Cardiac Emergencies & Unconscious Choking
advertisement
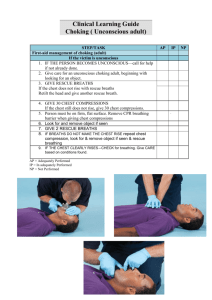
Do Now: Color the heart as shown below Cardiac Emergencies & Unconscious Choking Part 3: Chapter 7 Cardiovascular Disease Abnormal condition that affects the heart and blood vessels Leading cause of death for men and women in the USA (~950,000 per year) How does it Happen? Cholesterol Fatty substance made by the body and found in certain foods Too much in the blood can cause fatty deposits on artery walls that may restrict or block blood flow Atherosclerosis A condition in which fatty deposits build up on the walls of the arteries Coronary Heart Disease Most common type of disease Occurs when the arteries that supply oxygen rich blood to the heart muscles harden or narrow from the build-up of fatty deposits. This lack of oxygen rich blood flow causes the muscles around the heart to die. Blood Flow Through the Heart Cardiac Emergencies Heart Attack Blood flow to some part of the heart muscle is compromised and the heart begins to die If enough dies the heart will not be able to circulate blood effectively Cardiac Arrest Condition in which the heart stops beating Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Cardio = Heart Pulmonary = Lungs CPR artificially takes over the functions of the lungs and heart, increasing the victims chance of survival by keeping the brain supplied with oxygen until advanced medical care can be given Greatest Chance of Survival 1. Early recognition and early access 2. Early CPR Keeping oxygenated blood circulating 3. Early defibrillation Calling 9-1-1or local emergency number Electric shock that disrupts activity of the heart long enough to allow the heart to spontaneously develop an effective rhythm on its own 4. Early advanced medical care Getting the victim to a hospital quickly Signals of a Heart Attack Chest pain (Angina Pectoris) Squeezing, pressure, tightness, aching, constricting or heavy sensation in the chest Shoulder, arm, neck & jaw pain Trouble breathing The body is trying to much-needed oxygen to the heart Pulse may become faster or slower than normal Skin may become pale or ashen * Women are more likely to experience some other common signals Shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting and arm, back, neck, jaw or stomach pain Caring for a Heart Attack Victim Send someone to call 9-1-1 Have the victim stop what he or she is doing and rest comfortably. Loosen any restrictive clothing Monitor the victims closely until EMS personnel arrives Take note of any changes in appearance or behavior Be prepared to perform CPR or use an Automated External Defibrillators (AED) if the victim stops breathing or has no other signs of life Cardiac Arrest Heart stops beating or beats too ineffectively to generate a pulse Causes Cardiovascular disease Drowning Suffocation Certain drugs Severe injuries to the chest Severe blood loss Stroke and other types of brain damage CPR for an Adult Showing no signs of life Check, Call, Care If the person is not breathing give 2 rescue breathes 30 chest compressions Begin CPR with 100 chest compressions per minute How to Give Chest Compressions 1. Place the heel of one hand on the victim’s sternum, at the center of his or her chest 2. Place your other hand directly on top of the first hand interlacing the fingers of both hands 3.Use the heel of your hand to apply pressure on the sternum Compression Technique Rescuer should be kneel beside the victim Keep your arms straight and lock your elbows Compress only 1½ - 2 inches Keep the movements smooth, not jerky. Maintain a rhythm “One and two and three and four….” Counts up to 30 (every 18 seconds) After every 30 compressions you give 2 rescue breaths When to Stop CPR The scene becomes unsafe The victim shows obvious signs of life An AED becomes available and is ready to use Another trained rescuer arrives and takes over You are too exhausted to continue STOP CPR for Children or Infants Children Locate the proper hand position on the middle of the chest where you would an adult You can use one-handed technique by placing one hand on the child’s chest and the other hand on the forehead to maintain an open airway Place the shoulders over the hand Compress the chest 1½ inches 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths Infant Think of an imaginary line across the chest between the nipples Place pad of 2-3 fingers on that line on the victims sternum Compress the chest ½ - 1 inch. Push straight down Keep a rate of about 100 compressions per minute 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths Infant Chest Compressions 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths Child Chest Compressions -One-handed -Compress inches technique the chest 1½ Summarizer List 3 signs of a heart attack List the two examples of Cardiac Emergencies What do you do to care for a victim with no heart beat? Do Now: Describe the difference between a heart attack and a person in cardiac arrest What are the steps to care for a person with cardiac arrest. Unconscious Choking: Adult or Child Give 2 rescue breaths if they DO NOT go in, re-tilt the head and give 2 more Begin chest compressions Look for the foreign object by opening the victims mouth. 30 chest compressions 2 inches in depth (1½ inches for a child) every 18 seconds Remove with your fingers if it is visible If the object is not visible give 2 rescue breaths If they do not go in continue on with the compression cycle If the breaths go in and the chest clearly rises, check for signs of life Unconscious Choking Adult or Child Unconscious Choking: Infant Give 2 rescue breaths if they DO NOT go in, re-tilt the head and give 2 more Give 30 chest compressions with your finger pads about ½-1 inch in depth Look for the foreign object If it is seen remove it with your little finger Give 2 rescue breaths If the breaths do not go in repeat compression cycle If the breaths go in and the chest clearly rises, check for signs of life Unconscious Choking Infant AED Scavenger Hunt Each Group will have 10 minutes to locate as many of the AED’s as they can in our school. On our campus there are a total of 8. 5 of them are accessible inside the school. When searching stay out of the D circle and upstairs. You must take a picture of the AED and then document it’s location. Do not share with the other teams. Quiet. Phones only out when taking photo of AED. When not searching you must be working on AED worksheet.