Chapter 2 * Ratios, Rates, and Proportional Reasoning
advertisement

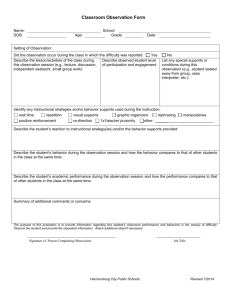
2.1 – Two – Term and Three – Term Ratios 2.2 – Rates 2.3 – Proportional Reasoning 2 to 3 2:3 2/3 2:3:4 Two Term Ratio: compares two quantities measured in the same units. Ex. 4 to 5 or 4:5 Three Term Ratio: same thing except compares three quantities measured in the same units. Ex. 2 to 4 to 6 or 2:4:6 Part-to-Part Ratio – compares different parts of a group to each other. (Ex. 3 girls to 1 boy) Part-to-Whole Ratio – compares one part of a group to the whole. (Ex. 1:4 - one girl to 4 students total) Two term or three term? 2 cars to 4 trucks 2 black cows to 4 brown cows to 5 white cows 2:6:9 2/56 3:54:109 Part to part or part to whole? 5 boys to 32 total students 3 spruce trees to 4 maple trees to 2 pine trees 3 soccer players to 5 volleyball players 3 hockey players to 20 total athletes 3/7 Example 1 – Counting Marbles Example 2 – Mixing Juice Practice Problems p. 51-54 #5 – 10, #14, #17, #19, #20, and #22 Rates – compares two quantities measured in different units List as many rates as you can think of: 72 beats per minute (72bpm) 100 kilometres per hour (100km/hr) $8.65/hr 30 gallons per mile Unit rate – a rate in which the second term is one. (Ex. 20km/hr or 20km/1 hour) Speed – a unit rate that compares distance to time, or distance over time. * You can figure out the unit rate of a rate by dividing the first number by the second. For example 200 km/2 hours = 100 km/hr (a big help for pricing – unit price) Example 1 – Unit rate of hummingbirds Example 2 – Pricing of Orange Juice Practice Problems p.60-62 # 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 14, and 17 Proportion – a relationship that says that two ratios or two rates are equal. 2/3 is proportional to 6/9 $10 per hour for a 7 hour shift is proportional to $70 for 7 hours of work Example 1 – Electricity rates Example 2 – Trout Practice Problems p. 67-69 #4, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 17, 19, 24, and 27