Thin film applications and friction
advertisement

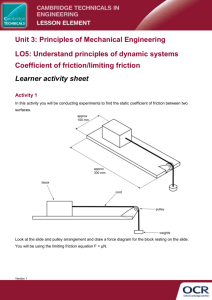
David Mortimer Physics Teacher Del Rio High School SFDR-CISD Haiyan Yang, Ph.D. Xinghang Zhang, Ph.D. Specific Application of Technology ◦ The concept of the application of material onto another surface to change or enhance, aka., exploit, materials. Future applications -The how and why of Vacuum Systems to include the gas laws. -The stacking of atomic crystal structures. -Testing of material properties. TEKS B1-4, Conducting field and lab experiments, building knowledge by physical, mathematical, and conceptual models, understanding the whole, Investigations led to changing understanding. C,1,a,b, Lab Safety C,2,a-e, use scientific method C,3,a-d, critical thinking and problem solving. C,4,a, laws governing motion TAKS Objective 1, The nature of Science Objective 5, Motion, Force, and Energy 1. 2. 3. 4. Pre-Testing Before starting this lesson the teacher would have covered the following: Changes in Motion a. Force is a vector quantity that causes changes in motion. b. Force can act either through the physical contact of two objects or at a distance. c. Free body diagrams. Newton’s first law a. “Law of inertia”-nothing will change what it is doing unless a net force>0 acts upon it. Newton’s second law a. Force = mass X acceleration Newton’s third law a. Rocket law – for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Students will be asked to come up with a plan to test certain materials that are applied to other materials so that they can test for the best reduction in friction. Students will be shown situations where the least friction will be of benefit to a consumer. Students will compete for longest slide at the end of the lab experience. XYZ Skateboard Co. Application for bids Dear Valued Future Vendor: XYZ Skateboard Company is accepting bids for a thin film product that will lessen the coefficient of friction on our line of very popular skateboards. XYZ Skateboard began in 1992 and has been know from the very beginning to be an innovator in skateboard design. This process is expected to be very competitive and the chosen bidder will likely reap financial and personal reward. Since we believe in the common man and his innovative ability, the following is provided to help you, the bidder, to better understand the concepts that we are dealing with. We will be offering a class where you may learn to test for the coefficient of friction, how hard is it to get something to move, and, also, you may test your own samples in our state of the art testing facilities. The goal of this lab is to determine the static and kinetic coefficient of friction for various materials in contact with one another and then apply a coating of some other materials to determine if the coefficient increases or decreases. The student will also try to show the effect of increased mass, increased/decreased surface contact, changes in the angle of the inclined board, and changes in velocity. The student will also be making conclusions about which materials work best together in different situations. The student will be asked to rank your findings and a contest for the best sliding mixture of materials will occur at the completion of the lab. Fourier Lab Pro Data loggers Distance Sensor Force Sensor 4’ shelf Ring stand Set of masses Aluminum block Steel block Brass block 3-Petri dishes Clamp Protractor Meter stick Graphing calculator Balance Scale Teflon Spray Silicon spray Graphite String 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Clean up your block so that it has the least amount of friction. Place wax paper onto the scale and zero out the scale. Find the mass (m) of the first block. Place the first block into the set up. Calculate Fgrav=m*ag and enter into the data sheet. If the weight is on an incline, the normal force will be reduced by the cosine of the incline angle. The equation is N = wcos(a) where: N is the normal force on the incline W is the weight, weight is a force, the force of gravity, Fgrav=mass*acceleration of gravity. a is the incline angle cos(a) is the cosine of the angle a Wcos(a) is W times cos(a) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Calculate the normal force, Fnormal=Fgrav *cosΘ and enter into the data sheet. Cos (0) = 1 Connect the force sensor to the string and pull, note what the force is when the sample starts to move. This is your Fapplied. Enter into the data sheet. Pull the mass again with constant velocity, enter the force required to keep the block moving. Replace the block onto the board and raise the board until the block begins to slide. Note the angle at which the block began to slide. Calculate the Fnormal using your new angle. 11) 12) 13) 14) Repeat steps 3-10 for each set of blocks. We are now going to apply a thin coat of three different materials, Teflon spray, Silicon spray, and graphite to see how these coating affect the coefficient of friction. It is very important that you clean the sample very well after each application of material. Place the first sample into the Petri dish with the graphite. Move it around to completely cover the bottom of the sample. We want a thin film. Excess material should not be evident. The thinner the layer the better. Repeat steps 3-10 using the new film and note your results. Material A/mass/ position/coating if applicable Material B Ex., aluminum, .5N,wide side forward, no coat Wood Shelf Ex., Aluminum, thin side forward,.55N, Graphite Steel bar Fgrav =mag Applied force to start movement Applied force to maintain movement Fstatic friction FKineticriction Calculated FNormal=Fgrav *cosΘ Angle of board Fnormal on angle Calc µStatic= Fstatic friction/ FNormal Calc µkinetic= Fkinetic friction/ FNormal Static Force Kinetic Force Force Distance 40 257 41 280 F=k*distance 48 47 y = 0.0238x + 34.184 R2 = 0.9934 46 42 327 43 365 44 413 45 446 46 489 40 47 550 39 Force 45 44 Linear ( ) 43 42 41 0 100 200 300 Distance 400 500 600 Post Testing Student should have mastered the concepts presented in the pre-testing phase. Newton’s laws and Force Diagrams The student should have a clear understanding of the difference between static and kinetic friction. The student should be able to determine the coefficient of static friction. The student should be able to make informed choices given information about coefficients of friction to choose the right supplies for the right job. Students should realize that they do not need sophisticated equipment to determine forces. Most importantly, students should realize that they have seen these concepts all of their lives and realize that we are only reinforcing what they already know. Generally, what is the normal force? What is the applied force? When does something begin to slide? Why does it not slide originally? Is the normal force more or less when the board is inclined? What helps make it slide when it is on an incline? Is the µkinetic ever bigger than the µStatic? Why don’t we consider air resistance? Draw a free body diagram of the horizontal plane and another one for the angled plane. Label all forces that are applicable. Is the coefficient of friction constant depending only on the types of surface in contact? (Remember it is very difficult to reproduce exactly the same value for the coefficient of friction on each run.) Does the surface area, positioning, change the coefficient of friction? Explain. Does the normal force change the coefficient of friction? What are your sources of experimental error? Xinghang Zhang, Ph.D. Haiyan Wang, Ph.D. Joon Hwan Lee Optical , transparency, transmittance South Korea Jie (Joyce) Wang High Temperature Super Conductor 3/21/2016 Roy Araujo : Functional Nitride Thin Films Peru Ick Chan Kim Prop. Of film through thickness change South Korea Harrison Tsai same as Joyce Jong Sik Yoon Functional Oxide Thin Films South Korea Sunmee Cho, South Korea Zhenxing Bi Deposition Patterns China Acknowledgements I am thankful to the following National Science Foundation All of the TAMU faculty and Staff Texas A&M Giggem Aggies Dr. Wang and Dr. Zhang Zhenxing Bi Ph.D. Candidate Joon Hwan M.S. Candidate All of the rest of the Pulsed Laser Deposition laboratory candidates Ms. Crystal Woods All of the E3 Participants Dixie Chicken