File
advertisement

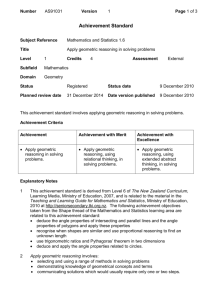
S t P a u l ’ s C o l l e g e MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIT PLAN Geometry and Measurement – Level Five & Six Term:4 Topic 6 Class:101MAT Duration: 2 weeks Context / Topic: Geometric Reasoning In a range of meaningful contexts, students will be engaged in thinking mathematically and statistically. They will solve problems and model situations that require them to: GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT ACHIEVEMENT OBJECTIVES - Level 6 GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT ACHIEVEMENT OBJECTIVES – Level 6 Measurement, Shape and Transformation Measurement and Shape Solve problems and model situations that require them to: Deduce the angle properties of intersecting and parallel lines and the angle properties of polygons and apply these properties Apply trigonometric ratios and Pythagoras’ theorem in two dimensions Solve problems and model situations that require them to: Deduce and apply the angle properties related to circles Recognise when shapes are similar and use proportional reasoning to find an unknown length Use trigonometric ratios and Pythagoras Theorem in 2 or 3 dimensions Achievement: GLOBAL LEARNING INTENTIONS Excellence Merit: selecting and using methods in solving problems Demonstrating knowledge of geometrical concepts and terms Communicating solutions which would normally require only one or two steps selecting and carrying out a logical sequence of steps connecting different concepts and representations demonstrating understanding of concepts forming and using a model; relating findings to a context, or communicating thinking using appropriate mathematical statements. devising a strategy to investigate or solve a problem identifying relevant concepts in context developing a chain of logical reasoning, or proof forming a generalisation using correct mathematical statements, or communicating mathematical insight. MAINTENANCE (Looking backwards and keeping skilful): HOMELINK ACTIVITIES: Yes Yes Yes Yes Responsibility Respect Yes Yes Computer/Word Processing Publisher/Excel/PowerPoint e-mail/Fax/Phone/Scan Internet-Research Digital Camera/Video Yes KEY COMPETENCIES Thinking perseverance Passion Courage Brotherhood Using Language, Symbols and Texts Managing Self Relating to Others Participating and Contributing English Mathematics and Statistics Science Social Sciences Technology OTHER CURRICU LUM LINKS ELEARNIN G (ICT) VALUES & PRINCIPLES faith Yes Yes Yes Yes yes Yes Yes yes Yes Pre-test (Diagnostic) ASSESSMENT CAREERS: GAPS TO COVER NOTES ABOUT ENTRY LEVEL OF STUDENTS (Prior Knowledge/Skills Required): Pythagoras’ theorem trigonometric relationships in right-angled triangles similar triangles angle properties of intersecting and parallel lines angle properties of polygons angle properties of circles. Post-test (Summative) Sample Formative assessment Self Assessment Peer Assessment ARB’s Other e.g. Exemplars, asTTle, etc Literacy Gaps: Lots of language in this unit – use lots literacy strategies Numeracy Gaps: a/std Yes Yes Yes Yes Internet – Webquests and Web 2.0 Video Conferencing Inspiration and Other Programmes The Arts (Music/Dance/Drama/Visual) Health and Physical Education Learning Languages (Te Reo etc) Programming EOTC SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTIONS We are learning to: (What should the students learn? What do I intend them to learn?) Other Gaps: Graphics calculator competency ACTIVITIES, THINKING TOOLS AND OTHER RESOURCES (What will I do to help my students achieve this? Strategies/activities linked to Key Competencies to help students achieve) SUCCESS CRITERIA We know we have achieved this when we can: (How will the students know they have achieved? Specific ideas on which to base teaching and activities) SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Revision: giving geometric reasoning in questions related to angles and parallel lines properties. SUCCESS CRITERIA: To be confident to use angle and parallel lines rules to solve problems and give reasoning consistently. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Revision: how to apply geometric reasoning related to the angle properties of polygons. SUCCESS CRITERIA: To be able successfully complete worksheets by: Identifying and naming shapes; Finding interior angles; Finding exterior angles of polygons; Work out the sum of interior angles of n-sided polygon. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Revision: Use Pythagoras’ Theorem to solve problems. SUCCESS CRITERIA: To be confident to use Pythagoras’ Theorem to: Find the hypotenuse; Find the shorter side; Apply your knowledge to worded problems. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: 2 Lessons Revision: Trigonometric ratios SUCCESS CRITERIA: To complete worksheets by applying trigonometric ratios and Pythagoras’ theorem to: Find unkown angles; Find unkown side lengths; Solving problems using trigonometry. