QUIZ Review - Brand Luxury Index
advertisement

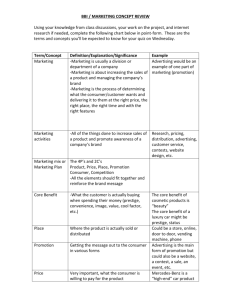
Basic Entrepreneurial Marketing Principles CSU Northridge Dept. of Marketing Franck VIGNERON “Marketing creates Needs” ... “Makes People Buy Things...” ? “Marketing creates Needs” ... “Makes People Buy Things...” Marketers can not create needs. Marketers can help people articulate their needs into wants. Marketers can help create wants. Marketers seek to create satisfactions What Motivates a Consumer to Take Action? Needs - states of felt deprivation including physical needs for food, social needs for belonging and individual needs for self-expression. i.e. I am thirsty. Wants - form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality. i.e. I want a CocaCola. How Do Consumers Choose Choose Among Many Products and Services? Customer Value - difference between the value the customer gains from owning and using a product and the cost of obtaining the product. Customer Satisfaction - depends on the product’s perceived performance in delivering value relative to a buyer’s expectations. Both are closely linked to Quality and Total Quality Management (TQM). Customer Satisfaction The extent to which a product’s perceived Performance matches a buyer’s expectations. Expectation Disconfirmation Perceived Performance Satisfaction Other Applications of Marketing Person Marketing: Mkg efforts for getting attention, interest, and preference of a target toward a person, e.g., Celebrities (Shaquille O’Neal) or political candidate (Bush). Place Marketing: Visitors, improve image, real estate, … Cause Marketing: “friends don’t let friends drive drunk” Event Marketing: Sporting, cultural or charitable activities; Salt Lake City 2002 Winter Olympics Organization Marketing: Navy = “let the journey begin” What is a “Problem”? Problem: perceived difference between an ideal and actual state The Ideal State Expectations Aspirations Cultural basis Effect of Changes in Life Basically: values, needs and goals The Actual State Actual Physical Situation External Prompts How to “Create” Problems for Consumers Create new ideal state Create dissatisfaction with actual state Where do People Search for Problem Solutions? INTERNAL Memory /Thinking Psychological Core EXTERNAL Word of mouth, media, store visits, trial CATALOG The Buyer Decision Process Need Recognition Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Decision Postpurchase Behavior 1/ Problem Recognition & 2/ Decision Making Less than Minimum Treshold Ideal State Actual State Intensity of Discrepency No Recognition of Problem Problem Recognition Greater than Minimum Treshold Information Search Satisfactory Internal Search? Yes Attributes Post-Purchase Evaluations Buy Brands No External Search Evaluate Alternatives A Model of Consumer Decision Making INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT A Simple Model of Consumer Decision Making External Influences Input Firm’s Marketing Efforts 1. Product 2. Promotion 3. Price 4. Channels of distribution Sociocultural Environment 1. Family 2. Informal sources 3. Other noncommercial sources 4. Social class 5. Subculture and culture Consumer Decision Making Need Recognition Process Prepurchase Search Evaluation of Alternatives Psychological Field 1. Motivation 2. Perception 3. Learning 4. Personality 5. Attitudes Experience Postdecision Behavior Output Purchase 1. Trial 2. Repeat purchase Postpurchase Evaluation THE PLANNING PROCESS 4. 5. 3. 2. 1. 6. Marketing Environment Macroenvironment Microenvironment Company The Marketing Environment Demographic Company Economic Cultural Publics Company Suppliers Customers Competitors Natural Political Intermediaries Technological ????????????????????????????? What the mix? What is the MKG mix? What are the 4 Ps? Four Ps of Marketing Marketing Mix Product Price Place Target Market Promotion What is a Product? Types of Consumer Products Convenience Shopping Specialty Unsought GENERIC term that Includes Goods Services Places Organizations People, etc.. Entrepreneurs vs Managers Source: http://www.entrepreneurship-isemi.com What is a SWOT Analysis? 