What is Ethics?
advertisement

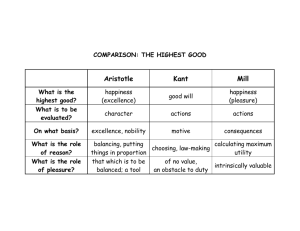
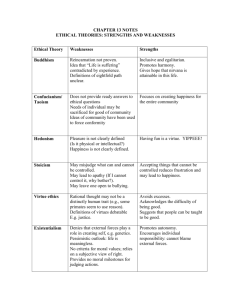
Ethics A look at the reasons behind decisions about what is right and wrong. What is the right thing to do? 2 Types of Moral Theories Teleological Theories: Moral judgments based on the effects of an act. You decide whether an act is good or bad by looking at its consequences. Also called Utilitarianism and Consequentialist Moral Reasoning. Deontological Theories: Disagrees that consequences are important. Instead there are certain acts that are right or wrong no matter what the consequences are. Also called Categorical Moral Reasoning. Decide whether these statements are teleological or deontological or could be both. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Drinking and driving is wrong. You only have to look at the deaths it causes to see that. “I knew studying was the right thing to do—I’ve passed all my exams!” I could never go to war because I think it is wrong to kill. Always tell the truth “Always obey your superiors.” When I am older I must not take sweets from strangers. Moral Dilemmas In groups of 3-4 people, decide: 1. What the teleological decision would be 2. What the deontological decision would be 3. What your decision would be Quick Check- On a separate piece of paper… In your own words, differentiate between teleological moral/ethical reasoning and deontological moral/ethical reasoning. 2. State which type of reasoning you lean towards. 1. Utilitarianism Utilitarianism states that an action is right if it produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people. What does this mean? What is the ‘greatest good’? 2 Main Philosophers Jeremy Bentham John Stuart Mill Bentham The idea that we ought to produce the greatest happiness for the greatest number is called ‘ The Principle of Utility or The Greatest Happiness Principle’. For Utilitarianism an action is right if it produces the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people. Happiness for utilitarianism is pleasure and the absence of pain. There are 3 bigger ideas which underlie The Greatest Happiness Principle/Utility Principle: 1. Consequentialism: Consequentialism involves deciding whether an action is good or bad by looking at the consequences of that action. If the consequences of the action are good then the action is a good one. If the consequences of the action are bad then the action is a bad one. 2. Hedonism Hedonism is the idea that pleasure is the only inherently good thing and that pain is the only inherently bad thing. Acts which bring about pleasure are good acts. Acts which bring pain are bad acts. How intense the experience is How long it lasts Whether it will lead to similar types of experiences How many people will be affected 3. Equality For Utilitarians, the pleasure and pain of everyone is equally important. Every person counts for one and only one. If your happiness is increased by 10 by doing something but the happiness of others is increased by 100 if you do something else then you should do the ‘something else’.