eStudy.us
Interdependence and the
Gains from Trade
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
• Two goods: Corn and Wheat
• Two counties: U.S.A. and Canada
• If U.S.A produces only corn and Canada
produces only wheat
– both gain from trade
• If both U.S.A. and Canada produce both corn
and wheat
– they still gain from specialization and trade
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
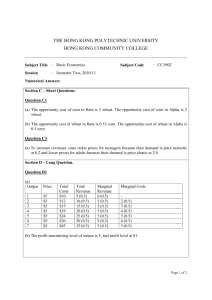
Production Possibilities Frontier
U.S.A. production
possibilities frontier
Wheat
50
Canada production
possibilities frontier
Wheat
If there is no trade, then
U.S.A. produces and
consumes.
If there is no trade, then
Canada produces and
consumes.
40
20
A
B
10
0
60
100 Corn
0
30
40
Corn
The left graph shows the combinations of corn and wheat that can be produced in
the U.S.A. The right graph shows the combinations of corn and wheat that the can
be produced in Canada. If there is no trade, each country’s production possibilities
frontier is also the consumption possibilities frontier.
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
Specialization and trade
– U.S.A specializes in growing corn
• more land growing corn
• less land raising wheat
– Canada specializes in growing wheat
• more land growing wheat
• less land growing corn
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
Comparative Advantage
• Absolute advantage producing a good using fewer inputs
than another producer
• Opportunity cost
– Whatever must be given up to obtain some item
– Measures the trade-off between the two goods that each
producer faces
The opportunity cost of corn and wheat
U.S.A.: 100 / 50 = 2 (opportunity cost of one bushel of wheat is
two bushels of corn in the U.S.A.)
Canada: 40 / 40 = 1 (opportunity cost of one bushel of wheat is
one bushel of corn in Canada)
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
Comparative Advantage
• A country has a comparative advantage if opportunity
cost is less than in other countries for a product
• A country
– can have absolute advantage in both goods
– can’t have comparative advantage in both goods
• Gains from specialization and trade
– Based on comparative advantage
– Total production in economy rises
• Increase in the size of the economic pie
• Everyone – better off
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
Gains from trade (expands consumption opportunities)
Would without Trade
Would with Trade
Corn
Wheat
U.S.A.
60
20
U.S.A.
Canada
30
10
Canada
World
90
30
World
Corn
Wheat
100
0
0
40
100
40
With specialization and trade the world adds 10 corn
and 10 wheat that can not be produced otherwise
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
• Trade can benefit everyone in society
– Allows people to specialize in activities
• The price of trade
– Must lie between the two opportunity costs
• Principle of comparative advantage explains:
– Interdependence
– Gains from trade
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
• Should Tiger Woods mow his own lawn?
Tiger Woods or Michael Roberson
– Tiger Woods can mow his lawn in 2 hours
– Michael Roberson can mow Woods’s lawn in 4 hours
– Film a TV commercial and earn $10,000 (2 hours)
– Work at McDonald’s and earn $36 (4 hours)
• Tiger Woods has the absolute advantage, but Michael
Roberson has the comparative advantage.
• Michael Robeson should mow Tiger’s yard
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved
eStudy.us
• Should the U.S. trade with other countries?
– Imports are goods produced abroad and sold domestically
– Exports are goods produced domestically and sold abroad
• Principle of comparative advantage
Good should be produced by the country with smaller
opportunity cost of producing that good (Comparative
advantage)
• Specialization and trade allow all countries
greater prosperity
copyright © michael .roberson@eStudy.us 2010, All rights reserved