5 Eyes Marketing Strategy Past Present Future Yourself Competitors Situation Analysis S Things the company does well. W Things the company does not do well. O Conditions in the external environment that favor strengths. T Conditions in the external environment that do not relate to existing strengths or favor areas of current weakness. SWOT Do not limit the S and W to the Product Threats: focus on specific competitors Opportunities: • Do not describe what you will do. EG, develop a market • • development strategy based on the growing senior population Avoid basic opportunities: population growth, economic slow down, health consciousness, obesity rate, gaz prices,… Identify opportunities outside the product/consumer level BENCHMARKING = Analyzing Competitors Identifying the company’s competitors Assessment of strengths and weaknesses of competitors. Assessing competitor’s objectives, strategies, strengths and weaknesses, and reaction patterns Selecting which competitors to attack or avoid Marketing Strategy and Tactics A marketing strategy is a means by which a marketing objective/goal is to be achieved, usually characterized by a specific target market and a marketing program to reach it. Marketing tactics are detailed day-to-day operational decisions essential to the overall success of marketing strategies. Generic Marketing Strategies Four Basic Types of Strategic Opportunities M A R K E T P r e s e n t N e w PRODUCT Present New Market Penetration Product Development Market Development Diversification Basic Competitive Strategies E-machines or Wal-Mart Subaru or IBM Overall Cost Leadership Focus Differentiation Middle of the Road Leica or Mephisto Sears or Holiday Inn Competitive Leadership Companies Gain Leadership Positions by Delivering Superior Value to their Customers Through These Strategies: Operational Excellence Alaska Airlines/Dell Customer Intimacy Ikea/VW Product Leadership Intel/Sony Competitive Marketing Strategies Market Leader Market Challenger Market Follower Market Nicher Developing an Effective Marketing Program Requires analyzing marketing problems/opportunities This analysis has 3 steps and is grounded in primary and secondary marketing research data Customer Analysis Competitive Analysis Analysis of Organization Capabilities Opportunity Identification •Product Differentiation 3 generic strategies for achieving •Overall Cost Leadership a differential advantage over •Special Market Focus Offering Product competitors are available: & Low Cost Once an opportunity has been identified Differentiation marketing strategy must be developed Strategies Lead to Tactics Strategy Possible Tactics Direct our promotion to males, ages 25 to 40 years old. Advertise in magazines read by this group of people . .. Advertise on television programs watched by this group 1 .. High Level Strategies HOW ?????? Low Level Strategies . 2 HOW ?????? 3 Tactics . PRODUCT Existing 1 Existing New Market Penetration NPD High Level Strategies Market Market Diversification Development New PRODUCT Low Level Strategies 2 PRICE PLACE PROMOTION E.g., Quality, Branding & Service, … E.g., skimming, captive, … E.g., direct, indirect, exclusive, hybrid, … E.g., skimming, captive, … 3 Tactics STP Segmentation Targeting & Positioning Market Segmentation Market Targeting Market Positioning Marketing Differentiation Strategy A Undifferentiated Marketing Company Marketing Mix B Concentrated Marketing Company Marketing Mix Market Target 1 Target 2 Target 3 C Differentiated Marketing rketing strategies Company Marketing Mix 1 Company Marketing Mix 2 Company Marketing Mix 3 Target 1 Target 2 Target 3 Two-Way Brand Extension: Marriott Hotels Quality Economy Standard Good Marriott Marquis (Top executives) Price High Average Fairfield Inn Low (Vacationers) Superior Marriott (Middle managers) Courtyard (Salespeople) Four Ps of Marketing Marketing Mix Products Price Place Target Market Promotion Branding The Sam's Club logo used from the 1990s until 2001. The second Sam's Club logo used from 20012006. The current Sam's Club logo used since 2006. Managing and Building a Brand Knowledge Perceived Meanings Recall versus Recognition Brand can possess an appealing image that consumers value directly BRAND AWARENESS •Familiarity Liking Expected Performance BRAND ASSOCIATIONS BRAND QUALITY • Reason-to-Buy • Help Process & Retrieve Information • Differentiate/ Position •Create Positive Attitudes/ Feelings • Line Extensions Price Sensitivity & Purchase rate BRAND LOYALTY • Create Reassurance • Time to Respond to Competitive