Internet Searches and Boolean Connectors - Grade 6 Design
advertisement

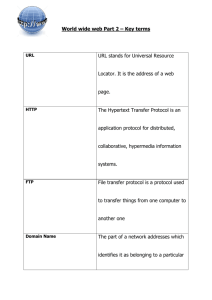
Searching the Internet Search Engines & Boolean Connectors What helps you find information in a book? An Index A Contents page Chapters, Sections, Categories etc. What can help you find information on the INTERNET?? A search engine Some examples of SEARCH ENGINES www.google.com www.yahooligans.com www.excite.com www.dogpile.com Using Search Engines What does WWW stand for? World Wide Web What does URL stand for? Uniform Resource Locator What is a URL? It is the address of a specific Website or file on the Internet What does HTTP stand for? Hyper Text Transfer Protocol HTTP defines how messages are formatted and transmitted What are URLs? URL stands for…. Uniform resource locator For example, www.bbc.co.uk is a URL Can you think of your favourite URL? Internet Information URL Stands for Uniform or Universal Resource Locator. The URL can tell you if the site is secure, the country it comes from and what type of site it is. .gov .edu .com .org .net Where was the site created? Government Website Educational Website Commercial business Organisation, such as a charity Network .sg – Singapore .uk – United Kingdom .au – Australia Searching for Information on the Internet Be specific and use as many KEYWORDS as possible: WHY?? there will be fewer results to look through the results will be more accurate This is how a search engine interprets your keywords: Search Engine Interpretation Results The Lion King The AND Lion AND King 1,090,000 “The Lion King” “As a whole phrase” 238,000 “The Lion King” London “As a whole phrase” AND London 12,100 Keywords “The Lion King” “As a whole phrase” “musical London” AND “As a whole phrase” 210 BOOLEAN CONNECTORS Most search engines automatically insert AND between each word There are other operators you can add yourself between words called Boolean connectors (or Boolean operators). These include: OR, NOT By using AND, OR, NOT you can narrow the search and focus on the exact information you need. HOW TO REFERENCE A WEBSITE -Reference List1. AUTHOR 2. YEAR 3. TITLE Last Name, First Name in ( ) underlined 5. Publisher & 6. Place Holland, M. (1996). Havard System. [Internet] Bournemouth University, Poole. <www.bournemouth.ac.uk> [Accessed 6 May 2006] 7. URL (website’s address) In < > 4. Internet in [ ] 8. Date you accessed the website in [ ] TIPS If there is NO AUTHOR, start with the TITLE (step 3) If there is NO DATE, write n.d. after the Author’s Name eg Hanson, B. n.d. If there is NO PUBLISHER or PLACE, go straight to the <URL> and [date accessed] (step 7 and step 8) HOW TO REFERENCE A WEBSITE - In text referencing Include the AUTHOR and COPYRIGHT YEAR if you can If you don’t have the Author, include the COPYRIGHT YEAR AND URL OF WEBSITE Remember to also reference IMAGES