File
advertisement

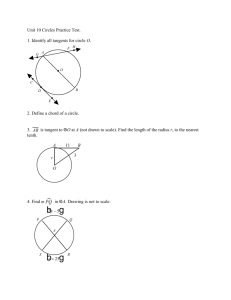
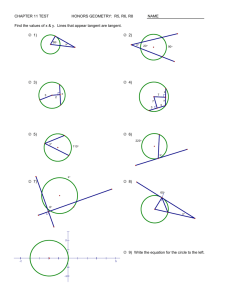
Circle Vocabulary C Circle – set of all points equidistant _________ from a given point called the _____ center of the circle. Symbol: C CHORD: A segment whose endpoints are on the circle DIAMETER: P Distance across the circle through its center Also known as the longest chord. RADIUS: P Distance from the center to point on circle Formula Radius = ½ diameter or Diameter = 2r WRITE THIS DOWN AND TELL ME WHY ALL CIRCLES ARE SIMILAR D = ? r = ? r = ? D = ? Use P to determine whether each statement is true or false. Q 1. RT is a diameter. False R 2. PS is a radius. True P 3. QT is a chord. True T S Secant Line: intersects the circle at exactly TWO points Tangent Line: a LINE that intersects the circle exactly ONE time Forms a 90°angle with one radius Point of Tangency: The point where the tangent intersects the circle Name the term that best describes the notation. Central Angles An angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle 3 Types of Arcs A Major Arc Minor Arc More than 180° Less than 180° P ACB To name: use 3 letters C AB B To name: use 2 letters APB is a Central Angle Semicircle: An Arc that equals 180° D E To name: use 3 letters P F EDF THINGS TO KNOW AND REMEMBER ALWAYS A circle has 360 degrees A semicircle has 180 degrees Vertical Angles are CONGRUENT Linear Pairs are SUPPLEMENTARY Formula measure Arc = measure Central Angle Find the measures. EB is a diameter. m AB = 96° A E m ACB= 264° Q m AE = 84° 96 B C Arc Addition Postulate A C B m ABC = m AB + m BC Tell me the measure of the following arcs. AC is a diameter. m DAB =240 m BCA = 260 D C 140 R 40 100 80 B A Congruent Arcs have the same measure and MUST come from the same circle or of congruent circles. C B A 45 45 D 110 Arc length is proportional to “r” Textbook p. 396 #11 p. 404 #11 – 16, 25 – 30, 38