6.1 – solving linear inequalities with addition and subtraction When
advertisement

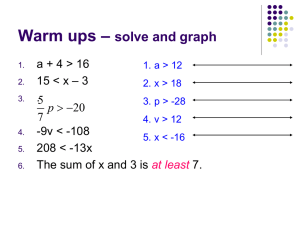
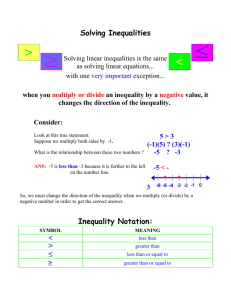
6.1 – solving linear inequalities with addition and subtraction When solving for x, know how to undo an operation. Be able to graph a linear inequality on a number line. 6.2 – solving multi-step linear inequalities with multiplication and division When solving for x, do you undo the addition/subtraction or multiplication/division first? What happens to the linear inequality when you multiply/divide by a negative number? Be able to graph a linear inequality on a number line. 6.3 – solving compound inequalities When is an inequality a union of two inequalities? When is an inequality an intersection on two inequalities? Be able to graph both an and as well as an or inequality. 6.4 – solving absolute value inequalities Remember absolute value is the distance from zero. When solving an absolute value inequality, what are the steps? o Solve for the absolute value brackets first. o Write two inequalities from the absolute value. o Solve each for x. o Graph each on a number line. 6.5 – solving linear inequalities in two variables When is the boundary line dashed? When is the boundary line solid? What are the steps to graphing a linear inequality on a coordinate plane? What form must the inequality be in when graphing on a coordinate plane? How do you know which half-plane to shade? --- pick a test point Be able to graph a linear inequality with two variables on a coordinate plane. 6.6 – Mean, Median, and Mode & Stem-and-Leaf Plots Be able to find the mean, median, and mode from a set of data. Does the data set have to be in numerical order? Be able to construct a stem-and-leaf plot. 6.7 – Box-and-Whisker Plots What are the 5 parts of a box-and-whisker plot? What is the IQR of a box-and-whisker plot? What happens when you have an even number of pieces of data? Be able to construct a box-and-whisker plot.