3.1 Lines and Angles
advertisement
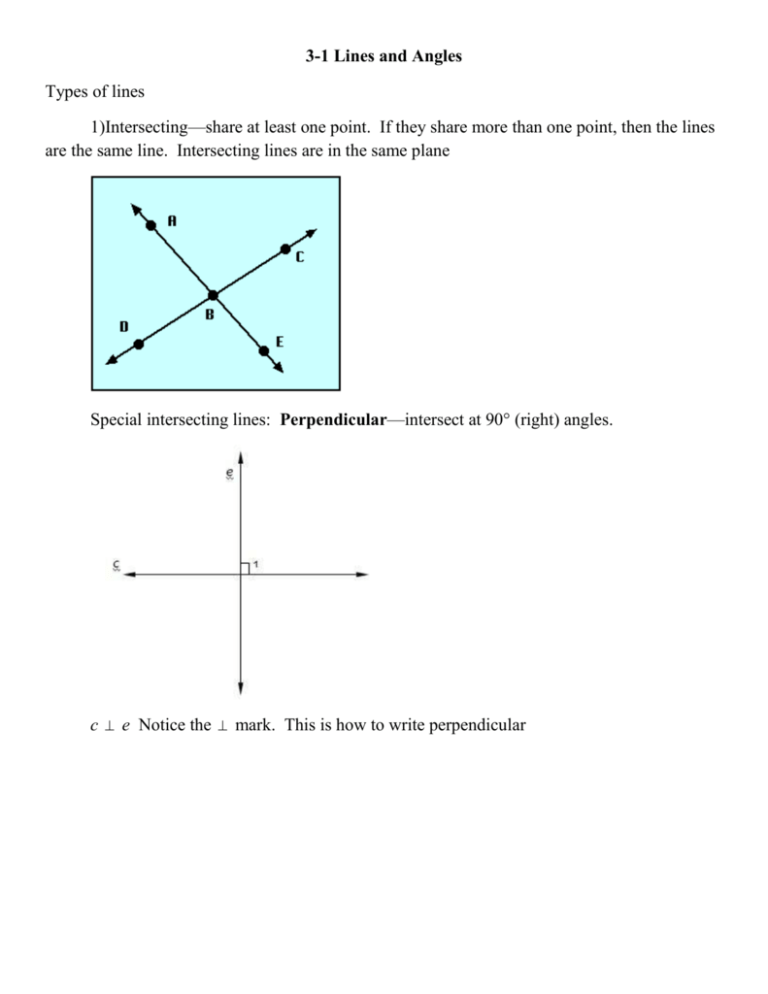
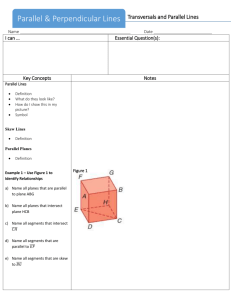
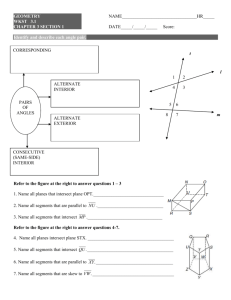
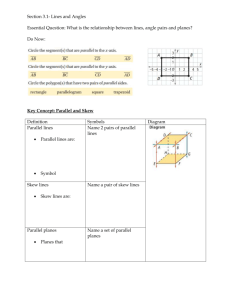
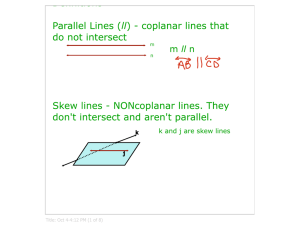
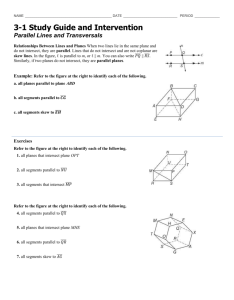
3-1 Lines and Angles Types of lines 1)Intersecting—share at least one point. If they share more than one point, then the lines are the same line. Intersecting lines are in the same plane Special intersecting lines: Perpendicular—intersect at 90° (right) angles. c e Notice the mark. This is how to write perpendicular 2) parallel. Parallel lines are coplanar, never intersect and are always the equidistant (same) distance apart. They are in the same plane p || q Notice the || marks. This is how to write it We mark parallel lines with arrows someplace on the lines 3) Skew lines—non-intersecting, non-parallel lines. Skew lines are in different planes Two planes can 1. Intersect. The intersection of two planes is a line 2. Not intersect. The planes are parallel A || B Transversal—a line that intersects two coplanar lines at two different points. Corresponding angles—lie on the same side of the transversal, on the same sides of the lines Pairs of Corresponding angles < 1 and < 5 < 3 and < 7 < 2 and < 6 < 4 and < 8 Alternate Interior Angles—are nonadjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the transversal, between the lines Alternate Interior angles < 3 and < 6 < 4 and < 5 Alternate Exterior Angles—lie on opposite sides of the transversal, outside the lines. In the above diagram, < 2 and < 7 and < 1 and < 8 are two pairs of alternate exterior angles.