Unit 1 - SchoolRack
advertisement

Lesson 1
Rational and Irrational Numbers
2
Vocabulary (Logs)
0 Real Numbers
0 Any number (point) on the number line
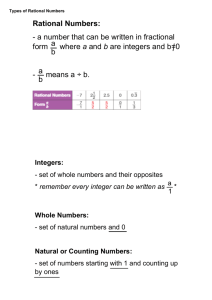
0 Rational Numbers
0 a number that can be written as a simple fraction
0 a/b where b ≠ 0
0 Terminating or repeating decimals
0 Irrational Numbers
0 A number that cannot be written as a simple fraction
0 √2 or π
3
Vocabulary (Logs)
0 Integers
0 zero, counting numbers, & negative of counting
numbers {…, -1, 0, 1, …}
0 Whole Numbers
0 Starts at 0 {0, 1, 2, 3, …}
0 Natural Numbers
0 Also counting numbers {1, 2, 3, …}
4
Real Numbers Venn Diagram
Draw in learning logs.
5
0 Flow charts are graphical representations of a process
0 Steps are shown in individual shapes and flow is indicated
with arrows connecting the symbols
YES
Can the
number
written as
a fraction?
NO
Can the
fraction
be
divided
evenly?
Rational
NO
Irrational
Integer
NO
Natural
YES
Is the
number
zero?
Is the
number
negative?
YES
Whole
YES
NO
6
Examples
0 Identify the following numbers as Irrational, Rational,
Whole Natural, and/or Integers:
0 9
0 Rational, integer, whole, natural
0 3.666666666
0 rational
0 -5
0 Rational, Integer
0 4.75
0 rational
0 7.154976352118568763215489736
0 irrational
7
Worksheet
0 Complete Worksheet in Groups
0 Complete Part I then stop
0 Complete Part II then stop
0 Complete Part III then stop
0 Review Time!!
0 Complete Page 1-12 for Homework
8
Lesson 2
Numeracy Review
9
Order of Operations
• When evaluating arithmetic expressions, the order
of operations is:
• Simplify all operations inside parentheses.
• Perform all multiplications and divisions, working from
left to right.
• Perform all additions and subtractions, working from
left to right.
• If a problem includes a fraction bar, perform all
calculations above and below the fraction bar before
dividing the numerator by the denominator
10
Vocabulary (Logs)
0 Whole Positive Exponents
0 Negative Exponents
0 Negative is the opposite of positive
0 Divide is the inverse
(opposite) of multiply
0 Negative exponents means
how many times to we
divide by that number
11
Exact vs. Approximate
0 Exact number
0 1. Any number obtained by a counting process. Example: 60
students in a class — 60 is an exact number
0 2. Any number given by definition. Example: One hour
equals 60 minutes — 60 is an exact number
0 Approximate Number
0 1. Any number obtained by a process of measurement
0 Example: The distance between two cities is 60 miles — 60 is
an approximate number.
0 The distance may be a little more or a little less than 60 miles
12
Significant Digits
0 digits that have meaning relative to the measuring process
1. Nonzero digits are always significant
2. Zeros that are preceded and followed by significant
digits are always significant.
3. Final Zeros to the right of a decimal point are significant
4. Final zeros on a whole number are not significant (unless
further information indicates otherwise).
5. If no digits left of the decimal point, zeros between the
decimal point and the first digit are not significant
13
Examples
0 14.24 has four significant digits (Rule 1)
0 .0036 has two significant digits (Rule 1 & 5)
0 14.0024 has six significant digits (Rule 3)
0 7001 has four significant digits (Rule 2)
0 8.9000 has five significant digits (Rule 3)
0 0.03600 has four significant digits (Rule 1 & 5)
14
Accurate to …
0 If you need to express your answer as being "accurate
to" a certain place, here's how the language works
with the above examples:
0 0.00035 is accurate to the hundred-thousandths place
0 0.000350 is accurate to the millionths place (note the
0
0
0
0
extra zero)
1006 is accurate to the units place
560 is accurate to the tens place
560. is accurate to the units place (note the decimal
point)
560.0 is accurate to the tenths place
15
Worksheets
0 Complete Review Worksheets
0 Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, & Dividing Integers
0 Order of Operations
0 Adding, Subtracting, &Multiplying Decimals
0 Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, & Dividing Fractions
16
Lesson 3
Scatter Plots
17
Vocabulary (Logs)
0 Cartesian Coordinate
System
0 formed by a horizontal axis
and a vertical axis
0 Domain
0 set of values of the independent
variable for which a function or
relation is defined; x-values
0 Range
0 set of values assumed by a
function or relation over all
permitted values of the
independent variables; y-values
18
Vocabulary (Logs)
0 Independent Variable
0 value freely chosen without considering values of any
other variable
0 Dependent Variable
0 depends on one or more other variables
0 Ordered Pairs
0 pair of numbers giving the location of a point (x, y)
19
Scatter Plots
0 Scatter plots are similar to line graphs
0 horizontal and vertical axes to plot data points
0 show how much one variable is affected by another.
