Atrazine-Induced Hermaphroditism
advertisement

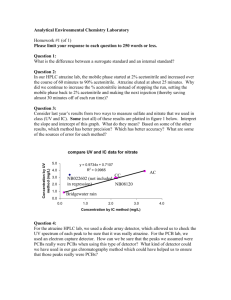
Atrazine-Induced Hermaphroditism By: Michelle Lin What is Atrazine? What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis Metabolized to four hydroxyatrazine compounds & to three chlorinated atrazine compounds. What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis Metabolized to four hydroxyatrazine compounds & to three chlorinated atrazine compounds. Predominate metabolites found in plants What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis Metabolized to four hydroxyatrazine compounds & to three chlorinated atrazine compounds. Predominate metabolites found in plants Desethylated atrazine, desisopropyl atrazine, & diaminochlorotriazine (DACT) predominate in animal tissues, & in soils and water What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis Metabolized to four hydroxyatrazine compounds & to three chlorinated atrazine compounds. Predominate metabolites found in plants Desethylated atrazine, desisopropyl atrazine, & diaminochlorotriazine (DACT) predominate in animal tissues, & in soils and water commonly detected pesticide in ground and surface water What is Atrazine? Systematic herbicide that blocks photosynthesis Metabolized to four hydroxyatrazine compounds & to three chlorinated atrazine compounds. Predominate metabolites found in plants Desethylated atrazine, desisopropyl atrazine, & diaminochlorotriazine (DACT) predominate in animal tissues, & in soils and water commonly detected pesticide in ground and surface water detected in streams, rivers, groundwater, and reservoirs is related directly to both its volume of usage, and its tendency to persist in soils and move with water. It’s a pesticide, so what? It’s a pesticide, so what? Most widely used herbicide in the world It’s a pesticide, so what? Most widely used herbicide in the world Most common contaminant in ground and surface waters It’s a pesticide, so what? Most widely used herbicide in the world Most common contaminant in ground and surface waters About 64 to 75 million lbs of active ingredient are applied per year It’s a pesticide, so what? Most widely used herbicide in the world Most common contaminant in ground and surface waters About 64 to 75 million lbs of active ingredient are applied per year Three-fourths of all field corn & sorghum are treated with atrazine annually for weed control It’s a pesticide, so what? Most widely used herbicide in the world Most common contaminant in ground and surface waters About 64 to 75 million lbs of active ingredient are applied per year Three-fourths of all field corn & sorghum are treated with atrazine annually for weed control Also used on sugarcane, wheat, guava, macadamia nuts orchard grass and hay What does Atrazine cause? What does Atrazine cause? Hermaphroditism in American Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens) What does Atrazine cause? Hermaphroditism in American Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens) 21 ppb atrazine exposure in 48 hrs can results in severe gonadal dygenesis in African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) What does Atrazine cause? Hermaphroditism in American Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens) 21 ppb atrazine exposure in 48 hrs can results in severe gonadal dygenesis in African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) at concentrations of 0.1 ppb, atrazine induces hermaphroditism The experiment The experiment Leopard frogs obtained from Sensiba March, Brown County, Wisconsin then shipped to the University of California Berkeley The experiment Leopard frogs obtained from Sensiba March, Brown County, Wisconsin then shipped to the University of California Berkeley Larvae were treated by immersion with nominal concentrations of 0, 0.1, or 25 ppb atrazine (98% pure) The experiment Leopard frogs obtained from Sensiba March, Brown County, Wisconsin then shipped to the University of California Berkeley Larvae were treated by immersion with nominal concentrations of 0, 0.1, or 25 ppb atrazine (98% pure) Atrazine was predissolved in ethanol, and all treatments contained 0.0036% ethanol The experiment Leopard frogs obtained from Sensiba March, Brown County, Wisconsin then shipped to the University of California Berkeley Larvae were treated by immersion with nominal concentrations of 0, 0.1, or 25 ppb atrazine (98% pure) Atrazine was predissolved in ethanol, and all treatments contained 0.0036% ethanol Exposed throughout larval period from 2 days posthatching until complete tail reabsorbtion. The experiment Leopard frogs obtained from Sensiba March, Brown County, Wisconsin then shipped to the University of California Berkeley Larvae were treated by immersion with nominal concentrations of 0, 0.1, or 25 ppb atrazine (98% pure) Atrazine was predissolved in ethanol, and all treatments contained 0.0036% ethanol