Developing an Assessment of Sustainability Knowledge (ASK)
advertisement

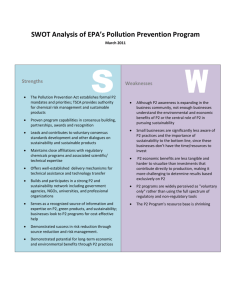
Environmental and Social Sustainability Lab Adam Zwickle Tomas Koontz Andrew Bodine Kristina Slagle Developing an Assessment of Sustainability Knowledge (ASK) for undergraduate students 2 Overview Need for a systematic way of measuring knowledge of sustainability concepts Developing an assessment Results Where we go from here 3 Need for measuring knowledge Lacking in the scientific community “Sustainability” myriad of ways has been defined and measured a Often focused merely on the environmental aspect Commonly tangled with values, attitudes, and beliefs Needed to operationalize abstract goals… 4 Need for measuring knowledge University goals- More along the lines of: “Become carbon neutral by 2050” Less common: “Create sustainably minded citizens of tomorrow” 5 Developing an assessment Built upon the “triple bottom line”, the “three legged stool”, the “3 p’s” Environmental (planet) Economic (prosperity) Social (people) Basic knowledge from each knowledge domain? ~OR~ Knowledge bridging the different spheres? 6 Developing an assessment Replicated questions used in the past Coyle, 2005. “Environmental Literacy in America.” Solicited topics and questions from experts Held expert focus groups Pilot tested among professors, graduate, and undergraduate students Narrowed down to 30 questions 7 Conceptualizing sustainability knowledge Social Environmental Sustainability Economic 8 Phase 1 Administered 30 question assessment Through an online survey Sent to over 10,000 currently enrolled undergraduates 14.3% response rate 9 Phase 1 - Analysis Utilized Item Response Theory (IRT) To remove 14 questions IRT Developed in the educational testing field Used for standardized tests (GRE) 10 An example of IRT… “Over the past 3 decades, what has happened to the difference between the wealth of the richest and poorest Americans?” Correct Information 50/50 threshold Incorrect 11 Questions - Environmental What is the most common cause of pollution of streams and rivers? Ozone forms a protective layer in the earth's upper atmosphere. What does ozone protect us from? What is the name of the primary federal agency that oversees environmental regulation? What is the primary benefit of wetlands? Which of the following is an example of sustainable forest management? In the U.S., what do we currently do with the nuclear waste generated by nuclear power plants? 12 Questions - Social Which of the following is the most commonly used definition of sustainable development? The wealthiest 20% of people in the U.S. own approximately what percent of the nation’s privately held wealth? Over the past 3 decades, what has happened to the difference between the wealth of the richest and poorest Americans? Higher levels of education generally lead to... Which of the following populations has the highest rate of growth? 13 Questions - Economic Many economists argue that electricity prices in the U.S. are too low because… Which of the following countries has now passed the U.S. as the biggest emitter of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide? Which of the following is a leading cause of the depletion of fish stocks in the Atlantic Ocean? Which of the following is the most commonly used definition of economic sustainability? Which of the following is the primary reason that gasoline prices have risen over the last several decades in the U.S.? 14 Results Environmental 6 questions Mean: 4.39/6 SD: 1.48 73% Social Economic 5 questions 5 questions Mean: 3.55/5 SD: 1.23 71% Mean: 3.03/5 SD: 1.27 61% Total 16 questions Mean: 11.08/16 SD: 3.21 69% 15 Example Analysis 16 13 10 9.57 10.57 10.95 11.34 Freshman Sophomore Junior 7 Senior 4 ANOVA F(3,1330)=8.09, p<.001 1 Mean 16 Example Analysis Compare sub score by major Economic score Economics: Aerospace 3.82 engineering: 4.00 Animal science: 3.15 Finance: 3.02 English: 2.80 Accounting: 2.63 17 Phase 2 Combined our shortened set with a separate assessment developed at the University of Maryland Administered survey at both campuses 18 Phase 2 - Analysis IRT to compare information richness of questions across campuses using local descriptives (“Fishermen on Lake Erie” vs. “Fishermen in the Chesapeake Bay”) different ways of asking about the same topic Structural equation modeling Compare question types (multiple answer?) Knowledge structures (3 or 1 domain?) 19 Structural equation modeling Social Environmental Sustainability Economic 20 Survey Implementation Best practices to maximize response rates: Invitation script (from authority vs. student) Page length vs. number of pages Use of incentives Time of academic calendar Time of day, day of week Reminders 21 Moving Forward Adjust the instrument: Be clear about limitations: Some answers change over time Develop test bank of validated questions – try this on your campus and send us questions Multiple choice format Measures knowledge only Publish Phase 1 – International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 2014 22 Moving Forward Goals: Evaluate sustainability themed majors, programs, and courses Serve as an indicator for comparison within institutions Encourage friendly competition Hopes: Help solidify the concept of “sustainability” Provide some credence for more abstract educational goals 23 Acknowledgements Funded by: The Ohio State Office of Sustainability http://sustainability.osu.edu/ OSU’s School of Environment & Natural Resources http://senr.osu.edu/ 24 Thank You! Questions? Environment and Social Sustainability Lab www.ess.osu.edu Contains: This presentation The 16 phase 1 questions with multiple choice answers Email Zwickle.1@osu.edu Koontz.31@osu.edu