Physics Review Sheet: Formulas, Examples, & Problems
advertisement

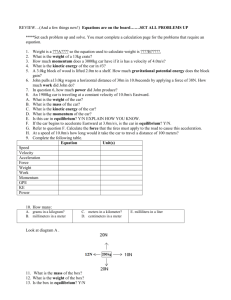
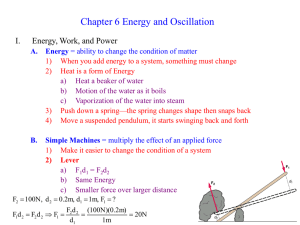
Physics Review Sheet: w = mg weight = mass (kg) x acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2) p = mv momentum = mass (kg) x velocity (m/s) F = ma Force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (m/s2) Newtons = kg m/s2 W=Fd Work (J) = Force (N) x distance (m) Joules = N * m = kg m2/s2 P=W/t Power (W) = work (J) / time (s) Watt = J / s Gravitational Potential Energy (energy due to position) Potential Energy = (mass)(gravity)(height) PE = mgh Example: What is the potential energy of a 2.14 kg book that is on a bookshelf 1.0 m above the floor? PE = mgh = (2.14 kg)* (9.8 m/s2)* (1.0 m) = 21 kg m2/s2 = 21 J Problem: How much work can a 5.0kg mass do if it is 5.0 m above the ground? Kinetic Energy (energy due to movement) Kinetic Energy = ½ (mass) (velocity)2 KE = ½ mv2 Example: A 7.0 kg bowling ball is moving in a bowling lane with a velocity of 5.0 m/s. What is the kinetic energy of the ball? KE = ½ mv2 = ½ (7.0kg) (5.0 m/s)2 = ½ ( 7.0 kg) (25 m2/s2) = 87.5 kg m2/s2 = 87.5 J Problem = A 100 kg football player moving with a velocity of 6.0 m/s tackles a stationary quarterback. How much work was done on the quarterback? Practice Problems: 1) What is the weight of a 60kg person on the surface of the Earth? 2) A 60 kg person weighs 100 N on the Moon. What is the value of g on the Moon? 3) What is the acceleration of a 20 kg cart if the net force on it is 40 N? 4) If 5000 J of work is used to raise a 102 kg crate to a shelf in a warehouse, how high was the crate raised? 5) What is the kinetic energy of a 2000 kg car moving at 72 km/h? 6) How much work is needed to stop a 1000 kg car that is moving straight down a highway at 54 km/h?