What is Selling - Sheffield-Sheffield Lake City Schools Home
advertisement

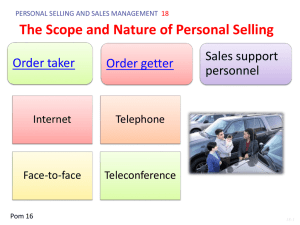
Marketing Ch 13 What is Selling? Knowing your product and your customer • Selling – Helping customers make satisfying buying decisions – Do this by communicating how products and their features match customers needs and wants Why do we want customer satisfaction • We want repeat customers Goal of selling 1. Help customers decide on purchase 2. Ensure customers are satisfied and become return customers Feature-Benefit Selling • Process of matching the features of each product to a customer’s wants and needs • Two types 1. Product Features 2. Customer Benefits Product Features • Salesperson needs to learn how a product features will benefit the customer. • Product Feature – Physical characteristics or quality of a good or service that explains what it is. • Most basic feature is its intended use Tangible Product Features • Certain qualities in the product that differentiates competing brands and models • Physical characteristics of the product – Examples in a car • • • • Color Automatic Transmission Stereo Anti-lock breaks Tangible Product Features • Additional features add value to a product • Physical features help provide the reason for price difference among product models Extended product features • Not always physical part of the product but they are important to the purchase decision • Example: – Warranties – Service Policy – Available financing – Reputation of Company Customer Benefits • Advantages or personal satisfaction a customer will get from a good or service • A salesperson will need to answer two questions about each product feature: 1. How does the feature help the product’s performance? 2. How does the performance information give the customer a personal reason to buy the product? • What value is it to the customer Product Information • Product knowledge is essential for success in selling. • Knowing about product helps explain why one product is better than another • Know how to use (demonstrating) and care for a product is essential when educating consumers Customer Buying Motives • What motivates people to buy a product • Is their motive Rational or Emotional Rational Motive • Conscious, factual reason for buying – Include: • • • • • • • • Product Dependability Time or Monetary Savings Convenience Comfort Health or Safety Considerations Recreational Value Service Quality Emotional Motive • Feeling experienced through association with a product – Social approval – Recognition – Power – Love – Affection – Prestige Motives • Both rational and emotional motives can present in the same purchase Customer Decision Making • Three distinct types of decision making 1. Extensive 2. Limited 3. Routine Extensive Decision Making • Used when there has been little or no previous experience with the item because it is infrequently purchased • High degree of risk and very expensive • Examples – Expensive Machinery – Land for a new building site – First home Limited Decision Making • Used when a person buys goods and services that he or she has purchased before but not on a regular basis. • Moderate degree of risk • Examples: – Second car – Furniture – Vacation – Household appliances Routine Decision Making • Used when a person needs little information about a product because of a high degree of prior experience • Low degree of risk • Customer have develop brand loyalty Is Selling the Career for You? • Type of Sales positions – Retail Sales • Sales Associates –Know their products and how to sell • Salesclerks –Simply order takers or cashiers • Sales Representatives –Extensive Training and product knowledge Is Selling the Career for You? • Type of Sales positions – Retail Sales • Sales Associates • Salesclerks • Sales Representatives • Telemarketing Sales Associate • Expected to know their product and how to sell Salesclerk • Simply order taker or cashier Sales Representative • Requires extensive training and product knowledge • Often requires college degree • Command high salaries and commission Telemarketing • Process of selling over the telephone • Items sold over the phone: – Magazine subscriptions – Service contracts Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Good Communication skills – Excellent listening and speaking skills – Read between the line when listening – Know proper grammar and pleasant speaking voice Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Good Interpersonal skills – Know how to get along with different people – Be able to handle customers who are demanding as well as those who are reserved – Know what to say and how to say it Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Solid Technical Skills – Good math and computer skills and product knowledge – Be an expert in your field – Read trade magazines/papers to keep up with the trends – Study company products and competitors Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Positive Attitude and Self-Confidence – Involves learning from your mistakes and looking for something useful in all situations – Be secure enough to accept rejections Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Goal Orientation – Keeps effective salespeople focused and striving for success – Persistence is needed – Do not give up on a customer Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Empathy – The essence of customer-oriented selling – Be able to see things from a customer’s point of view and be sensitive to their problem – Learn the says “I can understand why you feel that way. I would feel the same way.” – Have the customers best interest at heart Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Honesty – Salespeople are honest because they know integrity is the cornerstone of professional selling – Salespeople want repeat sales and customer relationships Characteristics of Effective Salespeople • Enthusiasm – Be excited about the products you sell – Believe in the products – Lack of enthusiasm will come through Fact and Idea Review • Complete and Fact and Idea Review on page 184 • And Critical Thinking