Presentation
advertisement

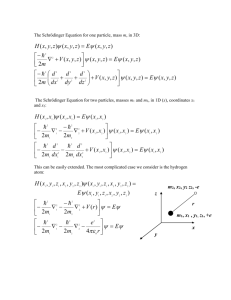
Solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the ground helium by finite element method Jiahua Guo Introduction • • • • Schrödinger equation Problems with traditional methods Helium atom system Challenge of solving He with FEM Governing equations In Cartesian coordinates, the spin-independent, nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation for the two electrons in the helium atom is: 1 1 2 2 1 H 12 22 2 r1 r2 r12 2 In spherical coordinates: H E 1 1 2 1 2 L12 L22 2 2 1 r1 2 r2 2 2 H 2 2 r1 r1 r1 r2 r2 r2 r1 r2 r1 r2 r12 L is the angular momentum operator and can be written as: L12 ( L2ix L2iy L2iz ) 1 sin 12 sin 12 12 12 Thus the Hamiltonian operator can be finally written as: 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 1 r1 2 r2 2 2 sin 12 H 2 2 r1 r1 r1 r2 r2 r2 r1 12 r1 r2 r12 r2 sin 12 12 Boundary conditions & Formulation • Boundary conditions r1 , r2 (0, rc ] 0 12 [0, ] When out of the boundary • Formulation Coefficient form of eigenvalue PDE in FEMlab: (cu u) u au d u 0.5 c 0.5 1 1 1 2 2 2 r1 r2 1 r1 a 1 r2 ctg 12 2 1 1 2 2 r2 r1 2 2 1 r1 r2 r12 r22 2r1r2 cos12 Solution E = -2.7285 hartree = -74.22eV (Experimental result: Eexp = -78.98eV The slice scheme of the helium wave function with the lowest eigenvalue Validation • Energy levels for hydrogen atom Energy level Energy value based on Bohr model (hartree) Energy value calculated by FemLab (hartree) Error n=1 -0.5000 -0.5014 0.28% n=2 -0.1250 -0.1247 0.24% • Atomic orbits 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz Conclusion • Schrödinger equation can be simplified by decreasing some variables, making it an equation with fewer dimensions. • FEMlab is a good tool when trying to find out the eigenvalues of energy of some threedimensional systems (e.g. hydrogen and helium atoms). However, it can’t deal with a complicated many-body Schrödinger equation. Thank you!