Puzzle Cub Lesson
advertisement

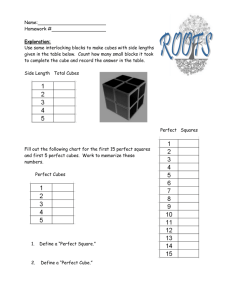
EDCI270 Educational Technology Case 2-STEM Lesson Plan Coots, Michael Hinton, Lauren Neel, Mary Overview: Through the creation of a wooden puzzle cube students will be introduced the design process and how it applies to their lives. Using modern 3D modeling software and traditional graph paper students will experience the difference between the tools used in the design process and how they both are still integral to good design. Objectives: At the end of the activity the students will have: Designed a puzzle cube on 3D graph paper using 4 unique pieces without any gaps or overlaps, overall cube size should be 3” X 3” X 3” Created a 3D model in IronCAD by creating 3D parts of the 4 pieces drawn on graph paper Produced the cube as a final product using premeasured 1” wooden cubes while adhering to the 3D IronCAD model and the 2D drawings Teaching Standards: Engineering and Technology Education 2.1 System Models and steps in the Engineering design Process 2.2 Applications of the Engineering design process Required Materials: 3D graph paper Pencils Computer with IronCAD Premeasured 1” wood cubes Markers Rulers Wood glue or alternate adhesive Procedures: 1. Group students individually with their College Mentor. 2. Explain the process of Design to the students. The design process starts by defining the problem or the need that will be addressed by the product or solution. Next the design needs constraints and criteria to guide the design process and keep the original problem in focus. Constraints are specific details that need to be addressed or followed by the design, while the criteria are means by while the design will be evaluated. Following this is the brainstorming or idea generation step. Once ideas are formed and a solution starts to develop then a prototype is created to implement the solution. The prototype is tested and then retooled to account for new information gained from testing. The new prototype is 1 EDCI270 Educational Technology Case 2-STEM Lesson Plan Coots, Michael Hinton, Lauren Neel, Mary tested and the process continues until an acceptable prototype is produced. The final prototype is then evaluated by an outside source to confirm whether or not it solves or meets the needs or problem that was defined at the beginning of the process. 3. Explain how the project relates to the design process. Through this project students will need to discuss and define a problem or need with the instructor, i.e. students want a puzzle cube. Once they understand the need they will be given constraints and criteria for their designs, which can be adjusted to better relate to the students. When the students understand the problem, the constraints, and the criteria they will be ready to start brainstorming ideas for their pieces. Using these pieces they will then start “prototyping” their puzzle cubes, deciding which pieces fit together and which will give them the final product that they want. After these “prototypes” are finished they will transcribe the designs into IronCAD and create a 3D model of their puzzle cube. When the model is finished they will evaluate it to make sure it meets the constraints and criteria of the design. Passing this evaluation they will use their 3D model and 2D design to create their pieces out of the premeasured wooden cubes. The product is finished when the pieces are assembled to create puzzle cube. They will then evaluate their puzzle cubes for the final time before submitting them for grading. 4. Discuss constraints and criteria with students such as: (how large the final cube will be, how many pieces the cube should consist of, etc). a. Assembled cube should be 3 blocks cubed, 27 1” cube blocks total (constraint) b. Each piece should be unique and interconnected (criteria) c. Each piece should consist of at least 3 blocks (constraint) d. The puzzle should consist of 4-6 pieces (constraint) e. The pieces should fit together without overlapping pieces or gaps between pieces (criteria) 5. Brainstorm puzzle piece ideas and draw those ideas out on graph paper. Students will need to produce about 15 different ideas. 6. Students should select their favorite idea and start constructing their puzzle cube on graph paper. 7. Once the puzzle cube is on graph paper, the students will need to model them in IronCAD. Each piece should be a separate part file. 8. In a new project file, import the new puzzle pieces, and piece them together. Using the tools in IronCAD use the pieces to construct the puzzle cube, then with another tool create an exploded view. 9. Students should print out a copy of the exploded view of the puzzle cube. 10. Students should start constructing puzzle pieces with pre-measured cubes with the use of glue. 11. Once the pieces are all created have students assemble the finished puzzle cube. Assessment: 2 EDCI270 Educational Technology Case 2-STEM Lesson Plan References: 3 Coots, Michael Hinton, Lauren Neel, Mary