Testing in Software Life Cycle
advertisement

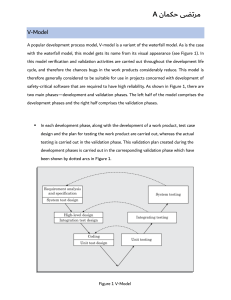
Software Development Model 0 The development process adopted will depend on the project aims and goal 0 There are numerous model have been developed to achieve different required objectives 0 The life cycle model that is adopted for a project will have a big impact on the testing that is carried out 0 Testing are highly related to software development activities 0 Testing is organized to fit the development life cycle Software Development Model 0 In every development life cycle, a part of testing is focused on verification testing and validation testing 0 Verification testing is concerned with evaluating a work product, component or system to determine whether it meets the requirement set 0 Validation testing is concerned with evaluating a work product, component or system to determine whether it meets the user needs and requirements Waterfall Model Need, wish, policy, law User Requirements Systems Requirements Global Design Detail Design Implementation Testing Testing at the End V-Model 0 Was developed to address some of the problems experienced using the traditional waterfall: 0 Defects were being found too late 0 The V-model provides guidance that testing needs to begin as early as possible 0 Testing – in parallel with development V-Model 0 Common V-model uses four test levels 0 Component testing – search defects & verifies the functioning of software components (module, programs, objects, classes) 0 Integration testing –tests interface between components, interface with OS, file systems and hardware 0 System testing – concerned with the behavior of the whole system 0 Acceptance testing – validation testing with respect to user needs, requirements, business process V-Model Need, wish, policy, law Operational systems Preparation Acceptance Test User Requirements Preparation Systems Test Systems Requirements Global Design System Test Execution Preparation Integration Test Detail Design Acceptance Test Execution Integration Test Execution Component Test Execution Implementation Iterative Life Cycle Implement Test Build Develop Define Phase 3 Implement Test Build Define Implement Test Build Develop Define Develop Phase 2 Phase 1 Delivery is divided into increments or builds Subsequence increments will need testing for new functionality, regression testing of the existing functionality, and integration testing of both new and existing parts Iterative Life Cycle Example 0 Rapid Application Development (RAD) – parallel development Function 1 Define Develop Build Test Function 2 Define Develop Build Test Function 3 Define Develop Build Test Function 4 Define Develop Build Test Iterative Life Cycle Example: Agile Development 0 Currently one of the most well-known development life- cycle model & human friendly 0 Characteristic: 0 Promotes the generation of business stories to define 0 0 0 0 functionality Promotes pair programming and shared code ownership State component test scripts shall be written before the code is written States that integration and testing of code shall happen several times States that we always implement the simplest solution to meet today’s problem Testing within a Life Cycle Model 0 Which ever life cycle model is being used, there are several characteristic of good testing: 0 Every development activity, there is a corresponding testing activity 0 Each test level has test objectives specific to that level 0 The analysis and design of tests for a given test level should begin during the corresponding development activity 0 Tester should be involved in reviewing documents as soon as drafts are available in the development cycle Test Levels: Component Testing 0 Also known as unit, module and program testing 0 Searches for defects and verifies the functioning of software 0 May be done in isolation from the rest of systems 0 Most often stubs and drivers are used to replace missing software 0 May include testing of functionality and specific nonfunctionality characteristic 0 Test cases are derived from work products – software design, data model 0 Occurs with access to the code being tested Test Levels: Component Testing Component A A Driver Component B Stub B Test Levels: Integration Testing 0 Test interfaces between components, interaction between different parts of systems 0 There are may be more than one level of integration testing 0 Greater the scope of integration – the more difficult to isolate failures 0 Approaches: 0 Big-bang 0 Incremental-testing Test Levels: Systems Testing 0 Concerned with the behavior of the whole system/product as defined by the scope of development project or product 0 Tests based on risks or requirement specification, business processes, use cases or high level descriptions of systems behavior 0 Should investigate both functional and non-functional requirements 0 Requires controlled test environment