Viewing Plant Cells
advertisement

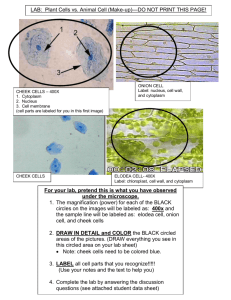
Name____________________________ Biology Lab: Viewing Plant and Animal Cells Period_____________Date___________ ___ Purpose: To observe plant and animal cells and describe the differences between them. Part I: Plant Cells 1. What is the function of chloroplasts? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Name two structures found in plant cells but not animal cells. a.___________________________ b.___________________________ 3. Name three structures found in plant cells AND animal cells. a.___________________________ b.___________________________ c.___________________________ 4. Which structure surrounds the cell membrane (in plants) and gives the cell support. _________________________ Important Note: Please use colored pencils for all diagrams and label all structures listed!! Part A: Cork Cells 1. Repeating Hook’s observations under the microscope, we will now observe cork cells. Carefully slice off a thin piece of cork with a razor blade and prepare a wet mount of it. View the slide and make a drawing of what you see. Record the total magnification that you are viewing it under! Label: Cell Wall Cork Magnification:_____________ 1 2. Why are the cork cells empty? __________________________________________ 3. Is cork produced by an animal or a plant? ________________________________ 4. Use your text to determine the name of the chemical which makes up the cell wall: __________________________________________ PART B - Onion Cells 1. Make a wet mount of a piece of onion epidermis. Use the diagram below to help you follow the correct procedure when adding the Lugol’s iodine. 2. Put on your safety goggles. CAUTION: Iodine can stain clothing and skin. 3. Add Lugol’s iodine solution to one side of the cover slip and put a paper towel on the other side to pull the stain under the cover slip. 4. View under low and high power. Sketch the cells at each magnification in the circles below: Low Power High Power Label the: -- Cell Wall -- Nucleus -- Cytoplasm 5. Estimate how many cells you can see under low power: _______ high power: _______ 6. Why was Lugol’s iodine used in viewing onion cells? __________________________________________________________________ 2 PART C: Elodea Cells 1. View a prepared slide of an elodea (a simple water plant). Sketch the cells at each magnification. As the slide warms, you may see chloroplasts moving. Label the: -- Cell Wall -- Chloroplasts -- Cytoplasm Low Power High Power 1. Describe the shape and the location of chloroplasts in Elodea. Shape: _____________________________________ Location: ___________________________________ 2. Why were no chloroplasts found in the onion cells? (hint: where do you find onions?) ____________________________________________________________________ 3. Which type of cell was smaller – the onion cells or the elodea cells? ___________________________________________________________________ Part II: Animal Cells Part A: Human Cheek Cells 1. Place a drop of water on a clean slide. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek with a clean toothpick as shown in the diagram on the following page. Stir the toothpick in the water on the slide. Throw the toothpick away! 3 2. Put on your safety goggles. Add a drop of methylene blue stain to the slide. (Methylene blue can stain clothing and skin.) Use a clean toothpick to stir the cells on the slide. Throw the toothpick away. Place a cover slip on the slide. 3. Examine the slide under low and high power. Draw three to four cheek cells as they appear under high power. Label the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus on one of the cells. 4. Describe the shape of a cheek cell _______________________________________ 5. Are the cheek cells produced by plants or animals? __________________________ 6. Is a cell wall present? ______________________ 7. Are cheek cells alive? ______________________ 8. Why was a stain added to the cheek cells? __________________________________ 4 Part B: Frog Blood 1. Observe a prepared slide of frog blood under low and high power. 2. Draw several frog blood cells as they appear under high power. Label any cell structures that you can see. 3. Describe the shape of frog blood cells: _________________________________ 4. Can a cell wall be seen in frog blood cells? ______________________________ 5. Are blood cells from a producer or consumer?____________________________ 6. Which cell part name is used to describe the outer edge of a frog blood cell?_____________________________________________________________ 7. Which cell part name is used to describe the dark center of a frog blood cell? _________________________________________________________________ Analysis and Conclusions: 1. You looked at cork cells, onion cells, Elodea cells, human cheek cells, and frog blood cells. a. Which of these cells come from plants? ___________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ b. Which of these cells come from animals?___________________________________ 5 2. Which cell structures are present in the plant cells that are not present in the animal cells? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. How do the shapes of the plant cells differ from the shapes of the animal cells? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Extra for Experts! Choose 2 slides from the “Extras” to diagram below. Please label your diagrams with the names of the organisms and their magnification: Organism____________________ Organism____________________ Magnification_________________ Magnification_________________ 6