File
advertisement
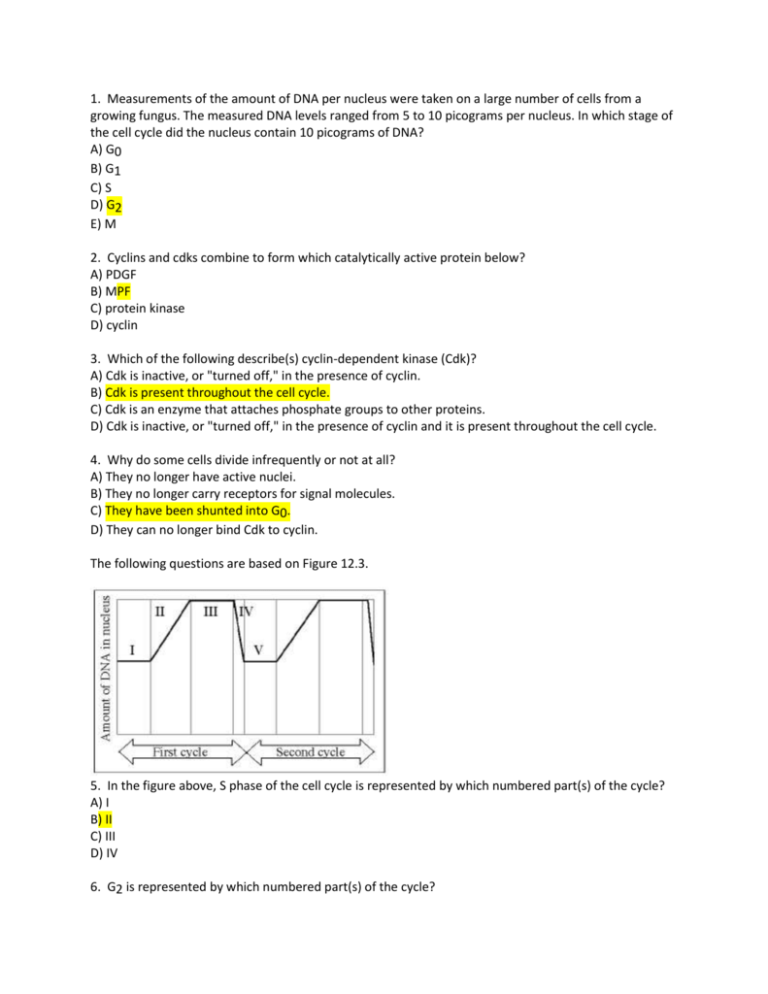
1. Measurements of the amount of DNA per nucleus were taken on a large number of cells from a growing fungus. The measured DNA levels ranged from 5 to 10 picograms per nucleus. In which stage of the cell cycle did the nucleus contain 10 picograms of DNA? A) G0 B) G1 C) S D) G2 E) M 2. Cyclins and cdks combine to form which catalytically active protein below? A) PDGF B) MPF C) protein kinase D) cyclin 3. Which of the following describe(s) cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)? A) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the presence of cyclin. B) Cdk is present throughout the cell cycle. C) Cdk is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins. D) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the presence of cyclin and it is present throughout the cell cycle. 4. Why do some cells divide infrequently or not at all? A) They no longer have active nuclei. B) They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules. C) They have been shunted into G0. D) They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin. The following questions are based on Figure 12.3. 5. In the figure above, S phase of the cell cycle is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle? A) I B) II C) III D) IV 6. G2 is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle? A) I or V B) II or IV C) III only D) IV only 7. Which number represents DNA synthesis? A) I B) II C) III D) IV 8. Which number represents the point in the cell cycle during which the chromosomes are replicated? A) I B) II C) III D) IV 9. Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of n = 16? A) The species is diploid with 32 chromosomes per cell. B) The species has 16 full sets of chromosomes per cell. C) Each cell has eight homologous pairs of chromosomes. D) During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 64 separate chromosomes. 10. The karyotype of one species of animal has 24 chromosomes. In a particular female, cell division goes awry and she produces one of her eggs with an extra chromosome (13). The most probable source of this error would be a mistake in which of the following? A) prophase B) metaphase C) anaphase D) telophase 11. Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis II? A) Homologous chromosomes are separated. B) The chromosome number per cell remains constant. C) Sister chromatids are separated. D) Four haploid daughter cells are formed. 12. Chromatids are separated from each other. A) The statement is true for mitosis only. B) The statement is true for meiosis I only. C) The statement is true for meiosis II only. D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II. 13. Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of A) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I. B) the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm. C) lagging and leading strands in DNA replication D) the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes. 14 . A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a two X chromosomes is A) a sperm. B) an egg. D) a somatic cell of a male. E) a somatic cell of a female. A woman who has blood type B positive has a daughter who is type O positive and a son who is type A negative. Rh positive is a trait that shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the alleles R (for positive) and r (for negative), respectively. 15. Which of the following is a possible partial genotype for the son? A) RR B) Rr C) rr 15. What are some possible blood types of the father of both of her children? a. A negative b. B negative c. AB positive d. a or b e. any of the above are possible blood types of the father 16. How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCc? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 8 E) 64 17. In the cross AaBbCc × AaBbCc, what is the probability of producing the genotype AaBBCC? (Remember, math is your friend!) A) 1/4 B) 1/8 C) 1/16 D) 1/32 E) 1/64 18. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive human disorder in which an individual cannot appropriately metabolize a particular amino acid. Therefore, the most efficient and effective treatment is which of the following? A) Feed them the amino acid. B) Transfuse the patients with blood from unaffected donors. C) Regulate the diet of the affected persons to severely limit the uptake of the amino acid. D) Feed the patients the missing enzymes in a regular cycle, such as twice per week. In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A truebreeding dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to selfpollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in Figure 14.1, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square. Figure 14.1 19. Which of the plants will be true-breeding? A) 1 and 4 only B) 2 and 3 only C) 1, 2, 3, and 4 D) 1 only The following questions refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle. Figure 14.2 20. What is the genotype of individual II-4? A) WW B) Ww C) ww 21. What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 75% Tallness (T) in snapdragons is dominant to dwarfness (t), while red (R) flower color is dominant to white (r). The heterozygous condition results in pink (Rr) flower color. 22. A tall, red snapdragon is crossed with a plant homozygous for tallness and white flowers. What are the genotype and phenotype of the F1 individuals? A) ttRr—dwarf and pink B) ttrr—dwarf and white C) TtRr—tall and red D) TtRr—tall and pink E) TTRR—tall and red 23. When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result? A) The gene involved is on the Y chromosome. B) The gene involved is on the X chromosome. C) The gene involved is on an autosome, but only in males. 24. Males are more often affected by sex-linked traits than females because A) male hormones such as testosterone often alter the effects of mutations on the X chromosome. B) female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome. C) X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females. D) males have only one (are hemizygous for the) X chromosome. Figure 15.3 25. The pedigree in Figure 15.3 shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely A) autosomal recessive B) Y-linked. C) autosomal dominant. D) X-linked recessive. A man who is an achondroplastic dwarf with normal vision marries a color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was 6 feet tall, and both the woman's parents were of average height. Achondroplastic dwarfism is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is X-linked recessive. 26. How many of their sons might be expected to be color-blind dwarfs? A) all B) none C) half D) one out of four E) three out of four 27. What proportion of their daughters would be color-blind and of normal height? A) none B) half C) one out of four D) three out of four 28. 29. 30.





