Section 13.1
advertisement

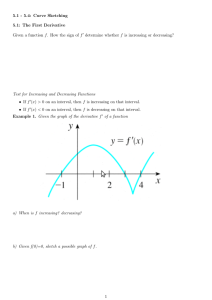
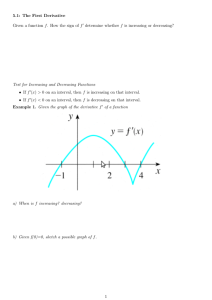
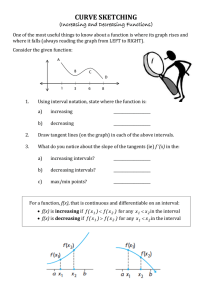
Section 13.1 – 13.2 Increasing/Decreasing Functions and Relative Extrema Facts If f ’(x) > 0 on an interval (a,b), then f (x) is increasing on (a,b). If f ’(x) < 0 on an interval (a,b), then f (x) is decreasing on (a,b). Definition: A number c for which f ’(c) = 0 or f ’(c) = undefined is called the critical number (critical value). Example: Find the intervals where the function is increasing/decreasing 2 3 f ( x) 5 3 x x Definition A function f has a relative maximum (or local max) at c if f (c) > f (x) for all x near c. A function f has a relative minimum (or local min) at c if f (c) < f (x) for all x near c. The First Derivative Test: If f ’(c) changes from + to – at c, then f has a local maximum at c. If f ’(c) changes from – to + at c, then f has a local minimum at c. No sign change at c means no local extremum (maximum or minimum) How to find local max/min and interval of increasing/decreasing: 1) 2) 3) Find all critical values by solving f ’(x) = 0 or f ’(x) = undefined Put all critical values on the number line and use test values to determine the sign of the derivative for each interval. Determine the interval of increasing/decreasing based on the sign of derivative. Examples Find the intervals of increase/decrease and all local extrema. f ( x) 4 x 9 x 30 x 6 3 2 x g ( x) 2 x 3 2 h( x) x e 2 x y 6x 3 4x 1 2 Examples A small company manufactures and sells bicycles. The production manager has determined that the cost and demand functions for q (q > 0) bicycles per week are 1 3 C (q ) 10 5q q 60 p D(q) 90 q where p is the price per bicycle. a) Find the (weekly) revenue function. b) Find the maximum weekly revenue. c) Find the maximum weekly profit. d) Find the price the company should charge to realize maximum profit. 7
![∈ [ ( ) = ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010601535_1-6f70cc477c07d559090667d6567ce3dc-300x300.png)