Chapter 3 Study Guide Directions: This study guide is part of your
advertisement

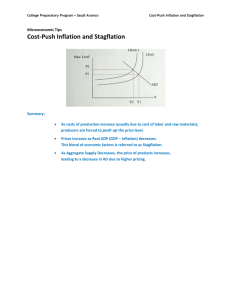
Chapter 3 Study Guide Directions: This study guide is part of your grade and is due on the day of the quiz. You may use the textbook, PowerPoint notes, and class notes to complete this guide. 1. What happens to your purchasing power when prices rise faster than your level of income? It decreases or goes down. You lose purchasing power. 2. Explain the difference between demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and real-cost inflation. Demand-Pull Inflation: Prices increase based on consumer demand of a product Cost-Push Inflation: Prices increase because the cost to create the product is increasing. Businesses push this additional cost onto you as the consumer Real-Cost Inflation: Prices increase because of scarcity. The resources needed to create the product are difficult to find 3. What percent of inflation is said to be good for the economy? 2-3 % 4. Explain the difference between disinflation, reflation, hyperinflation, and deflation. Disinflation: When prices start to slow down Reflation: When prices are high, then drop, then go back up again Hyperinflation: Rapidly rising prices that are out of control Deflation: A decrease in price 5. What does COLA stand for? What does it do? Cost of Living Adjustment When you employer gives you a raise in an effort to keep up with the cost of inflation to keep your purchasing power equal 6. What does CPI stand for? What does it do? Consumer Price Index Measures inflation (the increase in price for products and services) 7. Explain the difference between cost-recovery, cost-plus, value-based, and market-based. Cost-Recovery: R&D: Because of the high costs of research and development of certain products, businesses will initially charge a high price when the product first comes to market in an effort to make up for these costs After a while, these prices will drop. Cost-Plus: Businesses charge the cost it took to make the product, plus a markup cost. The markup cost is based on how much profit the business wants to make on each product Value-Based: What value do you, as the consumer, put on a product? How much are you willing to spend? Market-Based: The value of products is based on competition. What are your competitors charging? 8. What type of buying strategy results in acting in your own best self-interests? Rational Buying 9. What does the Consumer Technology Bill of Rights give consumers? The right to …. Time-Shift Space-Shift Translate content to other formats 10. What does the FTC stand for? What does it do? Federal Trade Commission – federal clearinghouse for complaints of identity theft 11. Define “The Time Value of Money” A dollar you receive in the future will be worth less than a dollar you receive today 12. What does it mean to time-shift? (Consumer Technology Bill of Rights) Record video or audio so that you may listen to it or see it later 13. This federal agency enforces laws and prevents or stops the selling of mislabeled foods, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices. FDA – Food and Drug Administration 14. What do businesses use to stimulate demand for a product? Advertising 15. Compute the unit prices for the following products: a. Case (24) bottles of water for $4.99 4.99/24 = $0.21 per bottle b. 15 cookies for $6.99 6.99/15= $0.47 per cookie c. Carton of 12 eggs for $2.69 2.69/12 = $0.22 per egg