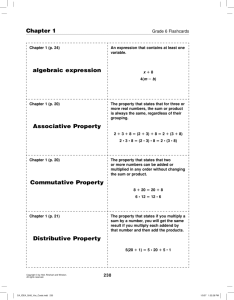
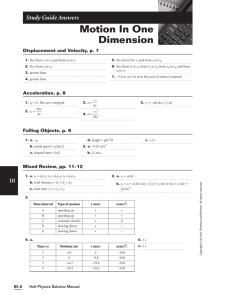
psychology principles in practice
advertisement

PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Phi Phenomenon The perception of movement as a result of sequential presentation of visual stimuli HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE 2 HOLT, RINEHART AND 3/19/2016 WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE 3 HOLT, RINEHART AND 3/19/2016 WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE 4 HOLT, RINEHART AND 3/19/2016 WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Depth Perception ability to see objects in three dimensions allows us to judge distance HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Monocular Cues – depth cues available to either eye alone HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Linear Perspective PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Perceiving parallel lines as coming closer together, or converging, as they recede from us. The more the lines converge, the greater their perceived distance. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Relative Size PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Perceiving larger objects as being closer to us. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Texture Gradient PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Perceiving objects with rougher textures as being closer HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Interposition PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Objects that block other objects tend to be perceived as closer. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Light and Shadowing PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Perceiving shadows and highlights as giving depth to two-dimensional objects. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Chapter 4 PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Monocular Cues The most complex of monocular cues of depth is called motion parallax. Motion parallax is the tendency of objects to seem to more forward or backward depending on how far away they are from the viewer. 12 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY Perceptual Constancies PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Refers to the tendency to perceive an object as remaining stable and unchanging despite any changes that may occur to the image cast on the retina. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Size Constancies Size constancy involves recognizing that an objects actual size remains the same, even though the image it casts on each retina changes. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Size Constancy Cylinders at positions A and B are the same size even though their image sizes differ Point B The depth cues such as linear perspective and texture help the visual system judge the size accurately Point A HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Shape Constancies It is the tendency to perceive an object as maintaining its shape despite any change in shape of the image of the object on the retina. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE 3D Side View Flat Front View HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Shape Constancy PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE It is hard to tell if the figure on the upper right is a trapezoid or a square slanted backward If we add texture, the texture gradient helps us see that it is actually a square HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Brightness Constancy Is the tendency to perceive an object as maintaining its level of brightness in relation to its surroundings. HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Color/Brightness Constancy HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON Perception PSYCHOLOGY PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE Müller-Lyer Illusion – The two lines above are the same length, but the diagonals extending outward from both ends of the lower line makes it look longer than HOLT, RINEHART WINSTON the upper line AND