Student Version - Parkway C-2
advertisement

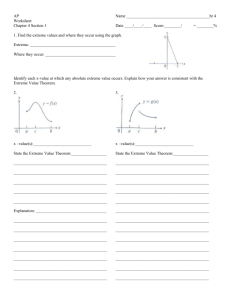
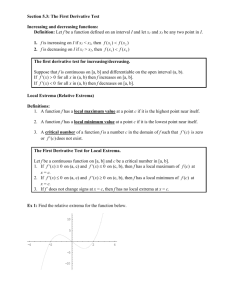
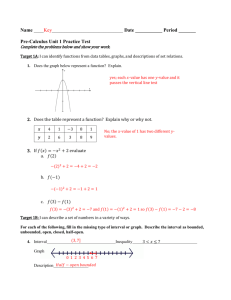
1. 2. 3. 4. Objectives: Be able to define various vocabulary terms needed to be successful in this unit. Be able to understand the definition of extrema of a function on an interval and “The Extreme Value Theorem”. Be able to find the relative extrema and critical numbers of a function. Be able to find extrema on a closed interval. Critical Vocabulary: Extrema, The Extreme Value Theorem, Critical Numbers I. Vocabulary Extrema (Plural of Extreme): This means we are talking about ______ (plural of maximum) and _______ (plural of minimum) of a function. Interval: Means we are talking about a part of a function, denoted by interval notation ____ or _____ ___________ __________ II. Extrema of a Function Let f be defined on an interval I containing c 1. f(c) is the _______ of f on I if ____ ≤ ____ for all x in I 2. f(c) is the _______ of f on I if ____ ≥ ____ for all x in I The _______ and ________ of a function on an interval are the ________ values, or ______, of the function on the interval. The minimum and maximum of a function on an interval are also called the ________ minimum and ________ maximum on the interval. Example 1: Function: f(x) = x2 + 3, Interval: [-2, 2], Let c = 0 II. Extrema of a Function If f is _______ on a closed interval [a, b], then f has both a _________ and ___________ on the interval. To illustrate this, we will look at the graph of f(x) = x2 + 1 on the following intervals: III. Relative Extrema and Critical Numbers Point where a graph changes its behavior (increasing/decreasing) help in determining the maximum and minimum values of a graph. Relative Minimum: _____________________________________ Relative Maximum: _____________________________________ III. Relative Extrema and Critical Numbers 1. If there is an open interval containing c on which f(c) is a maximum, then f (c) is called a _____________ of f. 2. If there is an open interval containing c on which f(c) is a minimum, then f (c) is called a _____________ of f. The plural of relative maximum is ___________ and the plural of relative minimum is _________________. III. Relative Extrema and Critical Numbers Example 2: Find the value of the derivative at each of the relative extrema shown in the graph 9 x2 3 f ( x) x3 When the derivative is zero, we call the x-value associated with it a ____________________. III. Relative Extrema and Critical Numbers Example 3: Find any critical numbers algebraically: f(x) = x2(x2 - 4) 1st: Find the derivative 2nd: Set f’(x) = 0 3rd: Check for any places where the derivative is undefined IV. Finding Extrema on a Closed Interval To find the extrema of a continuous function f on a closed interval [a, b], use the following steps: 1. Find the ____________________ of f in (a, b) 2. Evaluate f at each ________________ in (a, b) 3. Evaluate f at each _____________ in [a, b] 4. The least of these values is the ________ and the greatest is the ______________. IV. Finding Extrema on a Closed Interval Example 4: Locate the absolute extrema of the function on the x2 closed interval f ( x) 1st: Find the critical numbers 2nd : Evaluate at the endpoints x2 3 , [1,1] IV. Finding Extrema on a Closed Interval Example 5: Locate the absolute extrema of the function on the closed interval f ( x) x1/ 3 , [1,1] Page 319-321 #7-27 odd, 33, 43, 45, 47