What is the cost of Quality? - wos-sqa
advertisement

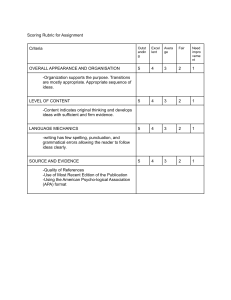
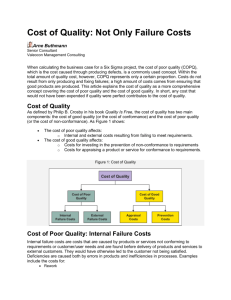
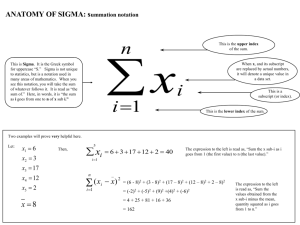
By: Sarah Abdallah The Definition Wikipedia says: “The concept of quality costs is a means to quantify the total cost of quality-related efforts and deficiencies.” “The cost of quality planning, control, assurance and rework.” cio.osu.edu/projects/framework/glossary.html “The cost of quality is the expense of all the activities within a project to meet quality objectives.” pmpbank.googlepages.com/glossary The Father of Quality Revolution Philip B. Crosby (known as the Father of Quality Revolution) has written various essays and books on the topic of Quality. He was a local businessman, author, and teacher. His philosophies and concepts helped change the ways business is conducted worldwide. Examples of his books Quality is Free… As told by Philip. B Crosby, the cost of quality has two main components: The cost of good quality (or the cost of conformance) and The cost of poor quality (or the cost of non-conformance) The Quality Triangle Quality Triangle Rules If you want something fast and cheap, it won’t be of good quality. If you want something of good quality and in good timing, it won’t be cheap. If you want something with good quality and cheap it won’t be fast. The cost of Poor Quality affects The cost of poor quality affects Internal and External costs resulting from failing to meet requirements. Cost of Good Quality affects Costs for investing in the prevention of nonconformance to requirements. Costs for appraising a product or service for conformance to requirements. Cost of Poor Quality: Internal Failure Costs “Internal failure costs are costs that are caused by products or services not conforming to requirements or customer/user needs and are found before delivery of products and services to external customers.” Examples would be: -Rework -Delays -Re-designing -Shortages -Failure analysis -Re-testing -Downgrading -Downtime -Lack of flexibility and adaptability Cost of Good Quality: Prevention Costs Prevention costs are costs of all activities that are designed to prevent poor quality from arising in products or services. -Quality planning -Supplier evaluation -New product review -Error proofing -Capability evaluations -Quality improvement team meetings -Quality improvement projects -Quality education and training Measurement of quality Reliability Validity Measurement errors Correlation Causality SIGMA What is Six Sigma? A statistics-driven approach to quality control. Six steps to Six Sigma Identify the product you create or the service you provide in other words Identify the customer(s) for your product or service, and determine what they consider important Identify your needs Define the process for doing your work Mistake-proof the process and eliminate wasted efforts Ensure continuous improvement by measuring, analyzing and controlling the process using “DMAIC” (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)