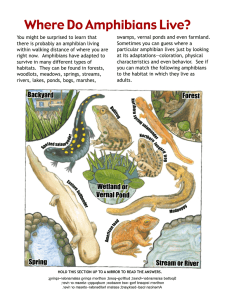
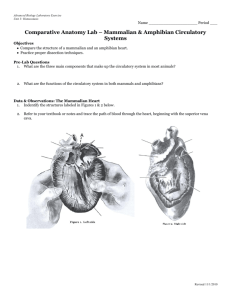
Amphibians Powerpoint
advertisement

Modern Amphibians = Lissamphibia Apoda (caecilians) Urodela (Caudata) (salamanders and newts) Anura (frogs and toads) Shared derived traits of Lissamphibia Table 10-1 Pedicellate teeth Operculum-columella complex – Transferring air waves into fluid waves and ground vibration into sound. Levator bulbi muscle Closed Eye Thin skin with mucus and poison glands Implications for physiology and ecology Breathing via the skin Water through the skin – a boon and a bane The skin as a storehouse for toxins Chapter 10.5 And warning and cryptic pigments Aposematic coloration Apoda (Gymnophiona) Caecilians Reduced eyes, sensory tentacles, dermal folds Apoda Reproduction Internal fertilzation with phallodeum Cloaca Oviparous (egg guarding) or viviparous Adult teeth Baby teeth grappling Urodele – Caudata Distribution Holarctic Terrestrial Aquatic Hedonic (scent) glands Reproduction Visual displays and olfaction Sexual dimorphism Nasolabial groove Egg mass Fertilization external (few) or internal (most) Spermatophore Fire salamander - viviparous Anura most diverse, most widespread Highly derived body form Urostyle Illia Anura Reproduction dominated by vocalization Expense? See text Functions of reproductive calls? Explosive versus prolonged breeding? Tungara frogs Whine Males alone – whine only Males with males – Whine- chuck Females prefer whine- chuck call Explain the pattern Chuck External fertilization via amplexus Male Female Function of sexual dimorphism? Biphasic Lifestyle Advantages? Disadvantages? Amphibian Conservation Issues Cane Toads (Bufo marinus) Introduced into Australia Conservation concerns? Bullfrog (Rana catesbiana) introductions Major Conservation Concern: Amphibian Declines 2006 report: 1,856 species, 32.5 percent of the known species of amphibians, are “globally threatened,” (vulnerable, endangered or critically endangered). By comparison, 12 percent of bird species and 23 percent of mammal species are threatened. 435 amphibian species are in rapid decline, at least 9 species have gone extinct since 1980 and another 113 species have not been reported from the wild in recent years and are considered to be possibly extinct. Causes? Amphibian characteristics that increase susceptibility to environmental changes?? Habitat Loss Over-exploitation as: Food 6 million into Hong Kong/yr Pets - Goliath frog Introduced Species 99% of lakes in Sierra Nevada originally without trout. Rana mucosa (native frog) declining in part due to trout predation Amphibian egg survival and ultraviolet light at high elevations Hyla Rana Bufo Increased ultraviolet radiation due to reduced ozone Worldwide studies of UV on amphibians Red = negative effect of UV UV protected No UV protection Pollutants Nitrogen, pesticides, acidification, Deformities Trematodes parasites cause abnormalities Eggs Meracidium Cysts Cercaria Chytrid Fungus Global Climate Change? Direct: Loren’s paper Interaction with: disease susceptibility to toxins susceptibility to parasites Species Introduction?