Week 17-18 notes
advertisement

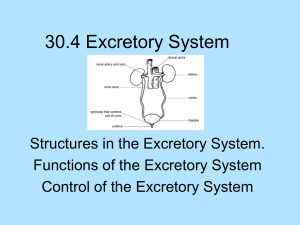
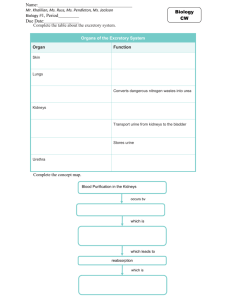
Biology 20 Excretory System Excretion Introduction • Humans are 70% water – 1/3 of this is in plasma • Blood – carries nutrients, picks up waste • Wastes need to be removed • Composition of fluids need to be kept in balance • Excretion: monitor, analyze, select, reject EXCRETION • Excretion is the process of __________________________________. • During the metabolic processes of the body waste products are removed from the site of production by the ____________. • As these wastes accumulate, the kidney removes them from the blood and ____________ them to the environment • The excretory product becomes ________________. EXCRETION • Process of removing cellular waste • Balance pH of blood • Maintain water balance • Happens in Kidney 1 Biology 20 Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM • Functions: • ___________________________________________________ • Regulates and stabilise the internal environment by controlling 4 groups of chemicals 1. ______________________ 2. ________________________________: Elimination of poisonous by-products of chemical reactions: 3. _________________________________: regulation of hydrogen, sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride ions: 4. _________________________________: Removal of essential nutrients that dangerous in excess: WASTE PRODUCTS • The principle metabolic wastes in most animals are: o ____________________– is excreted through the respiratory surfaces o ______________ – excreted through respiratory surfaces, skin as sweat as well as kidneys o _________________________ – products of protein and nucleic acid digestion 2 Biology 20 Excretory System NITROGENOUS WASTES • Ammonia –The first metabolic product of amino acid _________________ – hydrolysis (protein digestion) o highly toxic o cannot accumulate in body o must be converted into ________________________________ • Uric Acid – produced from ammonia o not very soluble – can be excreted as a paste with little water loss o non - toxic Deamination & Urea • Proteins – contain a nitrogen molecule – Amino acid – building blocks of protein • Nitrogenous base • Removal of N and H • Occurs in the ________________ • Byproduct – ammonia – Toxic substance • Ammonia combines _______________________________ • Urea –less toxic • Uric acid – waste product from the breakdown of nucleic acids (DNA) • Urea – converted from ammonia – less toxic than ammonia – produced in the liver – can be excreted in concentrated form – requires more water to excrete than uric acid 3 Biology 20 Excretory System 4 Biology 20 Excretory System ORGAN: Function • ________________ : site of blood filtration • ________________: brings blood to kidney • ______________: brings blood back to heart • ____________: Brings waste TO bladder • _____________: Temporary urine storage site • _____________: Brings waste FROM bladder, out of system The Kidney Structure Function Cortex Medulla Renal Pelvis 5 Biology 20 Excretory System STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF KIDNEY Three distinct regions of the kidney o Cortex – outer region o Medulla – just below cortex o Pelvis – a hollow chamber within the medulla • The cortex and medulla of each kidney are made up of a approximately ___________________________ 6 Biology 20 Excretory System • NEPHRON – __________________________________________ STRUCTURE FUNCTION Brings blood to glomerulus Leaves glomerulus, goes to vein Ball of capillaries – site of filtration Filter First tube in nephron. From BC… 7 Biology 20 Excretory System Leads to collecting duct Empties waste into renal pelvis Collecting site for all nephrons – waste out to ureter • BOWMAN’S CAPSULE o a double walled chamber – start of the tubule. • GLOMERULUS o network of capillaries within the Bowman’s capsule o __________________ (4x higher than in capillaries) • PROXIMAL TUBULE o active transport of many valuable substances back into blood network ________________, ________________, ________________ 8 Biology 20 Excretory System • LOOP OF HENLE o the long hair-pin turn!! o some of the remaining water and salt will be _____________to the blood o lies in the medulla which is relatively salty (hypertonic) • DISTAL TUBULE and COLLECTING DUCTS o _____________________________________________ • This depends on the presence of certain hormones • (ADH) Anti diuretic Hormone o Exact amounts of substances are reclaimed to the blood • very precise • Urine Formation • Depends on three functions: – __________________ • Movement from blood – Bowman’s capsule – _____________________ • Transfer of needed nutrient back INTO blood • Tubules – ______________________ • Movement of material from blood back into nephron 9 Biology 20 Excretory System Four Steps to Urine Formation 1) FILTRATION – Occurs at the junction of the ______________ and the wall of the ___________________ – Each glomerulus receives blood from an _____________ and discharges its blood into an __________________ (hypertonic). – Fluid and dissolved materials (nutrients, wastes, ions) in the blood plasma pass from the _______________ into Bowman’s capsule • due to a local increase in blood pressure within the glomerulus – this material is then called ________________. – blood cells, plasma proteins and platelets are too large to pass through the wall of the capillary and therefore remain within the capillary. 