File - Science with Mr. B
advertisement

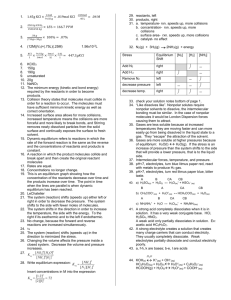
Acid / Base Chemistry Acid & Base Strength & pH pH of common materials Strong vs. Weak Acids Strong Acids A strong acid is one that ionizes completely in aqueous solution. HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl– 100% Weak Acids A weak acid releases few hydrogen ions in aqueous solution – it does not ionize completely. HCN + H2O H3O+ + CN– ???% Strong Acids & Bases Strong Acids HI HBr HCl HNO3 H2SO4 HClO4 HClO3 Strong Bases NaOH KOH RbOH CsOH Ca(OH)2 Sr(OH)2 Ba(OH)2 Self-Ionization of Water H2O + H2O H3 + O + [H3O+] = 1 x 10-7 M [OH-] = 1 x 10-7 M [H3O+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 M – OH Hydronium vs. hydroxide concentrations [H3O+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 M Where do we get pH from? The pH of a solution is defined as the negative of the common logarithm of the hydronium ion concentration, [H3O+] or [H+]. pH = -log[H+] example: if a solution has [H+]= 2.5 x 10−5 pH = −log[H+] = −log(2.5x10-5) = 4.6 pH Scale What is the pH of 0.050 M HNO3? Nitric Acid is a strong acid, so it ionizes completely: HNO3 H+ + NO3– pH = -log[H+] pH = -log[0.050] pH = 1.3 C. Johannesson pH is a Logarithmic Scale Every unit of pH means there is 10x more H+ ions! Stomach acid: pH 1 Battery acid: pH 0 Battery acid is 10x more acidic than stomach acid! pH is a Logarithmic Scale Coffee is pH 5 Apple Juice is pH 3 How much more acidic is apple juice compared to coffee? Apple juice is 2 pH units more acidic than coffee, so 10 x 10 = 100 times more acidic than coffee! Equations you need to know! pH = -log[H3O+] pOH = -log[OH–] pH + pOH = 14 [H3O+] = 10(–pH) [OH–] = 10(–pOH) [H3O+][OH–] = 1 x 10-14 M pH Scale What is the pH of 0.030 M NaOH? Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, so it ionizes completely: NaOH Na+ + OH– pOH = -log[OH–] pOH = -log[0.03] = 1.5 pH + pOH = 14 pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 1.5 pH = 12.5 C. Johannesson pH Scale What is the molarity of HBr in a solution that has a pH of 4.4? [H3O+] = 10(–pH) [H3O+] = 10(–4.4) [H3O+] = 4.0 10-5 M HBr C. Johannesson pH of Rainwater across United States in 2001 Why is the eastern US more acidic? http://nadp.sws.uiuc.edu/isopleths What is acid rain? Acid rain has a pH lower than 5.3 Dissolved carbon dioxide naturally lowers the pH CO2 (g) + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3- Atmospheric pollutants from combustion acidify rain a lot! NOx : NO, NO2 + H2O … HNO3 SOx : SO2, SO3 + H2O … H2SO4 Marble + Hydrochloric Acid CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 The photo on the left was taken in 1908. The effects of acid rain on the statue are clear in the photo on the right, taken 60 years later, in 1968 Effects of acid rain Limestone and acid rain Limestone is primarily CaCO3 Neutralizes excess acid and adds buffers against pH changes … just one little problem …