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Revision: how to apply angle properties in different types of triangles and special quadrilaterals to solve problems and give reasoning. SUCCESS CRITERIA: Be cofident to complete worksheets by applying angle rules as a reasoning to solve problems related to special triangles and quadrilaterals. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Revision: Learning to apply geometric reasoning to solve problems with angles related to circles. Prior knowkedge: brainstorming ideas (concept map) about anything you know about angle and parallel lines rules; Summary on white board; Geometric reasoning cards – abbreviation self – check; Vocabulary: acute, right, obtuse, adjacent, parallel, transversal, corresponding, alternate, co-interior. Class=13A, 13B Home=187-195 Mon. 20/10/14 Group work, pair-to-share. Worksheets: Matching exercise; Fill in gaps, boxes and tables; Work out values of the marked angles; Multi choice questions and Solving complex problems by using rules in reverse. Modelling: the thinking process (think aloud); giving written geometric reasoning. Vocabulary: regular polygon, interior and exterior angles, diagonal, vertex/vertices, isosceles, equilateral, scalene triangles, trapezium, mediator, bisector, axes of symmetry. Class=13c Home=13e, 189-192 Tuesd. 21/10/14 Prior knowledge: labelling the sides of right-angled triangle. Worksheet: Examples of two problems with diagrams providing prompts to follow and modelling how to form right-angled triangle by including extra lines on a diagram and drawing the axes of symmetry. Group work, pair-to-share. Vocabulary: hypotenuse, square root Advanced students to do worksheet with more complex practical problems. Class=16A / 16B Home=226-232 Wed. 22/10/14 Prior knowledge: labelling the sides of right-angled triangle in relation to a given angle. SOH, CAH and TOA. Group work: completing worksheets by solving problems using trigonometric ratios. Use calculator to work out angles - shift option. Vocabulary: hypotenuse, opposite side, adjacent side, sine, cosine, tangent, angles of elevation and depression. Class=16E, 16A advanced 16G Home=233-243 Thurs 23/10/14 double Prior knowledge: Matching cards – quadrilaterals with special properties. Emphasis on symmetry. Vocabulary: Work in pairs. Worksheets: find with reasons. Excellence: prove with reasons. Class=13C, 13D Home=197-201 Tues 28/10/14 Relevance: AS 91031 geometric reasoning. Circle geometry. Prior knowledge: group work 2 min – brainstorming 4 main circle rules, cyclic quads; summary - on white board using different colours for pictures, abbreviation; Vocabulary: arc, chord, radius, tangent, cyclic, semi - circle, minor and major arcs, sector, SUCCESS CRITERIA: Successfully solve problems on worksheets by deducing and applying angle properties and giving reasons. segment, circumference, concyclic points. Class=15A, B, C (some problems) Home=215-226 (rest of the problems) Wed 29/10/14 SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: Learning to understand geometric reasoning: The criteria that makes two polygons similar; What bearing is. SUCCESS CRITERIA: To be able successfully Recognise similar shapes; Identify similar triangles; Use proportional reasoning to find an unknown length; Work out bearings; Apply your knowledge to solve worded problems with bearings. SPECIFIC LEARNING INTENTION/S: To revisit and clarify some aspects of exam papers indentified as ares of need by students. SUCCESS CRITERIA: Set by students. Revision: AS 91031 geometric reasoning. Similar shapes and objects. Bearings. Prior knowledge: in groups discussing aspects of similarity and bearings using coloured handouts. Summarising by highlighting the main facts. Connection with prior knowledge: links to angle properties, parallel lines, Pythagoras’ Theorem, trigonometric ratios. DAT: group work, pair-to-share. Scaffolding, prompting and explaining. Advanced students will be given individual tasks to work on. Vocabulary: scale factor, proportional, image, corresponding angles and sides. Class=14, exam papers-“blue book”, worksheets Home=14A, Thurs 30/10/14 double Clarify AME Group work / or pair-to-share. Revisit vocabulary. Class=”blue workbook” Home= notes revision, self study Mon 3/11/14 ASSESSMENT APPROACH (How will I assess the Success Criteria? How can learning achievement be measured? Remember to include Formative Assessment) BEFORE THE UNIT Diagnostic Test to see what the students remember (covered) about geometric reasoning in relation to AO from Y 10 and Term 2. DURING THE UNIT Complete assignments from ESA AND Learning workbook as formative assessment at the end of each lesson After the unit Apply geometric reasoning in solving problems (AS 91031) 4 Credits External UNIT EVALUATION (Consider: Planning and preparation; catering to individual students’ needs; challenging all students; use of class time; overall delivery; success of unit based on assessment and anecdotal observations; areas for future improvement – what would have worked better) CHILDREN’S LEARNING PERSONAL TEACHINGS ASSESSMENT FOR FUTURE PLANNING