0 The relationship between two variables is called their
correlation .
0 Scatter plots usually consist of a large body of data.
0 The closer the points come to making a straight line, the
higher/stronger the correlation between the two variables
0 If the line going from the origin out to high x- and y-values,
then positive correlation
0 If the line goes from a high-value on the y-axis down to a highvalue on the x-axis, then a negative correlation .
0 Remember when making a scatter plot, DO NOT connect
the dots
20
Scatter Plots
0 Positive
0 y increases as x
increases
0 Negative
0 Y decreases as x
increases
0 No Correlation
0 No relationship
between x and y
21
Line of Best Fit
0 A straight line that best represents the data on a
scatter plot.
0 May pass through some of the points, none of the
points, or all of the points.
0 Also called
linear regression
equation
22
Slope
0 Rate of Change-for each change in the independent
variable, the dependent variable will change by m
0 Negative slope defines negative correlation. Positive
slope defines positive correlation.
23
Activity
0 At your tables:
0 Use ruler to measure the length of each student’s foot
0 Inches
0 Centimeters
0 Use measuring tape to measure each student’s height
0 Inches
0 Centimeters
0 Record data on chart at front of room and graph on
scatter plot
0 Answer questions on worksheet
24
Lesson 4
Exponential Growth & Decay
25
Exponential Functions
The variable is the exponent, not the base. y = 3x
Decay
Growth
26
Activities
0 Complete the
Exponential Growth &
Decay Activity
27
Lesson 5
Putting it all Together
28
0 Complete the Linear or
Non-Linear Activity and
turn in your posters
when you are finished
OR
0 Create scatter plots
based on the free throw
and field goal
percentages and answer
questions that follow.
29
Review
30
Vocabulary
0 Real Numbers
0 Cartesian Coordinate
0 Rational Numbers
0 Domain
0 Irrational Numbers
0 Range
0 Integers
0 Independent Variable
0 Whole Numbers
0 Dependent Variable
0 Natural Numbers
0 Ordered Pairs
0 Flow Charts
0 Line of Best Fit
0 Exponent
0 Slope
31
Learning Log Checklist
0 Vocabulary
0 Scatter Plots Rules
0 Real Numbers Venn
0 Order of Operations
Diagram
0 Real Numbers Flow
Chart
Rules
0 Exact vs. Approximate
0 Significant Figures Rules
32
Assessments & Review
2-3 days
33
Test Question 1
0 Cary’s Bakery sells cupcakes for $1.00 each. Cary is not
making any profit, so she needs to raise the price. She
wants to make the increase gradually to $1.80.
0 Plan A: Raise the price by $0.05 per week
0 Plan B: Raise the price by 5% per week
0 Plan C: Raise the amount by the same amount over 8 weeks
0 Make a table for each plan and determine how many weeks
each plan will take and the increase amount each week.
0 Create one graph displaying all three plans simultaneously.
0 Answer the following questions:
0 Are the graphs linear?
0 In your opinion, which plan should Cary implement? Give
reasons for your choice.
34
Test Question 2
0 Table listing rental prices for a car including mileage
charges
0
0
0
0
0
0
Explain what the data in the table means
Determine rental cost before any miles are driven
Graph
Create a regression equation
Calculate cost for 100 miles
How far can you go on $60
0 Extension: Compare cost for two different pricing
schemes
35
Test Questions
0 Classify Numbers
0 Graph a linear and non-linear set of data and analyze
0 Perform operations on integers, decimals, fractions,
exponents
0 Order of Operations
0 Significant Figures
0 Find Slope
36