neurotransmitter
advertisement

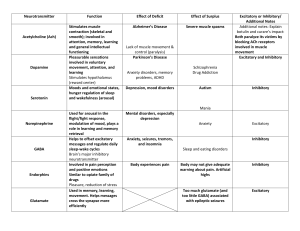
Introduction to CNS pharmacology By S.Bohlooli, PhD School of Medicine, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences Ion channels & neurotransmitter receptors Voltage gated channels Ligand gated channels Ionotropic receptors Metabotropic receptors Membrane delimited Diffusible second messenger Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor The synapse & synaptic potentials Excitatory Excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP) Ionotropic receptor Inhibitory Inhibitory post-synaptic potential (IPSP) Presynaptic inhibition Table 21-1. Some toxins used to characterize ion channels. Channel Types Mode of Toxin Action Source Voltage-gated Sodium channels Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Blocks channel from outside Puffer fish Batrachotoxin (BTX) Slows inactivation, shifts activation Colombian frog Apamin Blocks "small Ca-activated" K channel Honeybee Charybdotoxin Blocks "big Ca-activated" K channel Scorpion Omega conotoxin (w-CTXGVIA) Blocks N-type channel Pacific cone snail Agatoxin (w-AGA-IVA) Blocks P-type channel Funnel web spider Irreversible antagonist Marine snake Blocks channel South Pacific plant Competitive antagonist Indian plant Blocks channel Wasp Potassium channels Calcium channels Ligand-gated Nicotinic ACh receptor a-Bungarotoxin GABAA receptor Picrotoxin Glycine receptor Strychnine AMPA receptor Philanthotoxin Site of drug action Identification of central neurotransmitters More difficult for CNS Anatomic complexity Limitation of available techniques Criteria for neurotransmitter identification Localization Microcytochemical immonocytochemical Release Simulation of Brain slices Calcium dependency of release Synaptic mimicry Microiontophoresis Physiological view Pharmacological view Cellular organization of the brain Hierarchical systems Sensory perception, motor control Phasic information, delineated pathways Two types of neurons Projection or relay Local circuit neurons Limited number of transmitters Nonspecific or diffuse neuronal systems Affecting global function of CNS Small number of neurons, projections to wide area of CNS Central neurotransmitters Amino acids Neutral amino acids Acidic amino acids Acetylcholine Monoamines Dopamine Norepinephrine 5-hydroxytryptamine Peptides Nitric oxide endocananbiniods Table 21-2. Summary of neurotransmitter pharmacology in the central nervous system. (Many other central transmitters have been identified [see text].) Transmitter Anatomy Cell bodies at all levels; long Acetylcholine and short connections MotoneuronRenshaw cell synapse Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Pirenzepine, atropine Excitatory: in K+ conductance; ↑ IP3, DAG Muscarinic (M2): muscarine, bethanechol Atropine, methoctramine Inhibitory: ↑ K+ conductance; cAMP Nicotinic: nicotine Dihydro-berythroidine, abungarotoxin Excitatory: ↑ cation conductance Muscarinic (M1): muscarine Transmitter Anatomy Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Dopamine Cell bodies at all levels; short, medium, and long connections D1 Phenothiazines Inhibitory (?): cAMP D2: bromocriptine Phenothiazines, butyrophenones Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+; Inhibitory (postsynaptic): in K+ conductance, cAMP Bicuculline, picrotoxin Inhibitory: Cl–conductance 2-OH saclofen Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+ conductance; Inhibitory (postsynaptic): K+ conductance GABA Supraspinal and spinal GABAA: muscimol interneurons involved in pre- and postsynaptic inhibition GABAB: baclofen Transmitter Anatomy Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Glutamate Relay neurons at all levels and some interneurons N-Methyl-D-aspartate 2-Amino-5(NMDA): NMDA phosphonovalerate, dizocilpine Excitatory: cation conductance, particularly Ca2+ AMPA: AMPA CNQX Excitatory: cation conductance Metabotropic: ACPD, quisqualate MCPG Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+ conductance cAMP; Excitatory: K+ conductance, IP3, DAG Taurine, -alanine Strychnine Inhibitory: Cl–conductance Kainate: kainic acid, domoic acid Glycine Spinal interneurons and some brain stem interneurons Transmitter Anatomy 5-Hydroxytryptamine Cell bodies in midbrain (serotonin) and pons project to all levels Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms 5-HT1A: LSD Metergoline, spiperone Inhibitory: K+ conductance, cAMP 5-HT2A: LSD Ketanserin Excitatory: K+ conductance, IP3, DAG 5-HT3: 2-methyl-5-HT Ondansetron Excitatory: cation conductance 5-HT4 Excitatory: K+ conductance Transmitter Anatomy Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Norepinephrine Cell bodies in pons and brain stem project to all levels a1: Prazosin Excitatory: K+ conductance, IP3, DAG a 2: clonidine Yohimbine Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+ conductance; Inhibitory: K+ conductance, cAMP b1: isoproterenol, Atenolol, practolol Excitatory: K+ conductance, cAMP Butoxamine Inhibitory: may involve in electrogenic sodium pump; cAMP phenylephrine dobutamine b2: albuterol Transmitter Anatomy Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Histamine Cells in ventral posterior hypothalamus H1: 2(mfluorophenyl)histamine Mepyramine Excitatory: K+ conductance, IP3, DAG H2: dimaprit Ranitidine Excitatory: K+ conductance, cAMP H3: R--methylhistamine Thioperamide Inhibitory autoreceptors Transmitter Opioid peptides Tachykinins Anatomy Cell bodies at all levels; long and short connections Primary sensory neurons, cell bodies at all levels; long and short connections Receptor Subtypes and Preferred Agonists Receptor Antagonists Mechanisms Mu: bendorphin Naloxone Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+ conductance, cAMP Delta: enkephalin Naloxone Inhibitory (postsynaptic): K+ conductance, cAMP Kappa: dynorphin Naloxone NK1: Substance P methylester, aprepitant Aprepitant Excitatory: K+ conductance, IP3, DAG NK2 NK3 Endocannabinoids Widely distributed CB1: Anandamide, 2- Rimonabant arachidonyglycerol Inhibitory (presynaptic): Ca2+ conductance, cAMP Schematic diagram of a glutamate synapse