Naming Acids - BC Learning Network
advertisement

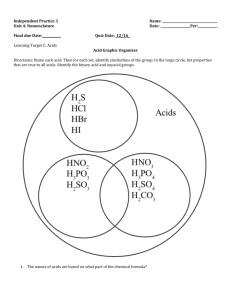
Names and Formulas for Acids Naming Acids Acids have their own unique system of naming. Acids have their own unique system of naming. Once you are familiar with the system of naming acids given their formulas, Acids have their own unique system of naming. Once you are familiar with the system of naming acids given their formulas, it will be fairly easy for you to determine the formula for an acid, given the name. Acids can be divided into two main categories: Acids can be divided into two main categories: 1. Binary Acids Acids can be divided into two main categories: 1. Binary Acids 2. Acids Containing a Polyatomic Ion Acids can be divided into two main categories: Contain 2 elements: 1. Binary Acids Hydrogen, and a non-metal Acids can be divided into two main categories: 1. Binary Acids 2. Acids Containing a Polyatomic Ion Contain Hydrogen and a Polyatomic Ion Acids can be divided into two main categories: 1. Binary Acids 2. Acids Containing a Polyatomic Ion Contain Hydrogen and a Polyatomic Ion Polyatomic Ions Naming Binary Acids A Binary Acid consists of hydrogen, and a non-metal. Hydrogen Non-metals A Binary Acid is named as follows: A Binary Acid is named as follows: hydro A Binary Acid is named as follows: hydro The root + of the non-metal name A Binary Acid is named as follows: hydro The root + of the + “ic” acid non-metal name Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF Binary Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrofluoric acid Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrofluoric acid Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid fluorine hydrofluoric acid Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid fluorine hydrofluoric acid Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrofluoric acid Let’s do an example: Name the acid HF hydrofluoric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid Binary Acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrosulfuric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrosulfuric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrosulfuric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrosulfuric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydro + The root of the non-metal name + “ic” acid hydrosulfuric acid Let’s do another example: Name the acid H2S hydrosulfuric acid An Acid with a polyatomic ion (PAI) is named as follows: An Acid with a polyatomic ion (PAI) is named as follows: 1. If the name of the PAI ends in “ate”, replace “ate” with “ic” and add “acid” An Acid with a polyatomic ion (PAI) is named as follows: 1. If the name of the PAI ends in “ate”, replace “ate” with “ic” and add “acid” 2. If the name of the PAI ends in “ite”, replace “ite” with “ous” and add “acid” Acids with Polyatomic Ions ate ic ite ous + acid Use this to name acids with polyatomic ions Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate Replace the “ate” with “ic acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate perchlorate Replace the “ate” with “ic acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate perchloric Replace the “ate” with “ic acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 H+ ClO4– perchlorate perchloric acid Replace the “ate” with “ic acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO4 perchloric acid Name the acid with the formula: HClO Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite Replace the “ite” with “ous acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite hypochlorite Replace the “ite” with “ous acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite hypochlorous Replace the “ite” with “ous acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO H+ ClO– hypochlorite hypochlorous acid Replace the “ite” with “ous acid” Name the acid with the formula: HClO hypochlorous acid Writing Formulas for Acids Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Because the name starts with “hydro”, we know that it’s a Binary Acid Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion The root “iod” corresponds to the non-metal iodine Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion The root “iod” corresponds to the non-metal iodine Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion The root “iod” corresponds to the non-metal iodine anion charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid The root “iod” corresponds to the non-metal iodine I– Iodide anion Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid Requires 1 H+ ion I– Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid ions H+ I– Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for hydroiodic acid H+ I– HI Formula Write the formula for hydroiodic acid HI Formula Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for nitrous acid Write the formula for nitrous acid There is no prefix “hydro” and the name ends in “ous” Write the formula for nitrous acid There is no prefix “hydro” and the name ends in “ous” This is an acid with a polyatomic ion Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary With a PAI Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge Write the formula for nitrous acid Name ends in “ous”, so we find a PAI ending in the letters “ite” Write the formula for nitrous acid Name ends in “ous”, so we find a PAI ending in the letters “ite” Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge With a PAI If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance the negative charge on this PAI Write the formula for nitrous acid requires 1 H+ ion Write the formula for nitrous acid H+ NO2– ions –1 charge requires 1 H+ ion Write the formula for nitrous acid HNO2 Formula H+ NO2– –1 charge requires 1 H+ ion Write the formula for nitrous acid HNO2 Formula Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge With a PAI If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance the negative charge on this PAI Writing Formulas for Acids Is the acid binary or does it have a PAI? Binary Locate the non-metal and find the charge on it’s anion Add the number of H’s needed to balance this charge With a PAI If its an “ic” acid, find the PAI ending in “ate” If its an “ous” acid, find the PAI ending in “ite” Add the number of H’s needed to balance the negative charge on this PAI This is found in the Science 10 Data Booklet This is found in the Science 10 Data Booklet or CH3COOH