Exposed throughout larval period from 2 days posthatching until complete tail reabsorbtion. All dosing and analyses were conducted blindly with color-coded tanks and treatments. The experiment continued The experiment continued At metamorphosis, each animal was weighed and measured then euthanized in 0.2% benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative, and preserved in 70% ethanol until further analysis. The experiment continued At metamorphosis, each animal was weighed and measured then euthanized in 0.2% benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative, and preserved in 70% ethanol until further analysis. Sex of all individuals were determined based on gross gonadal morphology using a Nikon SMZ 10A The experiment continued At metamorphosis, each animal was weighed and measured then euthanized in 0.2% benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative, and preserved in 70% ethanol until further analysis. Sex of all individuals were determined based on gross gonadal morphology using a Nikon SMZ 10A Tissues dissected and dehydrated in graded alcohols followed by infiltration with Histoclear and paraffin The experiment continued At metamorphosis, each animal was weighed and measured then euthanized in 0.2% benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative, and preserved in 70% ethanol until further analysis. Sex of all individuals were determined based on gross gonadal morphology using a Nikon SMZ 10A Tissues dissected and dehydrated in graded alcohols followed by infiltration with Histoclear and paraffin Serial histological sections cut at 8µm through entire gonad The experiment continued At metamorphosis, each animal was weighed and measured then euthanized in 0.2% benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative, and preserved in 70% ethanol until further analysis. Sex of all individuals were determined based on gross gonadal morphology using a Nikon SMZ 10A Tissues dissected and dehydrated in graded alcohols followed by infiltration with Histoclear and paraffin Serial histological sections cut at 8µm through entire gonad Slides were stained in Mallory’s trichrome stain and images of gonads were recorded The collection sites The collection sites Localities based on atrazine use determined by sales The collection sites Localities based on atrazine use determined by sales Countries with <0.4kg/km² atrazine use were chosen as potential control sites The collection sites Localities based on atrazine use determined by sales Countries with <0.4kg/km² atrazine use were chosen as potential control sites >9.3 kg/km² were chosen as potential atrazineexposed sites The collection sites Localities based on atrazine use determined by sales Countries with <0.4kg/km² atrazine use were chosen as potential control sites >9.3 kg/km² were chosen as potential atrazineexposed sites Collection sites continued Collection sites continued Sampled in Utah on 15 July 2001 and moved eastward Collection sites continued Sampled in Utah on 15 July 2001 and moved eastward Collected 100 animals in 8 sites for a total of 800 animals Collection sites continued Sampled in Utah on 15 July 2001 and moved eastward Collected 100 animals in 8 sites for a total of 800 animals Selected small individuals in an attempt to sample newly metamorphosed animals Collection sites continued Sampled in Utah on 15 July 2001 and moved eastward Collected 100 animals in 8 sites for a total of 800 animals Selected small individuals in an attempt to sample newly metamorphosed animals Animals were euthanized in benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative for 48 hours and preserved in 70% ethanol Collection sites continued Sampled in Utah on 15 July 2001 and moved eastward Collected 100 animals in 8 sites for a total of 800 animals Selected small individuals in an attempt to sample newly metamorphosed animals Animals were euthanized in benzocaine, fixed in Bouin’s fixative for 48 hours and preserved in 70% ethanol They were measured and sex was determined and histological analysis was conducted on the gonads of 20 males from each site and a subset of females from each site Chemical Analysis Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Atrazine levels were determined Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Atrazine levels were determined Water sample extracted in organic solvent followed by aqueous/organic extraction Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Atrazine levels were determined Water sample extracted in organic solvent followed by aqueous/organic extraction Analyzed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrophotometry using daughter ion Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Atrazine levels were determined Water sample extracted in organic solvent followed by aqueous/organic extraction Analyzed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrophotometry using daughter ion Positive controls contained mixtures of pesticides at both 0.1 and 10.0 ppb Chemical Analysis At each site, 100mL of water was collected Frozen on dry ice Atrazine levels were determined Water sample extracted in organic solvent followed by aqueous/organic extraction Analyzed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrophotometry using daughter ion Positive controls contained mixtures of pesticides at both 0.1 and 10.0 ppb detection limits at 0.1 ppb Gonadal analysis on lab-animals Gonadal analysis on lab-animals Control animals sexually differentiated at metamorphosis Gonadal analysis on lab-animals Control animals sexually differentiated at metamorphosis earliest males to metamorphose had solid testicular lobules Gonadal analysis on lab-animals Control animals sexually differentiated at metamorphosis earliest males to metamorphose had solid testicular lobules testes were more differentiated (contained more distinct tubules and germ cells) anteriorly than posteriorly Gonadal analysis on lab-animals Control animals sexually differentiated at metamorphosis earliest males to metamorphose had solid testicular lobules testes were more differentiated (contained more distinct tubules and germ cells) anteriorly than posteriorly Gonadal analysis continued Gonadal analysis continued Animals that metamorphosed later had open lobules Gonadal analysis continued Animals that metamorphosed later had open lobules Contained both primary spermatogonia and spermatids Gonadal analysis continued Animals that metamorphosed later had open lobules Contained both primary spermatogonia and spermatids Females had numerous oocytes in their gonads and a central ovarian cavity Gonadal analysis continued Animals that metamorphosed later had open lobules Contained both primary spermatogonia and spermatids Females had numerous oocytes in their gonads and a central ovarian cavity The Results The Results Atrazine-treated males (0.1 and 25 ppb) were sexually differentiated at metamorphosis The Results Atrazine-treated males (0.1 and 25 ppb) were sexually differentiated at metamorphosis 36 and 12% of males treated with 0.1 and 25 ppb atrazine suffered gonadal dysgenesis The Results Atrazine-treated males (0.1 and 25 ppb) were sexually differentiated at metamorphosis 36 and 12% of males treated with 0.1 and 25 ppb atrazine suffered gonadal dysgenesis Gonadal dysgenesisunderdeveloped testes with poorly structured, closed lobules or no lobules at all and low to absent germ cells The Results Atrazine-treated males (0.1 and 25 ppb) were sexually differentiated at metamorphosis 36 and 12% of males treated with 0.1 and 25 ppb atrazine suffered gonadal dysgenesis Gonadal dysgenesisunderdeveloped testes with poorly structured, closed lobules or no lobules at all and low to absent germ cells The Results Continued The Results Continued 29% of the 0.1 ppb-treated animals and 8% that were treated with 25 ppb displayed varying degrees of sex reversal The Results Continued 29% of the 0.1 ppb-treated animals and 8% that were treated with 25 ppb displayed varying degrees of sex reversal Testicular lobules of sex-reversed males contained oocytes The Results Continued 29% of the 0.1 ppb-treated animals and 8% that were treated with 25 ppb displayed varying degrees of sex reversal Testicular lobules of sex-reversed males contained oocytes Males that metamorphosed later contained large number of oocytes The Results Continued 29% of the 0.1 ppb-treated animals and 8% that were treated with 25 ppb displayed varying degrees of sex reversal Testicular lobules of sex-reversed males contained oocytes Males that metamorphosed later contained large number of oocytes Males that underwent complete sex reversal had gonads almost completely filled with oocytes and only a limited number of lobules remained. The Results Continued 29% of the 0.1 ppb-treated animals and 8% that were treated with 25 ppb displayed varying degrees of sex reversal Testicular lobules of sex-reversed males contained oocytes Males that metamorphosed later contained large number of oocytes Males that underwent complete sex reversal had gonads almost completely filled with oocytes and only a limited number of lobules remained. No observable effects in atrazine-treated females Observations in the Wild Observations in the Wild Chemical analysis of water revealed none of the sites were atrazine free Observations in the Wild Chemical analysis of water revealed none of the sites were atrazine free Only one site (Juab County, Utah) contained <0.2 ppb atrazine levels Observations in the Wild Chemical analysis of water revealed none of the sites were atrazine free Only one site (Juab County, Utah) contained <0.2 ppb atrazine levels Sites in Utah and Wyoming did not have detectable levels of atrazine metabolites Observations in the Wild Chemical analysis of water revealed none of the sites