ES9 17 Volcanoes I (Luigi)
advertisement

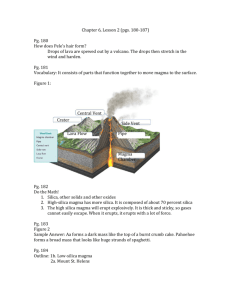
http://www.blastr.com/2015-1-13/nasa-deploys-special-robot-designed-explore-deep-inside-active-volcanoes Volcanoes I What determines whether a volcano extrudes magma violently or gently? • Composition • Temperature • Dissolved gasses (amount) Composition • Shield volcano- basalt lava flows • Stratovolcano- Highly variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra with an overall andesite composition Temperature • It can reach up to 700-1,200 °C (1,292 to 2,192 °F). Dissolved gasses • H2O- Water vapor • CO2- Carbon dioxide • SO2- Sulfur dioxide Which factors affect viscosity? • Higher temperature, less viscous; lower temperature, more viscous • Greater silica content, greater viscosity; lower silica, lower viscosity • Higher amount of volatiles (dissolved gases), lower viscosity; Lower amount of volatiles, greater viscosity How does a magma chamber form? • rocks closer to the surface become less dense • the magma stops rising • minerals with high melting temperatures • magma enriched with silica How is a Hawaiian-type of eruption triggered? • A Hawaiian-type of eruption is quiet or gentle • eruptions are triggered by the arrival of a new batch of magma • The magma chamber swells • The basaltic magma becomes more mobile What are lava fountains and how are they produced? • Fluid basaltic magmas • These pressurized gases are easily released • These gases may propel lava hundreds of meters What is the role of dissolved gases in explosive or violent eruptions? • Because of its high viscosity, dissolved gases in silicarich magmas • These dissolved gases begin forming tiny bubbles • These tiny bubbles build up over a long period of time • When the pressure overcomes the strength of the overlying rock • The sudden release of pressure may generate an explosive event What materials are extruded during an eruption? • Lava flows • Gases • Pyroclastic materials Lava Flows • AA lava flow- Basalt characteristically form flows known by the Hawaiian names pahoehoe and aa. • Pahoehoe lava flow- Are characterized by smooth, gently undulating, or broadly hummocky surfaces. Pyroclastic materials • • • • • ash and dust welded tuff Cinders Block and bombs Scoria and pumice References • • • http://www.blastr.com/2015-1-13/nasa-deploys-special-robot-designed-explore-deep-inside-active-volcanoes https://hedcenscience.wordpress.com/environmental-science-9/ www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcanoes_work/Volcano_types.html