Quiz #2- Topics Covered

Review for Comic Book Art Quiz #2- Units 5-7
Quiz Value: 25 pts.
Date of Quiz: _______________
Review the items on this list to study and prepare. You’ll find all of the information in the
Power Point slide-printouts and various other handouts. You can access the original
Power Points and handouts in my Outbox under the Quiz Review Folder or on my teacher webpage: http://www.hatboro-horsham.org/Page/6566
TOPIC SPECIFICS
Developing a Story
Types of Characters:
Protagonist- the most important character (hero
OR antihero)
Antagonist- character in conflict with protagonist
(often the villain)
Confidante- sidekick to the protagonist
Foil- sidekick to the antagonist
Dynamic Characters- well developed
Static Characters- underdeveloped (they don’t change throughout the story)
Narrative Arc:
The chronological construction of a story’s plot, consisting of 5 points:
1. Introduction of Protagonist
-The beginning of the story where the main character is introduced
2. Spark
-The event that propels the protagonist into action
3. Escalation
-Protagonist tries a series of approaches to put his or her life back into balance (the story builds)
4. Climax
-The ultimate event in the cycle of escalations
5. Denouement
-The loose ends of the story are quickly tied up;
French for “Resolution”
Storyboards:
Graphic organizers in the form of illustrations or images displayed in sequence for the purpose of pre-visualizing a story
Usually in the form of “thumbnail sketches”
(quick, small line drawings)
Elements of a Comic
Panels:
Definition- Still images in a sequence of juxtaposed images
Gutters- The spaces between and around the panels
Splash Panel- Takes up most of a page
Double-page Spread- One scene that covers two pages
Inset Panel- A panel contained within a larger panel
Bleed Panel- The imagery extends or “bleeds” out of the page
T-Square- Drafting tool that draws parallel and perpendicular lines (used to create panels)
Lettering:
Definition- Any text on a comic’s page
Bold Font- Used to emphasize words
Large Font- Indicates shouting
Small Font- Indicates whispering
Dialogue- Spoken (or thought) by a character
Captions- Used for narration
Display Lettering-
Text that isn’t dialogue or caption (ex. Street sign)
Sound Effects (SFX)- Stylized lettering that represents noises within a scene. o Onomatopoeia- A word that sounds like it is spelled (ex. Boom, Meow, Brrrring)
AMES Letting Guide- Creates evenly-spaced lines of different heights for text in a comic. Use a T-square with it!
Word Bubbles:
A bordered shape containing text
Comes in different shapes and sizes
Word Balloon- Contains dialogue with a tail pointed toward the speaker
Thought Balloon- Contains unspoken thought
Emanata:
Symbols or icons defining what is happening in a character’s head, or defining an action
Action Lines- Appear behind a moving object to show motion
Background in Perspective
Definition of “Perspective”:
Your point of view when you look at something
Creates the illusion of depth in an illustration
Was discovered during the Renaissance by architect Brunelleschi
Atmospheric Perspective:
Refers to the effect the atmosphere has on the appearance of an object as it is viewed from a distance.
Oftentimes- Landscape backgrounds
An illustrator creates depth by:
-Drawing objects in the distance smaller
-Increasing contrast in the foreground, and reducing it in the background
-Increasing the brightness and intensity of colors in the foreground
Linear Perspective:
A mathematical system for creating the illusion of space and distance on a flat surface
Terminology-
-Converging Lines- Parallel in reality, but appear to recede at an angle towards a common point
-Vanishing Point(s)- The intersection point of all converging lines
-Horizon Line- Passes through the vanishing point(s) at eye level
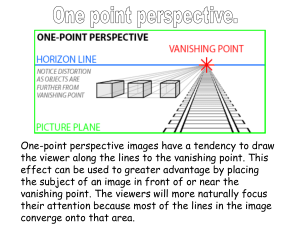
One-Point Perspective:
When a drawing has only one vanishing point
Example- A city street with buildings on either side
Two-Point Perspective:
When a drawing has two vanishing points
Example- The corner of a structure with both sides angled away from the viewer
Three-Point Perspective:
When a drawing has three vanishing points (the third is above or below the horizon line)
Used to show exaggeration
Example-
Bird’s-eye or Worm’s-eye views
Grayscale Prismacolor
Markers
Part of “Backgrounds in
Perspective” Unit
Cool vs. Warm Grays:
The difference between them is in the overall tone: o Cool Grays- Have a blue tone o Warm Grays- have a yellow tone
Different values- o Tints (lightest)= 10% - 30% o Midtones= 40% - 60% o Shades (darkest)= 70% - 90%
Use the range of options to create highlights and shadows, depending on your light source

![Questions for Analyzing Images [and other materials]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009709051_1-4c9a6501cb991fe1a0d2c31541094783-300x300.png)