Threats • Reduced Marketing Costs Trade leverage Individual Product Life-Cycles Programmed to Yield Expanding Company Sales sales Total Company Sales Individual Product Sales P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 Time P6 P7 P8 Managing product lines and brands over time: The Product Life Cycle (PLC) + Market Introduction Market Growth Market Maturity - Market Decline + time Product Life-Cycle Stages and Marketing Steps Sales MATURITY GROWTH Maximize share, grow market Maximize profit, Defend Mkt Share DECLINE Reduce/ Delete, milk the brand INTRODUCTION awareness and trial Launch Product Strategies Takeoff Rapid Shakeout Maturity growth Decline Time Stages in the Adoption Process Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Adoption Adopter Groups 2.5% Innovators 13.5% 34% Early Early Adopters Majority 34% Late Majority 16% Laggards Elements of the MKG Mix that compose a cohesive MKG program Marketing manager Product Price Features Brand name Packaging Service Warranty List price Discounts Allowances Credit items Payment period Place Promotion Advertising Personal selling Sales promotion Publicity Outlets Channels Coverage Transportation Stock level Cohesive marketing mix Promotion Promotion Product Price Place Place MKG PLAN I. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY • Recommend Alternative(s) The goals to be achieved through the marketing plan in such areas as customer satisfaction, sales volume or market share Overall Strategies & STP - used to achieve the objectives VI. ACTION PROGRAMS • • Evaluate Potential Strategic Alternatives V. MARKETING STRATEGIES • External Analysis: Opportunities & Threats IV. MARKETING OBJECTIVES • Internal Analysis: Strengths & Weaknesses III. ISSUE ANALYSIS • • A stimulating summary of the marketing plan II. CURRENT MKG SITUATION • • Memo 4P’s - that will be used to achieve the objectives Programs that pinpoint who is responsible for the marketing activities and that establish budgets and timetables for executing the MKG strategies VII. CONTROLS • Procedures for monitoring the plan over time and for taking corrective action if needed New Products from Sony 1975: Betamax VCR has initial success but loses out to bettermarketed VHS VCRs. 1955: First Japanese transistor radio starts its record of successes. 1946: Sony founded in bombed-out store. Its rice cooker never gets to market. 1950s 1968: Its Trinitron TV becomes and remains the standard for color TV quality. 1982: Compact- disc player becomes first digital consumer electronics product 1979: Walkman revolutionizes personal stereo tape players. 2000s: •MD Walkman •Cyber Shot •DVD Handycam 1995: PlayStation video-game system captures 80% of U.S. 32-bit market. 1985: 8mm Handycam arrives. 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Strategic Roles of Most Successful New Products Strategic Role Externally driven Internally driven Defend market share position Establish foothold in new market Preempt market segment Maintain position as product innovator Exploit technology in new way Capitalize on distribution strengths Provide a cash generator Use excess or off-season capacity Percentage of responses 0 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Major Stages in New-Product Development (Fig. 9.1) Marketing Strategy Concept Development and Testing Idea Screening Idea Generation Business Analysis Product Development Test Marketing Commercialization The Research Process STEP1: Defining the Problem and Research Objectives STEP 2: Developing the Research Plan STEP 3: Implementing the Research Plan STEP 4: Interpreting and Reporting the Findings Secondary Data Data that has been collected for reasons other than the specific research project at hand. Primary Research Original research undertaken by individual researchers or organizations to meet specific objectives. Designing Primary Research Quanti Research Quali Research Quantitative studies more likely for collecting descriptive information. • Qualitative studies may be used to get new ideas. Marketing Research Process Step 1. Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Types & Levels of Information Needed – Exploratory Research Descriptive Research Causal Research Gathers preliminary information that will help define the problem and suggest hypotheses. •Describes such things as market potential for a product or attitudes and demographics of consumers who buy the product. •Test hypotheses about causeand-effect relationships. preliminary information: identify issues problem definition first stage of descriptive or causal research – – – – – – – expand understanding of factors describe phenomenon representative sample test cause and effect hypothesis experimentation New Product Pricing Strategies Market Skimming Setting a High Price for a New Product to “Skim” Maximum Revenues from the Target Market. Results in Fewer, But More Profitable Sales. • • • Use Under These Conditions: Product’s Quality and Image Must Support Its Higher Price. Costs Can’t be so High that They Cancel the Advantage of Charging More. Competitors Shouldn’t be Able to Enter Market Easily and Undercut the High Price. New Product Pricing Strategies Market Penetration • Setting a Low Price for a New Product in Order to “Penetrate” the Market Quickly and Deeply. Attract a Large Number of Buyers and Win a Larger Market Share. • • Use Under These Conditions: Market Must be Highly PriceSensitive so a Low Price Produces More Market Growth. Production/ Distribution Costs Must Fall as Sales Volume Increases. Must Keep Out Competition & Maintain Its Low Price Position or Benefits May Only be Temporary. Communication Mix Strategies Pull Strategy Strategy that Calls for Spending A Lot on Advertising and Consumer Promotion to Build Up (Pull) Consumer Demand. Strategy Selected Depends on: Type of ProductMarket & Product LifeCycle Stage Push Strategy Strategy that Calls for Using the Salesforce and Trade Promotion to Push the Product Through the Channels. Continuum of Possible Channel-Target Market Relationships Many Outlets Intensive Distribution Cigarettes Chewing Gum Auto Parts Dry Cleaners Selective Distribution Men’s Suits Exclusive Distribution Machinery Automobiles Rolls Royce Dealer • Intensive Distribution: Maximise the number of points of sale • Selective Distribution: Evaluate sales potential, competency and location • Exclusive Distribution: Agreement to sell on a specific area One Outlet The Promotional Mix PR Advertising Sales Promotion Direct MKG Personal Selling Product Place Price (Distribution) Advertising Strategies Promotion 4P’s Place The Marketing Communications Mix (Promotion Mix) Advertising Personal Selling Advertising Strategies Any Paid Form of Nonpersonal Presentation by an Identified Sponsor. Personal Presentations by a Firm’s Sales Force. Sales Promotion Short-term Incentives to Encourage Sales. Public Relations Building Good Relations with Various Publics by Obtaining Favorable Publicity. Direct Marketing Direct Communications With Individuals to Obtain an Immediate Response. Basic Communication Model Sender (Source) Message Channel (Medium) Feedback Advertising Strategies Receiver (Consumer) What are the 4 main Com Objectives? I… P… R… C… Setting Communication Objectives Informative Advertising Inform Consumers or Build Primary Demand i.e CD Players Persuasive Advertising Build Selective Demand i.e Sony CD Players Advertising Objective Specific Communication Task Accomplished with a Specific Target Audience During a Specific Period of Time Comparison Advertising Reminder Advertising Compares One Brand to Another i.e. Avis vs. Hertz Keeps Consumers Thinking About a Product i.e. Coca-Cola Changes in Advertising Objectives during the Product Life Cycle Sales PreIntroduction Introduction Growth Time Define objectives and plan the promotional campaign General promotion objective Advertising strategy Develop product awareness, stimulate generic demand, and attract distributors Maturity and Create product Maintain brand acceptance and enhance loyalty convert brand and preference if buyers distributors of there are competitive competitive brands products Reminder and Screen concepts,primary demand Extensive emotional create advertising to get advertising expenditures advertising and advertisements, potential promotions to and plan media purchasers to try emphasizing advantages of the promote repeat selection the product. trade product and purchases and advertising to differentiate introduce product brand brands Advertising Strategies Decline Minimal expenditures just enough to phase product out Minimal advertising expenditures emphasizing low price to reduce inventory