Submandibular gland
advertisement

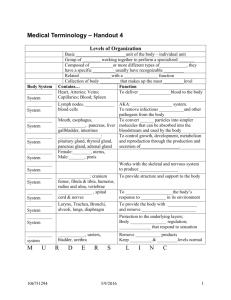
Lec. # 13 Tuesday 22-3-2011 Sub mandibular triangle Mostly occupied by submandibular gland. Superficial to the gland facial vein. Deep to the gland facial artery. Roof : 1- skin 2- superficial fascia 3- platysma muscle 4-cervical branch of the facial nerve (which supplies the platysma) 5-investing deep fascia note: the cervical deep fascia is divided into 3 parts : investing(outer) , pretracheal and prevertebral(inner). Boundaries : Anterior : by anterior belly of digastric muscle. Posterior : by posterior belly of digastric muscle. Superior : by the inferior border of the mandible. Floor : Consist of 3 muscles. From anterior to posterior : 1- Mylohioid 2- hyoglossus 3- middle constrictor of pharynx. Contents : 1-Submandibular gland. 2- Submandibular duct. 4-hypoglossal nerve. 5- mylohyoid nerve. 7- facial artery & vein. 3- Submandibular lymph nodes. 6- mylohyoid vessles. Submandibular gland : General notes : We have 3 glands: sublingual , submandibular & parotid gland. The function of these glands is secretion. All of them are originated from the mouth, so all of them open within the mouth. Submandibular gland is in the middle between the sublingual & the parotid glands. The submandibular gland is mixed gland ( mucus, serous) Called seromucous because most of the secretion is serous. It has 2 capsules : inner fibrous & outer investing fascia (like the parotid gland) It is U shaped on its side, looping around the posterior border of mylohyoid muscle. The mylohyoid divides the mandibular gland into 2 parts : 1- Large superficial part : External to the mylohyoid muscle. Inner to the mandible (to be more specific sub mandibular fossa). External to it we have also facial vein & platysma. 2- Smaller deep part : Lies within the floor of the oral cavity. Internal to mylohyoid. External to hyoglossus. It is sandwiched between mylohyoid and hyoglossus. Inner to it also hypoglossal nerve & facial artery. Gives the submandibular duct from anterior process. Submandibular duct : About 5 cm in length. Extending from the anterior aspect of the deep partruns forward & upward between the mylohyoid & the hyoglossus muscle. Pass below the floor of the mouth and open at the side of the frenulum of the tongue. It has specific relations to the lingual nerve : The lingual nerve loops (lateral, infiror and medial) around the submandibular duct. Arterial supply of the submandibular gland : Facial artery & lingual artery Venous drainage: facial & lingual vein. Lymph drainage: submandibular lymph nodes that will send it back to the cervical lymph nodes. (Mostly head and neck lymph nodes drain to the cervical lymph nodes). Nerve supply : Below the lingual nerve we have submandibular gangilion & it is Parasympathetic. (All the ganglia in the head and neck are parasympathetic ganglions except for 6 cervical) A submandibular ganglion gives the parasympathetic innervations to the submandibular gland. Parasympathetic innervation is secretomotor. Sympathetic innervation comes around arteries mostly. The submandibular gland receives the sympathetic innervations from the facial artery. The function of sympathetic innervations is to decrease the secretion. NOTES: The anterior belly of digastric & posterior belly of digastric is united in the intermediate tendon which will bind to the body of hyoid bone by facial stings. Hypoglossal nerve : 1-Passes in two triangles: carotid & submandibular. 2-Sandwiched between the posterior belly of digastric & hyoglossus muscles. 3- Sandwiched between mylohyoid & hyoglossus muscles Facial vein is superior to the submandibular gland Facial artery is deep to the submandibular gland DONE BY: Abdel-raheem yaseen. Good luck for all of you in the mid terms :D