The Russian Revolutions
advertisement

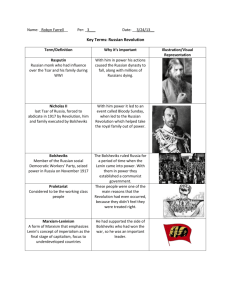
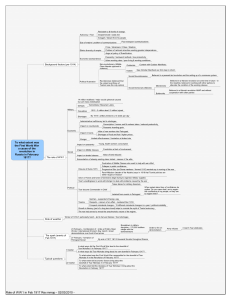
The Russian Revolutions: March 1917 November 1917 1928-1939 Precursor to March 1917 • Revolution of 1905 – Nicholas II agrees to become constitutional monarch – Dumas were created, but had no real power. One was dissolved by Tsar; he changed voting requirements for another. – Not much real reform; Stolypin land reforms ended with WWI. Causes of Revolution of March 1917 • Tsar ineffectual and weak • Reforms of 1905 failed, except for ending redemption dues and limited land distribution under Stolypin. • Peasant population exploded by 800,000 yearly in last years of 19th c-- wanted land. • Workers-only 2-3 % of population wanted representation in factories, better working conditions and pay. Causes of March 1917 Revolution continued • National minorities wanted autonomy. • Soldiers want representation, supplies (1 in 3 no boots or gun), and end to harsh discipline. • Bolsheviks called for peace, land, bread, power to the worker’s soviets. • World War I- brought problems to surface – Shortages – rampant inflation – massive losses Causes of March 1917 Revolution continued Tsarina seen as “German woman,” extravagant, and removed. Influenced policy in Tsar’s absence. When people were striking for bread and better working conditions in March 1917, she called them “Hulligans” in a letter to the Tsar and told him that they would go back inside when the weather turned cold. Causes of March 1917 Revolution continued Rasputin was resented. Seen as negative influence on policy and on Tsar and Tsarina. He is murdered with difficulty in Dec 1916. Events of March Revolution • March 8, 1917Women’s Day strikes”Bread” • March 15-Nicholas II abdicates • March 18- Provisional Committee takes over Bolsheviks gain strength • April 1917-Germans give free passage to Lenin. • July Days- 1917 • Kornilov Revolt-Kerensky discredited. • Lenin promises “Peace, Bread, Land, Power to Worker’s Soviets.” • Bols. not part of Provisional government. November (October) Revolution • November 8, 1917, unpopular Prov. Gov’t “falls like a piece of wet mud.” • November 1917- Constituent Assembly elected. • CHEKA (Secret Police) created and gains strength. • January 1918- Long awaited Constituent Assembly is dissolved by Bolsheviks. New Economic Policy, 19211928 • • • • Retreat from immediate socialism Allowed some private ownership Lenin died in 1924. By 1928, farm production reached 1913 levels, but Stalin did not like the success and independence of kulak farmers, who thrived with private ownership. Civil War and Allied Intervention • March 1918Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with GermanyRussia lost 1/3 of its land! Civil War and Allied Intervention, 1918-1921 • After Brest-Litovsk, allies move in to protect munitions and against the Bolsheviks (Reds). • White Army = Allies and other countries, plus monarchists, national minorities, Cossacks, and others. War did not go well for White Army, which had ambiguous leadership. Stalin’s Revolution: Collectivization, Industrialization, and Terror • Collectivization-results in starvation and deaths of approx. 10,000,000, especially in Ukraine • 5 Year plans- rapid Industrialization. • Terror- gulag, show trials, secret police = deaths of as many as 20,000,000.