2-10-Week-2-Answers-What-is- Economics
advertisement

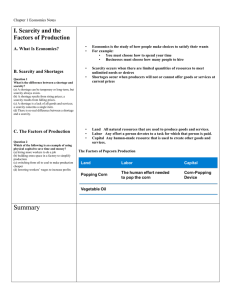
ECONOMICS What is Economics & Economic Systems - Ch 1-2 1. What is the difference between a good and a service? (4 points) Goods are physical objects and services are actions or activities. . 2. Why is the idea of scarcity a starting point for thinking economically? (4 points) Economics seek to solve the scarcity problem which exists because resources are limited whereas needs and wants are unlimited. 3. How is scarcity different from shortages? (4 points) Scarcity always exists because goods and services are produced from limited resources. Shortages can be temporary or long term and occur only when producers will not or cannot offer goods or services at current prices. 4. Describe the three factors of production. (4 points) Land – any natural resource used to produce goods or services Labor – effort that one person exerts for another and for which the first person is paid Capital - any human-made resource used to produce goods and services 5. What role do entrepreneurs play in the economy? (4 points) They decide how to combine factors of production to create new goods and services. 6. Present an example that illustrates how a decision involves a trade-off. (4 points) Should I spend my $500 on a vacation to Mexico (have fun) or buy textbooks (improve grades)? 7. Why must the opportunity cost of a decision always be something desirable? (4 points) Because there would be no meaningful decision to be made between a desirable option and an undesirable one. 8. How do economists use the phrase “guns or butter”? (4 points) It refers to a country’s decision to produce more military goods or more consumer goods. What is Economics & Economic Systems - Ch 1-2 Page 1 2/10/12 9. What does it mean to “think at the margin” (4 points) Making a decision about how much more or less to do. It allows people to evaluate options based on available resources; deciding whether to do or use one additional unit of some resource 10. How is underutilization shown on a production possibilities frontier? (4 points) It is shown by any point that appears inside the production possibilities frontier. 11. How does the production possibilities curve illustrate how efficient an economy is? (4 points) It shows the maximum possible output along the production possibilities frontier. If a country’s economic production is on the frontier, the economy is producing at top efficiency. 12. How does a production possibilities curve illustrate opportunity cost? (4 points) By comparing the data at various points on the production possibilities frontier. As the production of one element increases, the curve shows the decrease in production of the other element: the opportunity cost. 13. How do economic systems differ? (4 points) The difference arises from the ways each system answers production and distribution questions. 14. Why aren’t all people paid the same amount in factor payments for the resources they provide? (4 points) Factor of payments differ because societies place different values on different resources and products. A possible example is a doctor’s wages versus a janitor’s. 15. Why do governments provide safety nets for their citizens? (4 points) Governments provide safety nets to fulfill the goal of economic security and predictability. 16. Give an example of a market economic system. (3 points) USA 17. How does specialization make us more efficient? (4 points) It allows each of us to focus on individual tasks and not worry about all of our basic needs at once, thus making us more efficient. 18. What is profit? (4 points) The financial gain of a transaction What is Economics & Economic Systems - Ch 1-2 Page 2 2/10/12 19. How does competition among firms benefit consumers? (4 points) Competition benefits consumers by causing firms to sell higher-quality goods at lower prices. 20. Explain what Adam Smith meant by “the invisible hand of the market place”. (4 points) Using self interest as a tool, it guides a nation’s resources to their most productive use. Individuals, each purchasing what is best for him or her, make decisions that ultimately benefit the nation. 21. What is the connection between incentives and consumer sovereignty in a free market economy? (4 points) Consumer sovereignty has to do with the power consumers have to choose what they will buy, so that they exert control over what is produced by creating the incentive for firms to produce high quality goods and services. 22. How do socialism and communism differ? (4 points) In socialist countries the government often owns major industries. Socialism has been achieved peacefully through democracy. In Communist nations, all economic and political power rests in the hands of central government. Communist governments occur after a violent revolution and are authoritarian. 23. What characterizes an authoritarian government? (4 points) Authoritarian governments are strongly centralized and demand strict obedience from their citizens. They do not allow individuals freedom of judgment and action. What is Economics & Economic Systems - Ch 1-2 Page 3 2/10/12 Define (1 point each) Guns or Butter Underutilization Market Economy Scarcity Opportunity Cost Laissez Faire Competition Socialism Command Economy Phrase that refers to trade-offs that nations face when choosing to produce more or less military or consumer goods Using fewer resources than an economy is capable of using Market-based economic system with limited government involvement Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited needs The most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision French term meaning let them do as they please The struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers A social and political philosophy based on the belief that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout the society Economic system in which central authority is in command of the economy Opportunity Cost The most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision Trade-offs The most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision Week 2 of 10. The 1st quiz towards your midterm. What is Economics & Economic Systems - Ch 1-2 Page 4 2/10/12