulting from accident, chance, or negligence ◦ ___________________ – a type of casualty insurance that indemnifies against personal injury or property damage claims for which the insured is legally responsible Any exception to what is covered in an insurance policy is called an __________ and must be ____________ __________ in the policy. _______ and ___________ When someone dies ____________, a court will use the deceased’s ______ to pay all debts. The remainder of the property will be ______ ______________________________. _______ – a legal expression, ____________, by which a person directs how their property is to be distributed after death ◦ Testate – ______________________ ◦ _______________ – make of the will (male/female) ◦ __________________ – a personal representative named by the deceased to carry out the directions in the will (male/female) Creation and Execution of a Valid Will The basic requirements in almost every state are: ◦ The person creating the will must have __________ _______ (clear intention to make a will) and not be ___________ into signing the document ◦ The signer must not be ________ into thinking the document is something _________________ ◦ The testator/testatrix must have _______________ _________ (must know in at least a general way the kind and extent of the property involved, who stands to benefit, and they are making arrangements to dispose of their property after death) ◦ Must be in ________ and be _________ at the end of the document in front of ___________ who will _____________ under the will Amending and Special Types of Wills Wills may be changed as often as the _____________ wants to change it. In most states, changes must be made using a __________, which is a ______________ _________________ amendment. Special types of wills: ◦ Holographic Will – ______________________ ____________________________________ ◦ _____________________ – an oral, witnessed will that is often limited to controlling the distribution of personal property Distribution of an Estate Procedure for estate resolution: ◦ _____________________________________ the assets of the estate and collect the debts owed to it ◦ Give public notice of the estate and the necessity for filing claims within the statutory period ◦ ____________________________________ ◦ Distributing the ____________________ according to the _______ or ____________ ______________ will dictate how an __________ is distributed when there is ____________________. If there _____________, its terms are to be followed. If there are no inheritors, the deceased’s property ______________ (is given to the state). Trusts When the transferee of property is a separate entity under law, a __________ has been created. ◦ Trustee – _________________________________________ ◦ Settlor – _______________________ Types of trusts: ◦ _________________ – an express trust made during the lifetime of the settlor ◦ _________________ – express trust created after the death of the settlor in accordance with the will ◦ ________________ – an express trust created for the fulfillment of an unselfish purpose ◦ Private – __________________________________________ ◦ _____________ – an express trust that protects the beneficiary’s interest in the subject property from the beneficiary’s creditors ◦ ________________ – an implied trust where the entity intended to receive the benefit of an express trust can’t do so ◦ _________________ – implied trust created to require a person holding property to transfer it to another because retention of the property would be a wrongful and unjust enrichment of the holder Quick Review Answer the following questions on your handout: ◦ 1) What type of casualty insurance helps to protect the insured party for an injury they are legally responsible for? A) Indemnity B) Liability C) Property D) Automobile ◦ 2) A trust created by the will of a deceased settlor is known as a(n) ____________ trust. ◦ 3) True or False: Those who die without a valid will are legally termed to have died intestate. ◦ 4) True or False: The insertion of a codicil on a will does not have to be witnessed. ◦ 5) Which of the following is an example of an expressed trust? A) Resulting B) Constructive C) Charitable D) None of the above