were atrazine free Only one site (Juab County, Utah) contained <0.2 ppb atrazine levels Sites in Utah and Wyoming did not have detectable levels of atrazine metabolites All sites with atrazine sales exceeding 0.4 kg/km² and contaminant levels that exceeded 0.2 ppb had males that displayed sex reversal similar to those that resulted from laboratory Observations in the Wild Continued Observations in the Wild Continued Site 3, North Platte River in Wyoming had most advanced cases of hermaphroditism Observations in the Wild Continued Site 3, North Platte River in Wyoming had most advanced cases of hermaphroditism 92% testicular oocytes Observations in the Wild Continued Site 3, North Platte River in Wyoming had most advanced cases of hermaphroditism 92% testicular oocytes Advanced stages of complete sex reversal Observations in the Wild Continued Site 3, North Platte River in Wyoming had most advanced cases of hermaphroditism 92% testicular oocytes Advanced stages of complete sex reversal All other sites varied in frequency and severity of gonadal abnormalities Observations in the Wild Continued Site 3, North Platte River in Wyoming had most advanced cases of hermaphroditism 92% testicular oocytes Advanced stages of complete sex reversal All other sites varied in frequency and severity of gonadal abnormalities Contaminant levels Contaminant levels The Collection Sites The Collection Sites Contaminant levels continued Contaminant levels continued What does all this mean? What does all this mean? Atrazine exposure disrupts gonadal development in exposed larvae What does all this mean? Atrazine exposure disrupts gonadal development in exposed larvae Widespread atrazine contamination was accompanied by observation of hermaphroditic animals in the field What does all this mean? Atrazine exposure disrupts gonadal development in exposed larvae Widespread atrazine contamination was accompanied by observation of hermaphroditic animals in the field Studies suggest that atrazine impacts amphibians in the wild What does all this mean? Atrazine exposure disrupts gonadal development in exposed larvae Widespread atrazine contamination was accompanied by observation of hermaphroditic animals in the field Studies suggest that atrazine impacts amphibians in the wild Atrazine contamination of water coincides with amphibian breeding activity What does this mean to us? What does this mean to us? Not so much that amphibian population declines (decline is minimal) What does this mean to us? Not so much that amphibian population declines (decline is minimal) We drink the same water What does this mean to us? Not so much that amphibian population declines (decline is minimal) We drink the same water Atrazine effects on amphibians vs. atrazine effects on humans What does this mean to us? Not so much that amphibian population declines (decline is minimal) We drink the same water Atrazine effects on amphibians vs. atrazine effects on humans May cause reproduction problems if long term exposure to atrazine What does this mean to us? Not so much that amphibian population declines (decline is minimal) We drink the same water Atrazine effects on amphibians vs. atrazine effects on humans May cause reproduction problems if long term exposure to atrazine “Adverse effects on hypothalamic-pituitary function in humans”--Scientific Advisory Panel convened in June 2000 Risk and Exposure Risk and Exposure The Bigger Picture The Bigger Picture Why should we care? The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also May not be same effects exhibited in amphibians The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also May not be same effects exhibited in amphibians More aware of other pesticides The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also May not be same effects exhibited in amphibians More aware of other pesticides How do we solve Atrazine Contamination? The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also May not be same effects exhibited in amphibians More aware of other pesticides How do we solve Atrazine Contamination? Prohibit atrazine distribution The Bigger Picture Why should we care? Atrazine contamination may affect us also May not be same effects exhibited in amphibians More aware of other pesticides How do we solve Atrazine Contamination? Prohibit atrazine distribution Come up with new pesticide Sources UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20460 http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/reregistration/atrazine/ hed_redchap_16apr02.PDF Atrazine-Induced Hermaphroditism at 0.1 ppb in American Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens): Laboratory and Field Evidence http://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/members/2003/5932/5932.p df Feminized Frogs: Herbicide disrupts sexual growth http://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20020420/fob1.a sp