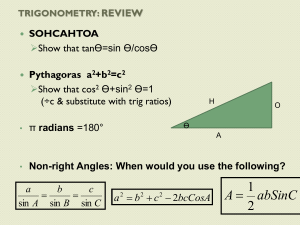
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
advertisement

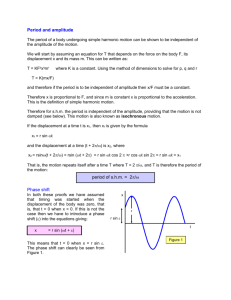
When Function values repeat at regular intervals the function
could be referred to as a cyclic function or periodic function.
You can model these types of behaviour with sine or cosine
functions.
Math 30-1
1
Math 30-1
2
Periodic Functions
Functions that repeat themselves over a particular interval
of their domain are periodic functions. The length of the
interval of repeat is called the period of the function.
Graph of sin x
Graph of cos x
One cycle
Math 30-1
3
Characteristics of a Periodic Function
Graph y = sin x , radians
The amplitude of a periodic function is one half the distance
between the maximum and minimum values.
1
max min
2
1 1
2
Period: 2p
Amplitude: 1
Domain: all real numbers
Range: {y| -1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
y-intercept: 0
zeros : 0, ±p, ±2 p, ...
GeneralMath
expression
for zeros
30-1
np , n I4
Graphing a Periodic Function
Graph y = cos x, radians
1
Period: 2p
Amplitude: 1
Domain: all real numbers
Range: {y| -1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
y-intercept: 1p 3 p
,
zeros:
2
2 p
np , n I
GeneralMath
expression
30-1
2
5
Parameters that affect the graphs of sine and cosine.
Vertical stretch factor |a|
Horizontal stretch factor
5.1 Transformations abcd
y = af(b(x - c)) + d
Horizontal and vertical translation
y = asin[b(x - c)] + d
amplitude
|a|
period
2p
b
phase shift
Math 30-1
displacement
6
Effect of parameter a in y = a sin x
Graph
y = 2siny x= 2sin x and y = 0.5sin x.
sinxx
yy==sin
y = 0.5sin x
Math 30-1
7
Comparing the Graphs of y = a sin x
y = sin x
Period
Amplitude
y = 2sin x
y = 0.5sin x
2p
2p
2p
1
2
0.5
All real numbers
All real numbers
Range
{-1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
{-2 ≤ y ≤ 2}
Zeros
np , n I
np , n I
Domain
All real numbers
{-0.5 ≤ y ≤ 0.5}
np , n I
The amplitude of the graph of y = a sin x is | a |.
When a > 0, there is a vertical stretch by a factor of |a|.
When a < 0, there is a vertical stretch by a factor of |a| and a
reflection in the x-axis.
Math 30-1
8
Determining the Period for y = sin bx, b > 0
Graph y = sin 2x
y = sin x
y = sin x
period
period of parent
b
period
2p
2
y = sin 2x
Length of period of parent
0 x 2p
transformed graph
0 2x 2p
0 x p
Math 30-1
9
Determining the Period for y = sin bx, b > 0
x
Graph y sin
period of
period
2
period
y = sin x
y = sin x
Length of period of parent
0 x 2p
Math 30-1
2p
1
2
parent
b
transformed graph
x
0 2p
2
0 x 4p
10
Comparing the Graphs of y = sin bx
0 x 2p
y = sin x
Period
Amplitude
period
y = sin 2 x
period of parent
b
2p
p
4p
1
1
1
All real numbers
All real numbers
Range
{-1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
{-1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
Zeros
np , n I
Domain
y = sin 0.5 x
All real numbers
{-1 ≤ y ≤ 1}
The period for y = sin bx is 2 p , b 0.
b
When b > 0, there is a horizontal
stretch by a factor of 1/|b|.11
Math 30-1
When b < 0, there is a reflection and a horizontal stretch of 1/|b|.
Determining the Period and Amplitude of y = a sin bx
Given the function y = 3sin 4x, determine the period
and the amplitude.
2p
.
The period of the function is
b
2p p
Therefore, the period is
.
4
2
The amplitude of the function is | a |.
Therefore, the amplitude is 3.
y = 3sin 4x
Math 30-1
12
Determining the Period and Amplitude of y = a sin bx
Determine the characteristics of y = -3sin 3x.
The period is 2 p . The amplitude is 3.
3
2p
3
4p
3
Math 30-1
5p
3
13
Writing the Equation of the Periodic Function
| maximum minimum|
Amplitude
2
| 2 (2) |
2
=2
2p
Period
b
2p
p
b
b=2
Therefore, the equation as a function of sine is
y = 2sin 2x.
Math 30-1
14
Writing the Equation of the Periodic Function
| maximum minimum|
Amplitude
2
| 3 (3) |
2
=3
2p
Period
b
2p
4 p
b
b = 0.5
Therefore, the equation as a function of cosine is
y = 3cos 0.5x.
Math 30-1
15
Suggested Questions:
Pages 233
1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11b, c
14, 17a, 20, C4
Math 30-1
16