Molecular Shapes
advertisement

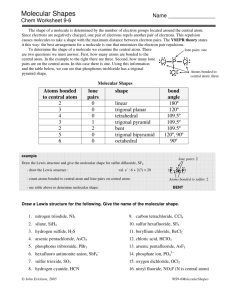
Molecular Shapes Mrs. Chan Molecular Structure • It mean the 3-D arrangement of atoms in a molecule • Lewis dot structures show how atoms are bonded together (2-D), but they often do not illustrate the true shape of a molecule (3-D). • How to determine the shape of a molecule? Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) VSEPR determines if a molecule is polar! VSEPR Theory Pairs of electrons around a central atom want to be as far away from each other as possible. Main idea: Bonding and Non-bonding e- pairs are positioned as far as possible so as to minimize repulsions between electron pairs. For VSEPR, treat double and triple bonds like single bonds. e- pairs: Bonding and Non-bonding pairs (lone pairs) around the central atom, don’t include central atom itself 5 Molecular Shapes • • • • • Linear Trigonal Planar Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramid Bent (2 kinds) Linear If two atoms bond to a central atom, like in CO2, the molecule will form in a straight line (Linear). 2 e- pairs, 3 atoms, angle = 180 degrees Trigonal Planar If three atoms bond to a central atom, with no lone pairs, like in BF3 , the molecule forms a Trigonal Planar shape. 3 e- pairs, 4 atoms, angle = 120 degrees Tetrahedral If four atoms bond to a central atom, like in CH4, the molecule takes a tetrahedral shape. 4 e- pairs, 5 atoms, angle = 109.5 degrees Trigonal Pyramidal If one lone pair of electrons and three atoms bond to a central atom, like in CH4, the molecule takes on a Trigonal Pyramidal shape. 4 e- pairs (1 lone pair + 3 bonded pairs), 4 atoms, angle = 107.2 degrees Remember, lone pairs take up space! Bent Bent 1 If two lone pairs of electrons and two atoms bond to central atom, like in H2S 4 e- pairs (2 lone pairs + 2 bonded pairs), 3 atoms, angle = 105 degrees Bent 2 If one lone pairs of electrons and two atoms bond to central atom, like in SO2 3 e- pairs (1 lone pair + 2 bonded pairs), 3 atoms, angle = 119.2 – 120 degrees Steps for Predicting Molecular Structures using VSEPR Model 1. Draw the Lewis Structure for the molecule. 2. Count the electron pairs and arrange them in the way that minimize repulsions (put the pairs as far apart as possible). 3. Determine the positions of the atoms from the way the electrons pairs are shared. 4. Determine the name of the molecular structure from the positions of the atoms. Lone Pairs around Central Atoms Lone pair: Valence e- pair that belongs to only 1 atom / is not involved in bonding Linear, Trigonal Planar, and Tetrahedral have NO lone pairs around the central atoms Just look at how many atoms around the central atom That is how many e- pairs Lone Pairs around Central Atoms What about if there are lone pairs around the central atom? REMEMBER: 1) Lone pairs also take up space!!! 2) Lone pairs repel each other 3) Lone pairs repel bonded pairs