introduction of the san diego city college
advertisement

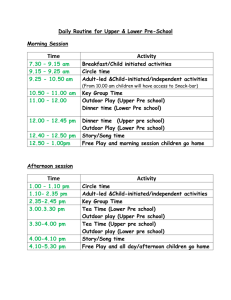
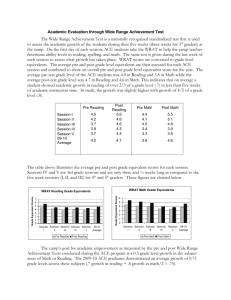
Teaching Basic Skills Mathematics: Outcome Assessment Xi Zhang, Campus Based Researcher, City College Jenny Kimm, Associate Professor, City College San Diego Community College District Presented at the: 2009 Strengthening Student Success Conference San Francisco, CA: October 7, 2008 INTRODUCTION OF THE DISTRICT San Diego Community College District 2nd largest district in the state Three 2-year colleges and eleven Continuing Education campuses Serves approx. 100,000 students each semester INTRODUCTION CITY COLLEGE OF THE SAN DIEGO San Diego City College is the first established community college in San Diego. San Diego City College is a public, two-year community college administered by the San Diego Community College District. Serving as the educational cornerstone of downtown San Diego, the college offers more than 100 majors, 100 certificate programs and 1,500 classes each semester to 16,000 students. PURPOSE OF THE PRESENTATION The primary purpose of this presentation is to share the research methodology and innovative techniques for data analysis and instrument refinement for SLO assessment rather than to disseminate results of the study. A second purpose is to support the teaching of Basic Skills Math in community colleges. PURPOSE OF THE STUDY Demonstrate SLO assessment cycle in the Math Department at San Diego City College Draw attention to measurement issues in assessing SLOs. Demonstrate methods of item analysis that has multiple advantages. RESEARCH DESIGN SLO assessment cycle A repeated measure design: pre and post design SLO ASSESSMENT IN THE MATH DEPARTMENT City College Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Cycle 6 Column Form For Developmental Math Program- Math 35, 95, 96 Year: 2008/2009 City’s Mission and Priorities Derived from City College Master Plan 1 MISSION The mission of City College has as its highest priority student learning and achievement in three state mandated areas. INSTITUTIONAL PRIORITIES (Details Listed on reverse Side) 1.Collaborative and Outreach Ventures 2.Student Success 3.Fiscal Adequacy and Efficiency 4.Accountability 5.Valuing Our Distinctions 6.Innovative Approaches 7.Long Range Strategic Planning Institutional Competencies 2 Institutional Competencies Communicat ion/Interpers onal Skills Critical thinking Analyses/Co mputation Cultural Sensitivity/ Global Awareness Information Managemen t/ Literacy Personal Responsibili ty Civic and Environmen tal Responsibili ty Student Learning Outcomes 3 1. Students will provide examples of on-campus resources for math support. 2. Students will develop competency and mastery in arithmetic operations involving numeric and algebraic rational expressions without the use of technology. 3. Students will translate word problems into mathematical expressions or equations. 4. Students will solve equations properly, logically and with written explanations. Means of Assessment/ Measurement & Criteria for Success 4 1 Students will attend Math 35 orientations. 2, 3, and 4 Students will take a pre-test and post-test. We aim to see a statistically significant increase in scores overall. 2, 3, and 4 Students must pass the departmental final exam with at least 36 out of 60 questions correct in order to be eligible to receive a passing grade in the class. Our goal is to see the following passing rates for the final exam: Math 35 = 80% Math 95 = 75% Math 96 = 70% Data/Results 5 Use of Results For Programmatic Improvement 6 Increase in number of students using tutorial services. Continue to develop Orientations/Workshops for Math 35, 95 and 96. Increase in scores from Pre to Post Tests out of 8 points. Math 35 mean scores: Pre = 4.4 and Post = 6.2 Math 95 mean scores: Pre = 5.1 and Post = 6.9 Math 96 mean scores: Pre = 4.4 and Post = 6.9 Develop the Pre- and Post-Tests online on our department website by fall 2009 to alleviate grading and taking up class time. Currently we have included an online version on MyMathLab. Passing rate for Dept Finals: Math 35 = 69.4% Math 95 = 75.7% Math 96 = 73.7% Expand the pre/post tests to include self-paced students. We have met our passing rate goals for Math 95 and 96, but we are below our goal for Math 35. Collect itemized data for each question on the pre/post tests as opposed to overall scores for each student. