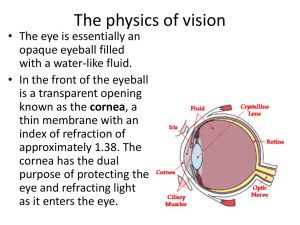
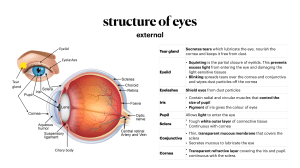
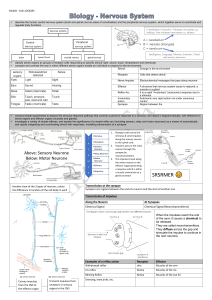
vision
advertisement

Refraction Glaucoma & Glaucoma test Degree of cell packing in retina Intrinsic Muscles of the Eye: The Iris • Iris – circular.....constricts – radial.....…dilates • Dilating pupil for eye exam: how to do it? Pharmacology of pupillary dilation: Atropine Intrinsic Muscles of the Eye: Ciliary Muscle • Ciliary muscle relaxed = tension on zonular fibers = tension on lens = flattened lens = distant focus • Ciliary muscle contracted = tension on zonular fibers reduced = less tension on lens = lens becomes more spherical =near focus • Eye strain Using a Microscope or Binoculars Accommodation animation 1) Demonstrate Convergence 2) Measure NPA With Convergence NPA Left eye _______________mm NPA Right eye ______________ mm Sex of subject ___ Age in months___ with corrective lenses/contacts? yes/no Presbyopia Disorders of Focus • Myopia = nearsighted – eyeball too long, cornea/lens to “strong” – image focused in front of retina – correct with concave lens • Hyperopia = farsighted – eyeball too short, cornea/lens to “weak” – image focused behind retina – correct with convex lens • Astigmatism – irregular surface of lens or cornea Cataract • Extraocular muscles • Actions of extraocular muscles • Motor innervation by CN III, IV, VI Strabismus= misalignment of eyes Storytime Suprachiasmatic Nucleus for diurnal cycling Visual reflexes: Aka. Area 17 and V1 Accomodation, Saccades, Tracking, Pupillary reflex Evolution of Binocular Vision Mapping the boundary of each visual field Retinotopy Goliath? The Retina • Photoreceptors – Rods – Cones • Bipolar cells • Ganglion Cells – axons converge at optic disk – axons constitute optic nerve • Horizontal cells • Amacrine cells Importance of abundant membrane Visual Acuity • 120,000,000 rods and 6,000,000 cones per retina • 1,200,000 retinal ganglion cells & axons • 105:1 convergence ratio • Fovea: cones only, 1:1 highest visual acuity but poor sensitivity Counting fingers and Reading the Writing on the Wall Demonstration of Blind Spot (diagram) •Differences due to opsin: 4 types Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision Web-based color deficiency test Stargazing Finding your car in a dark parking lot Choosing socks “Bleaching” of photopigments Visual Purple The Dark Current Phototransduction • In the DARK, rod is depolarized due to influx of Na+ (called dark current) • In the LIGHT, rod is hyperpolarized • cGMP keeps Na+/Ca++ channels open • Light results in decrease of cGMP and thus closure of ion channels, and • Hyperpolarization of cell, and • Reduced release of Neurotransmitter Glutamate Properties of Cortical Neurons • Simple – respond to stationary bar of light in certain orientation • Complex – respond to moving bar of light in certain orientation • Hypercomplex – respond to moving bar of light of a certain length in a certain orientation Parallel Processing in the Cortex • Motion sensitive • Color and shape sensitive Story of woman at street crossing Why so much emphasis on the Visual System?