Hemostasis: Hemo/Stasis
advertisement

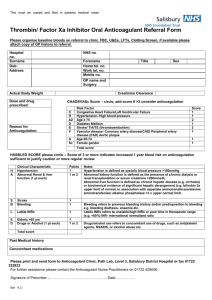
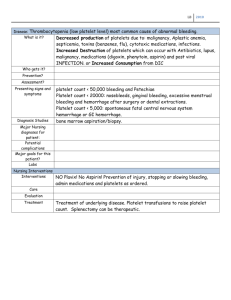
Hemostasis: Hemostasis: Hemo/Stasis Hemo=خون Stasis=سکون :مثلث هموستاز Platelets Blood Vessels Hemostatic Factors Causes of Bleeding(1) Thrombocytopenia: Primary: • ITP • Neonatal Isoimmune • TAR Syndrome • Wiskott-Aldrich Syn. Secondary: *Malignancy *Aplastic Anemia *DIC *Sepsis *HUS *Hypersplenism *Autoimmune(SLE) Causes of Bleeding(2) Coagulopathy: Primary: • vWF Deficiency • Hemophilia • Platelet dysfunction Secondary: • DIC • Anticoagulants • Vit K deficiency • Hepatic Failure • Renal Failure • Maternal Anticonvulsant Causes of Bleeding(3) Vascular(Non-Hematologic) • • • • • • • Child Abuse Vasculitis Ulcer Varices Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Telangiectasia Angiodysplasia تقسیم بندی هموستاز: )1هموستاز اولیه:چند ثانیه بعد از آسیب عروقی ایجاد میشود و از خونریزی از عروق کوچک و ونولها جلوگیری میکند. )2هموستاز ثانویه:چند دقیقه بعد از آسیب عروقی ایجاد میشود و از خونریزی از عروق بزرگ جلوگیری میکند. Differences of Primary and Secondary Hemostasis: Manifestations Onset of Bleeding Site of Bleeding Superficial Secondary Hemostasis: Delayed-hours or days Deep)joints,…) Physical Exams Petechia,Echymosis Hematoma,Hemarthrosis Family History AR or X-link R Response to Therapy Primary Hemostasis: Immediate AD Immediate; Local pressure Systemic Therapy Estimation of BT with desired Platelet count BT= 30.5- Platelet count (minute) 3,850 Vitamin K Related Factors: • • • • Factor II Factor VII Factor IX Factor X Prolonged PTT • No clinical bleeding ??? • Mild or rare bleeding ??? • Frequent,Severe Bleeding ??? Prolonged PTT • No clinical bleeding Factor XII , HMWK , PK • Mild or rare bleeding Factor XI • Frequent,Severe Bleeding Factors VIII and IX Prolonged PT • ??? • ??? • ??? Prolonged PT • Factor VII Deficiency • Vitamin K Deficiency(Early) • Warfarin anticoagulant ingestion Prolonged PT and PTT • ??? • ??? • ??? Prolonged PT and PTT • Factor II,V,X Deficiency • Vitamin K Deficiency(Late) • Warfarin anticoagulant ingestion Prolonged TT • ??? • ??? • ??? Prolonged TT • Mild or rare bleeding: Afibrinogenemia • Frequent,Severe Bleeding:Dysfibrinogenemia • Heparin like inhibitors or heparin administration Prolonged PT and/or PTT not corrected with normal plasma • Specific or nonspecific inhibitor Syndromes Clot Solubility in 5 M urea • Factor XIII deficiency • Inhibitor Secondary Hemostasis Approach: 1)What is diagnosis? 2)What is hemostatic level of Factor? 3)What is blood distribution of factor? 4)Which products contain desired factor? 5)What is half life of coagulation factor? APPROACH TO COAGULATION DISORDERS Clinical approach 1. 2. 3. 4. Is the bleeding significant ? Local Vs Systemic ? Platelet Vs Coagulation disorder ? Inherited Vs Acquired ? Laboratory Approach 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Demonstration of the defect Identification of the defect(s) Assessment of severity Consequential studies eg. carrier detection Monitoring of treatment Screening Tests 1. Platelet count & morphology 2. Bleeding Time(BT) 3. Prothrombin Time(PT) 4. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time(PTT) 5. Thrombin Time (TT) Collection of blood sample 1. Minimum circulatory stasis 2. Clean venous puncture 3. Proper anticoagulant 4. Proportion of blood to anticoagulant 5. Separation of plasma and storage 6. Effect of stress, pregnancy, drugs 7. Effect of PCV on the proportion of plasma to anticoagulant Prolonged PT/APTT • • • • Coagulation factor deficiency/inhibitor Test plus control plasma - 1:1 Repeat PT/APTT > 50% correction – Yes - Factor deficiency – No - inhibitor timed incubation abnormally increasing specific inhibitor no change Lupus Anticoagulant HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII X PT - APTT, TT, PLC - N * Factor VII deficiency * Anticoagulant therapy V II I TT HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII X APTT - PT, TT, PLC - N * Factor deficiency * vWD * Inhibitors * Heparin therapy V II I TT Mixing tests with APTT APTT of test plasma + Aged plasma Adsorbed plasma Diagnosis No correction Corrected VIII Corrected No correction IX Corrected Corrected XI,XII Prolonged APTT, BT von Willebrand’s disease Ristocetin Induced Platelet Agglutination VIII:C vWF:Ag vWF multimeric analysis Type 1 - Partial deficiency of vWF 2A - Absence of large and interm. multimers 2B - Absence of large multimers 2M- multimers normal, pl. function 2N - affinity for FVIII 3 - severe deficiency of vWF HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII X PT, APTT - TT, PLC - N * * * * V II I TT Common Pathway Factor deficiency Vitamin K deficiency Oral anticoagulant therapy Liver disease Mixing tests with PT PT of test plasma + Aged plasma adsorbed plasma Diagnosis Corrected Not corrected X Not corrected Corrected V Not corrected Partial II HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII X PT, APTT, TT - PLC - N * Hypo / dysfibrinogenemia * Heparin * Liver disease * Systemic hyperfibrinolysis V II I TT HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII APTT, PT,TT all PLC - low * DIC - FDP - D-dimer - Fibrin monomer X V II I TT HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII PT, APTT- TT - N PLC - Massive transfusion with stored blood X V II I TT HMWK VII XII PK XI APTT IX PT VIII X PT, APTT,TT-N PLC - V II I Thrombocytopenia Pseudo vs True Bone marrow biopsy to differentiate production destruction TT PT, APTT, TT, PLC - Normal • Factor XIII deficiency • Thrombasthenia – congenital – drug induced • Disorders of vascular hemostasis • Factor XIII - clot solubility • Platelet function – – – – BT clot retraction 1 minute platelet count aggregation • Tourniquet test Asymptomatic Patient Routine screening tests shows prolonged APTT – Inhibitor - lupus anticoagulant – Factor XII deficiency – Mild congenital factor deficiency Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Criteria by Branch and Silver 1996 • Clinical – Recurrent abortion – Recurrent venous thrombosis – Recurrent arterial thrombosis – Persistent thrombocytopenia – Livedo reticularis • Laboratory – IgG/IgM anticardiolipin Ab – Lupus anticoagulant • Diagnosis – 1 clinical + 1 lab criteria – Lab result must be positive on at least 2 occasions more than 3 months apart Lupus Anticoagulant • Kaolin clotting time • Dilute Russel’s viper venom time • Platelet neutralization test • Tissue thromboplastin inhibition test