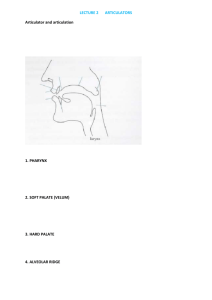
What is a linguist?
advertisement

What is a linguist? The Linguists: A Movie • http://thelinguists.com/ Linguistics has many subfields • • • • • • Phonetics Phonology Syntax Semantics Pragmatics Morphology Phonetics • The study of minimal sound units of a language • Example: beat, bit, bat Phonology • The language-specific study of the distribution of speech sounds Example: Ptolemy Pterodactyl Captive Example: thedogisplayinginthebackyard the dog is playing in the back yard Morphology • Study of word formation (breaking down individual words into smaller parts) Unbelieveability Ungiraffelike Baker vs. *erbake Nicley vs. *bookly Anytime you see a * it means you’re looking at an example that is ungrammatical Syntax • Study of how words combine to form phrases and sentences 1) 2) 3) 4) I will pick the package up at 8 o’clock. At eight o’clock, I will pick the package up. *Package up pick at o’clock will the eight I. *I will picks the package up at eight o’clock. Semantics • The study of the ability of determine the meaning of sentences • Couch vs. sofa • “duck” • • • • The green duck dawdled around the cactus. The duck dawdled around the green cactus. The platypus ducked under the sofa. !The sofa ducked under the platypus. Anytime you see a ! it means you’re looking at an example that is semantically anomolous Pragmatics • The study of meaning in context – Can you close the door? – What a beautiful cake! – “Dude, ‘sup?” vs. “Good morning, sir” – Chillaxin’ vs. resting When greeting a professor, it would be pragmatically awkward to use “#Dude, ‘sup?” Anytime you see a # it means you’re looking at an example that is pragmatically awkward POP QUIZ A. Syntax B. Semantics C. Phonetics D. Pragmatics E. Phonology F. Morphology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Context Meaning Sentences Words Distribution of speech sounds 6. Minimal speech sounds POP QUIZ A. Ungrammatical B. Semantically Anomolous (meaning is weird) C. Pragmatically Awkward (wouldn’t be used in that context) 1.# 2.! 3.* What linguists do besides teach? • • • • • Document (Endangered) Languages Work on voice recognition programs Perfect spell-check/grammar check Shape language-learning textbooks/software Search through large quantities of texts looking for new words While linguistics has many facets, all linguists have one thing in common: LANGUAGE What is language? Get in groups of 2-3 and write your very best definition of language. Some stats about language • 6,000 languages spoken in the world • But 90% of the population speaks only 10% of them • Languages are very diverse, yet there are many universal properties of languages • There are some characteristics shares by all languages as well as characteristics that no language has Competence vs. Performance • Competence = what we know about a language (hidden potential) • Performance = what we produce (observable) • Walking analogy (even when you’re sitting, you have the competence to walk) What language is NOT • Language is not writing (p. 13) – Archeological evidence – Writing does not exist everywhere – Writing must be taught – Neurolinguistic evidence – Writing can be edited • Language is not prescriptive grammar (p.14) Prescriptive vs. Descriptive • Prescriptive grammar is the socially embedded notion of the “correct” or “proper” way to use a language • Descriptive grammar describes what happens in a spoken language and, therefore, accepts the patterns a speaker uses without judgment • (see page 16 for double negative example) • (for practice, see page 31, question 12) Design Features of a Language by Charles Hockett • • • • • • • • • Mode of communication Semanticity Pragmatic Function Interchangeability Cultural Transmission Arbitrariness Discreteness Displacement Productivity