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Rasch Model Estimate both item difficulty and person ability Map both parameters on the same scale Inform instrument refinement Paired Sample t-test Statistically significant improvement from pretest to posttest TARGET POPULATION AND SAMPLE SIZE Developmental math courses: Pre-Algebra, Beginning Algebra, and Intermediate Algebra. This totals to over 1000 students taking the developmental math courses In Fall 2008, we collected pre/post paired data from about 250 students DATA COLLECTION: INSTRUMENT Developed one pre test and a similar post test TestGen testbank software 8 multiple choice questions Topics of the questions A Sample Instrument DATA COLLECTION: TEST ADMINISTRATION Pre-test administration Pre-test grading Post-test administration Post-test grading DATA MANAGEMENT For each student, itemized response per question and a total score were entered and paired in Excel Data then were exported to Winsteps for model fitting Estimates of item difficulty and student ability were analyzed in SPSS to compare pre test results to the post. DATA ANALYSIS Fit itemized responses rather than the total scores with the Rasch Model to obtain estimates of item difficulty and student ability. Name Pre 1 Pre 2 Pre 3 Pre 4 Pre 5 Pre 6 Pre 7 Pre 8 Total D 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 4 E 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 3 F 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 2 G 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 3 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 Name Post 1 Post 2 Post 3 Post 4 Post 5 Post 6 Post 7 Post 8 Total D 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 6 E 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 5 F 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 6 G 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 4 H 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 4 DATA ANALYSIS Map both item difficulties and person abilities on the same scale to produce the Item-Person Map. Compare Pre test and Post test Paired sample t-test Anchoring item difficulties MEASURES Item difficulty Student ability RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Pre-test Item difficulty Student ability RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Pre-test Person-item map RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Post-test Item difficulty Student ability RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Post-test Person-item map RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Pre and post comparison Anchoring item difficulties to produce a new set of student ability estimates RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Pre and post comparison Anchoring item difficulties to produce a new set of student ability estimates RESULTS (PRE-ALGEBRA FALL 2008 DATA) Pre and post comparison Paired sample t test Paired Samples Statis tics Pair 1 Math35PreR Math35PostR Mean -.9713 .7177 N 48 48 Std. Dev iation 1.40413 1.12064 Std. Error Mean .20267 .16175 Paired Sam ple s Te st Paired Dif ferenc es Mean Pair 1 Math35PreR Math35PostR -1.68896 Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean 1.53740 .22191 95% Conf idence Interval of the Dif f erence Low er Upper -2.13537 -1.24254 t -7.611 df Sig. (2-tailed) 47 .000 FINDINGS Results revealed that students scored statistically significantly higher in the post test compared to their performance in the pretest. Content areas that the instructors need to emphasize for teaching. Information for instrument refinement. INSTRUMENT REFINEMENT USE OF RESULTS FOR PROGRAMMATIC IMPROVEMENT Imbed the post test into the final exam to increase sample size. Also provide online version of pre test to collect data from online developmental classes. Rewrite or revise test questions based on results of item analysis. Identify difficult topics and disseminate the information to developmental math instructors for future teaching. Also disseminate the information to instructors of higher level math course for their preparation and planning. DISCUSSION Advantages of item analysis Solve measurement issues Conduct meaningful comparisons Bank good test items for constructing future tests Diagnostic function provides insight of the strength and weakness of student content knowledge. LIMITATIONS OF THE RESEARCH Small sample size Small number of test items Item stability Generalizability of the results QUESTIONS?