2) REABSORPTION – _________________________________ – returns about ________ of filtrate to the blood – efferent arteriole feeds second capillary network that surrounds the tubule – this network receives __________________________ • eventually leads to ______________________ • Water rushes into the blood because of _______________ Problem • Not enough water is returned this way. Solution • Just actively transport water into the blood right? Wrong!!! There is no way of ACTIVELY transporting water So how can we transport more water into the blood? 10 Biology 20 Excretory System o active transport of solutes into the capillary bed • _______________ • _______________ • _______________ • _________________ (Na+) o water is ________________ reabsorbed from the proximal tubule as these solutes are actively removed from the filtrate o Reabsorption and the distal tubule. o A more selective, precisely regulated reabsorption occurs in the _____________________ o Additional quantities of ________ and ______ may be reabsorbed o The exact amount of each substance reclaimed occurs in the ________________. o excess is excreted in urine e.g. glucose and diabetes 3) SECRETION – This is the last chance for anything to leave the blood and enter the urine – _______________________ – Occurs in the ________________ and _________________ – Hydrogen ion secretion – helps regulate blood ____________ • Distal tubule • Na+ moves into the blood and H+ moves into the tubule filtrate – ____________________ (ranges 7.3 - 7.4) – _____________________ (ranges 4.5 - 8.5) – potassium secretion 11 Biology 20 Excretory System • prevents accumulation of potassium that can create neural and muscular problems – some drugs are removed from the body by secretion – substances eliminated in this manner are • ___________________ – by product of protein metabolism • ___________________ • ___________________ 4) Elimination • Pathway o _________________ o _________________ o _________________ o _________________ o _________________ o _________________ 12 Biology 20 Excretory System What is in urine? • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ 13 Biology 20 Excretory System Control of Excretion Disorders and Treatments HORMONES • _____________ • The ___________________________ – influences the RATE of water reabsorption into blood from collecting ducts – released by the pituitary gland in the brain • Osmoreceptors in brain stimulated by low __________________ and increased _________________________ – both of those means that there is not enough water in the blood. – rate of ADH secretion is increased. ADH saves water. – More ADH = ___________________ = increased urine concentration – Very yellow concentrated urine • Most water reabsorbed in _______________________ – permeable • Rest of tubule permeable ONLY IF ADH is present – Ascending loop – Distal tubule Aldosterone and Sodium • Aldosterone – _____________________ – Produced in __________________ – Increased ____________________ – More water may also move out • Osmosis (high to low) 14 Biology 20 Excretory System • Blood pressure – Less fluid – _____________________________ – Angiotensin produced • Constricts blood vessels, increase blood pressure • Causes release of __________________ – Aldosterone acts on _______________ and ________________ • More sodium reabsorbed • Fluid level increase • BP increases Kidney Disease • Diabetes Insipidus – Problems with ADH production – No ADH, no H2O reabsorption – Huge urine output • Up to 20 L/day • Kidney Stones – Minerals forming solid crystals (Ca+, Na+) – Get lodged in pelvis or ureter – Can tear tissues as it moves out – OHMYGOODNESSMAKEITSTOPICANNOTSTANDTHE PAIN!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! • Stone removal – Surgery – Ultrasound – catheter • Kidney Dialysis – Cleaning of blood – Treatment of kidney failure – Blood goes through a filter – Concentration gradients remove waste 15 Biology 20 Excretory System • Kidney Donation – Human system built in twos – Extra kidney for backup – One kidney – can do all the work – With less than 20% kidney function, problems occur • Requires kidney dialysis – If problem gets really bad, might need a new one TRANSPLANT Week 11-12 formative Complete the assignment linked in PowerSchool and send it to me. 16