Central Nervous System
advertisement

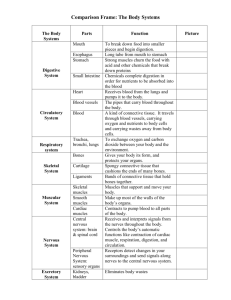
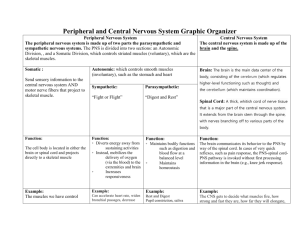
7th Grade Unit 5: The Structure and Function of Body Systems Lesson 2: Nervous, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Vocabulary of Instruction: Absorption • The uptake of water or dissolved chemicals by a cell or an organism (as tree roots absorb dissolved nutrients from the soil). Autonomic Nervous System • Part of the nervous system which controls involuntary bodily functions. Central Nervous System • Portion of the nervous system which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Chemical Digestion • Involves enzymes that break down starches, proteins, fats, etc. in the small intestine. • Each type of molecule is broken down into its simplest part through the use of enzymes. Excretion • Is the process of eliminating waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials. Involuntary Muscles • Muscles whose activity is not subject to conscious control. Kidney • Are two bean shaped organs that filters wastes (such as urea) from the blood and excrete them, along with water, as urine. Mechanical Digestion • Requires the use of energy and the mechanical breaking down of food via chewing. Motor Neurons • Applies to neurons located in the central nervous system (CNS) that project their axons outside the CNS and directly or indirectly control muscles. Neurons • Nerve cell, which is the basic functional unit of the nervous system. Peripheral Nervous System • Resides or extends outside the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) to serve the limbs and organs. Unlike the central nervous system, however, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), it is not protected by bone, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries. Peristalsis • Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep the food moving along in one direction through the digestive system. Sensory Neurons • Are nerve cells within the nervous system responsible for converting external stimuli from the organism's environment into internal electrical motor reflex loops and several forms of involuntary behavior, including pain avoidance. Somatic Nervous System • Is part of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements through the action of skeletal muscles, and with reception of external stimuli, which helps keep the body in touch with its surroundings. • Examples: – Touch – Hearing – Sight Toxins • Are poisonous substances produced by living cells of organisms. Voluntary Muscles • Drawn muscles; muscles whose activities can be controlled by the brain (e.g. skeletal muscles).