Theories to Explain the past
advertisement

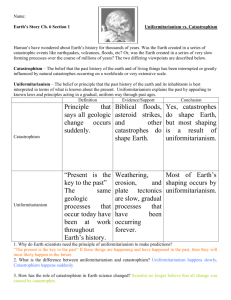
Theories to explain the past “I believe that the more you know about the past, the better you are prepared for the future.” -Theodore Roosevelt Theories to explain the past These theories will be used for the foundation of this Ancient Origins course. Catastrophism: Georges Cuvier The theory that the Earth has been affected in the past by sudden, short-lived, violent events, possibly worldwide in scope. Modern Interpretation (Modern catastrophism) The theory that evidence from catastrophic forces can have a major influence on shaping Earth. Example: Asteroid collision Uniformitarianism : James Hutton A contrast to catastrophism (sometimes described as gradualism), in which slow incremental changes, such as erosion, created all the Earth's geological features. Creationism: Bishop James Usher The belief that the Universe and Life originate "from specific acts of divine creation." For young Earth creationists, this includes a biblical literalist interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative and the rejection of the scientific theory of evolution. Superposition: Charles Lyell Older is lower! The lower strata contents will be older than those in strata near the surface. Three Age Theory: Christian Thomsen Every culture goes through three ages unless disturbed by a more advanced culture. Ages= Stone, Bronze & Iron 3:00 Catastrophism: Georges Cuvier anthro.palomar.edu www.ancient-wisdom.com http://bareket-astro.com/en/project/asteroid.files/image008.jpg Catastrophism -- Past Cataclysmic Activity Catastrophism is the idea that many of Earth’s crustal features (strata layers, erosion, polystrate fossils, etc.) formed as a result of past cataclysmic activity. In other words, the Earth’s surface has been scarred by catastrophic natural disasters. Cuvier stated that different groups of fossil organisms were created and then became extinct as the result of geologic catastrophes, the last of which was the Great Flood described in the Bible. Each catastrophe, according to Cuvier, killed the fossilized organisms and deposited the sediment that solidified into the rock surrounding the fossils. Modern Interpretation (Modern catastrophism) Armageddon (3:02) gencept.com www.dinosaurfact.net Twentieth century catastrophism, often called neocatastrophism, is founded entirely in science, relying solely on natural forces for its explanations. The argument states that these collisions have major effects on the geology and biology of Earth. www.britannica.com Uniformitarianism: The present is the key to the past Erosion (Example) 2:26 www.f21.org.au Theories of Geological Evolution Superposition Older is lower! The lower strata contents will be older than those in strata near the surface. Basically, rock layers can accumulate over time. Superposition (6:00) This particular theory is an amazing example of a good theory. It’s predictive, parsimonious (simple) and powerful! Creationism Creationism is the belief that the earth and universe and the various kinds of animals and plants were created by God or gods. Creationism is primarily based on: the Bible’s account which includes the idea that man is created in the image of God. This theory plays a major part in the belief system of Western Civilization. Three Age Theory: Christian Thomsen Every culture goes through three ages unless disturbed by a more advanced culture. Ages= Stone, Bronze & Iron BACKSTORY: During the 1800s many educated, wealthy young European men scattered around the globe, collecting artifacts from all corners. Some items were purchased, stolen, or dug up from archaeological sites. Many items ended up in museums. The curators of these museums were faced with displaying them in some manner. Thomsen sorted the museum's objects by the material culture, resulting in separate rooms for Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age. He suggested that the order was probably chronological; a fact established later by archaeologist J.A.A. Worsaae. For the first time, excavators began paying attention to layers or strata, in archaeological deposits. Applying the Principle of Uniformitarianism Processes that happen today happened in the past with the same results. In other words, the present is the key to the past. What does thisthis mean: "The present key to the What does mean: “ Theis the present ispast"? the key to the past”? How can this photo help you to figure out what happened in Earth's history? You see the molten lava. You see what the rock looks like when the lava cools. What if you see that type of rock in an outcrop? You can assume that it formed from molten lava. This is the best tool for understanding Earth history. Earth scientists use what they know about Earth in the present to figure out what happened in the past. HOW DID THIS ROCK FORM? This is at Checkerboard Mesa in Zion National Park, Utah. Notice the very interesting pattern on it. If you look carefully at the rock, you will see that it’s made of sand. This rock formation is called the Navajo sandstone. Does knowing that the rock is sandstone tell you how it formed? No, although it limits the possibilities. The next thing to do is to make observations now and apply them to this rock that formed long ago. Uniformitarianism James Hutton came up with this idea in the late 1700s. The present is the key to the past. He called this the principle of uniformitarianism. It works like this: we understand a geological process that happens now. We see the outcome of that process, say a rock. Then we find evidence that same process happened in the past, like a similar rock. We can assume that the process operated the same way in the past. Let’s think again about Checkboard Mesa... What would cause sandstone to have layers that cross each other, a feature called cross-bedding? Answer: EARTH HISTORY DINOSAUR RIDGE Use the media clip resource to answer the following questions in your history spiral notebook. 1. How does a geologist use observations about how and where ripple marks are found to understand ripple marks in a rock? 2. What do the colors of the rocks tell us? 3. Explain the principle of uniformitarianism. Dinosaur Ridge 3:40 LET’S WRAP IT UP!! You may need to apply what you know about the present to determine what happened in the past. If you see something forming by a process today and then find the end results of that process in the rock record, you can assume that the process operated the same way in the past.