Universal Design for Instruction
advertisement

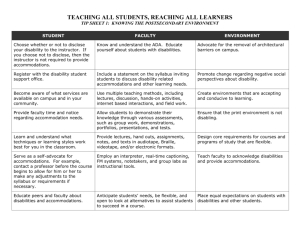
Curriculum Alice Anderson, Ph.D. E-mail: Alice.Anderson@purduecal.edu Ms. Jacqueline Bustos E-mail: jackibustos@gmail.com Mary Lee Vance, Ph.D. E-mail: Marylee.vance@purduecal.edu Universal Design (UD) Definitions From the Higher Education Opportunity Act of 2008 ... Flexibility In ways information is presented, in ways students respond or demonstrate knowledge and skills in the ways students are engaged Reduces barriers in instruction Provides appropriate accommodations, supports, and challenges Maintains high achievement expectations for all students A universal design approach to service delivery holds the promise of: creating more inclusive postsecondary environments alleviating the need for most individual accommodations creating a more collaborative, wide-reaching professional role for postsecondary service providers Keep in mind… There may always be the need for some accommodations, such as sign language interpreters for deaf students. Advantages!! Little, if any, re-development is necessary when diverse individuals enter your classes Planning ahead can be less time-consuming in the long run Allowing all students access to all materials can help all students learn by appealing to a variety of learning styles! Benefits to all!! You learn and grow as a professional educator! Syllabus Tips Write clear and specific learning objectives with expected outcomes/products Ensure activities and assignments are flexible, adaptable and match expected outcomes Use multiple accessible methods for assessment that test what is important Make information available in more than one formathard copy, digital, audio, video, narrated PPTs, etc. Give students varying resources to help them learn critical information Provide for choices in assignments- multiple avenues to accomplish course objectives (Adapted from: Equity and Excellence in Higher Education: Universal Course Design www.eeonline.org) Syllabus Tips- Make your “life” a bit easier!! Be familiar with technological resources (videos, pics, graphics, screen readers, etc.) Understand formats accessible to screen readers (Resource topic: universal web design) Keep in mind– Time invested up front decreases time demands later! Beyond the ADA CLASSROOM BEST PRACTICES Lectures ● Be as black and white as possible "Yes/No" not "Maybe” ● Use scaffolding techniques and concrete examples to teach abstract concepts (Gander 62). Lecture Usability Various theorists such as Dolmage, Kroll and Hinckley all encourage communication with the students. Dolmage refers to “collaborative communication” about the curriculum flexible usability. Knoll terms it “interdependency” and Hinckley prefers the term “collaboration”. Additional Classroom Aids ● Visual calendars for weekly assignments ● List objectives for each class on the board ● Do not speak to class while writing on the board Intent of Universal Design “Universal design is the design of products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design” Ron Mace Disability Models: Social Constructs Moral - Pity - Horror Medical Social Universal Design Teaching and Learning Expectations Student Learning Styles/Preferences Audio Haptic/kinetic Visual Teaching Preferences Audio (lecture) Visual (power point) Haptic (in labs) 7 UD Principles Equitable Use Flexibility Simple and Intuitive Perceptible Information Tolerance for Error Low Physical Effort Size and Space Areas Affected in Education Curricular (teaching and advising) * Technological Physical AT (Special Ed)/UDL Relationship Overcome Barriers Universal Design Assistive for Technology Learning Reduce Barriers Considerations for UD in Learning (AHEAD) What do I want my audience to know? What do I want my audience to be able to do? What lasting impact do I want to have? What challenges to inclusion might my presentation style create? How can I plan my presentation to provide meaningful access to all members of my audience and minimize the need for individual accommodations, without compromising the essential components that I’ve identified, and in the most inclusive way possible? Universal Design for Instruction Everyone benefits from a more universally accessible and accommodating information process In particular students: - with disabilities - non-native English speakers/ 1st gen - non-traditional age - technologically challenged - those with disabilities Remember DISABILITY IS A SOCIAL CONSTRUCT – WHAT ROLE YOU PLAY IN SOCIETY IS YOUR CHOICE Scenarios Case Study: Ch 19, Chuck Chuck is a low vision student who parlayed his hobby, inventing sports equipment for visually challenged people into national recognition in a competition for entrepreneurs. He is a perfect example of a freshman student with multiple identities who thrived in the PUC Writing program, owing to the use of universal design. The Writing Center helped Chuck acquire the knowledge and confidence to take what he had written in the classroom, and enter a nation-wide contest for entrepreneurs. He finished in the top 10. What UD approaches were utilized here? Case Study: Ch 16, Koino Koino attended one of the best schools in Taiwan, but struggled with reading and comprehension. Koino’s parents decided to send her to the US for postsecondary education. Within the first two weeks of the semester, Koino was struggling. She could not keep up with the required reading and was having trouble comprehending the lectures. She went to the international student office and disability resources for support. If this was your student, what would you recommend? Where does universal design fit in? Case Study: Ch 12, Sarah Sarah is a first-year student at the local university. She had an IEP for learning disability throughout HS, but did not contact the disability services office to request accommodations. As midterms approach, she is feeling overwhelmed, and having difficulty keeping up with the volume of reading assignments. She is scared but doesn’t want to talk to anyone. Why is Sarah afraid to request accommodations? What might be options for Sarah to improve her academics? Where does Universal Design fit in for her situation? Questions? Please speak loudly and clearly so all may hear.