American History I Review Power Point
advertisement

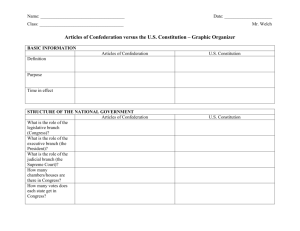
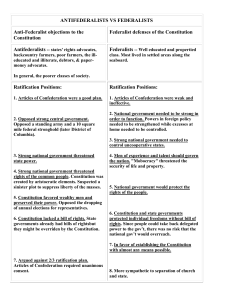
Articles of Confederation • During the Revolutionary War the American states began to adopt their own constitutions (written plan of government). • The states viewed themselves as free and independent nations, not as one nation. • The Continental Congress adopted a plan for a confederation during the Revolutionary War. • This became the basis for the first national government. Congress • • • Each state sent 2 – 7 representatives. Each state gets 1 vote. 9 of 13 states had to agree to pass a law. Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation • Congress could not levy taxes. • Congress could not regulate trade between the states (interstate commerce) or foreign trade. • No standing army. • No national court system. • No executive branch of government. • All 13 states had to agree to any changes to the Articles of Confederation. The Constitution Key Concepts • Checks and Balances (AOC, State Const.) • Separation of Powers (State Const.) • Popular Sovereignty (Locke, Rousseau) • Limited Government (Rousseau) • Judicial Review (Locke) • Federalism Popular Sovereignty • The power to rule belongs to the people. • “Consent of the governed” • “We the People of the United States …do ordain and establish the Constitution for the United States of America.” Limited Government Government can only do the things the people have given it the power to do. Government and its officials are subject to the law, never above the law. Checks and Balances Federalists vs. Antifederalists • The Constitution of the United States was approved by the convention and signed by 39 of the delegates on Sept. 17, 1787. • According to Article VII, the Constitution was to be ratified in conventions held in each state. Once 9 states had ratified the Constitution it would become the official plan of government for the United States. • Not all Americans, or all of the delegates to the convention, approved of the final document. This lead to a heated debate across the nation between proponents of the plan and opponents of the plan. • Federalists – supporters of the Constitution. • Antifederalists – opponents of the Constitution. Federalists vs. Antifederalists • There were several points of contention between these two groups. • Self Interests and Common Welfare • Central Authority and Active Participation • Supremacy Clause and Abuse of Power • Necessary and Proper Clause and Abuse of Power • Individual Liberties • Executive Power The American System • Developing an internal transportation system to link all regions of the nation (National Road, Erie Canal) • Establishing a protective tariff (tax on imports) to protect U.S. industries from foreign competition and fund internal improvements • Reestablishing the Bank of the United States to create a nationally recognized and equally valued currency to create financial unity among the regions of the country Impact on Politics and Government • Secession is not possible. The Union victory and occupation of the South settled that question forever. Secession=Treason • Presidential power to limit the rights of U.S. citizens increases during times of war and the Supreme Court says that is okay. 1. Conscription (draft) 2. Suspension of Habeas Corpus 3. Income Taxes • Slavery discussion is over thanks to the 13th Amendment. Impact on Economics North • South Manufacturing prospered due to the need for war materials. Industrialization speeds up. • Plantation economic system is dead and gone since slavery is abolished. • Inflation peaks at 7000% • Inflation did go up 182% • Costs = $1 Billion • Costs = $2.3 Billion • Debt = $1.8 Billion • Debt = $2.7 Billion