Monitoring, Audits, and Inspection
advertisement

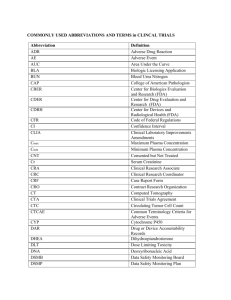
Monitoring, Audits, and Inspection Oh my! Rachel Sheppard Regulatory Director, OCRSS Types of Review • Routine monitoring • Quality assurance audit • IRB • Audit Services • Sponsor • Routine investigation • For cause investigation Key parties • • • • • • • PI Data coordinator/study coordinator Research nurse Investigational pharmacist IRB Parts of Hospital Contracts office Monitoring • Planned review of documentation and data • • • • • • ICF documentation Screening documentation Diagnostic test review documentation Source documentation Reporting of events to IRB/sponsor IP inventory and dispensation • Changes in monitoring • High turnover Monitoring continued • • • • • Important relationship Good monitor vs. bad monitor Collaborative works best Open items must be reviewed again Documentation of all requests IRB audit • • • • • Review of regulatory and clinical files Different levels Full board review Cause and not for cause Not for Cause triggered by • New investigator • Random • For Cause triggered by • External governing agency audit • CAR document review • Excessive deviations FDA Audit • Routine- verification of data quality, compliance and subject protection • High enrollment • First in data • High profile study • Directed – for cause • • • • Patient complaint Whistle blower Offshoot of other investigation Serious events • Credentials and 482 Steps to prepare • Do not panic • Get all the information • Timeline • Scope • Type of audit • • • • • Notify all parties Designate contact for auditor Assign duties to staff for audit Arrange workspace and meeting space Prepare staff for questions Responding to questions • • • • • • • Understand question – ask for clarifications Take your time answering (think first) Answer only what is asked Tell the truth Do not argue and be positive Tell the auditor/investigator if you do not know Take notes on what was asked (after) Documents • • • • • • • Regulatory files CRFs and source documents Ensure access to eCRFs SOPs IP accountability records List of all projects PI has ongoing Request medical records Close out meeting • • • • • Discussion of findings Notify investigator/auditors of any corrective actions taken FDA 483 Clarify any discrepancies on 483 Involve university offices in any written responses Best Practices • • • • • • • • • Document, document, document Keep a binder of ICF copies Consistency of documentation Have and know SOPs Have isolated workspace to limit access Control copy access Only supply requested information Designate an escort/assistant Be helpful Best Practices • • • • • Don’t wait for an audit to have good records Identify and report problems CAP (correct and prevent) Document correction methods Evaluate that CAP works Reference material • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 21CFR50, 21CFR56, 21CFR312, ICH E:6 21CFR: 312.68 Part 312 -- Investigational New Drug Application/Inspection of investigator's records and reports FDA: Bioresearch Monitoring: Clinical Investigators and Sponsor Investigators Guidance for FDA staff FDA: Bioresearch Monitoring: FDA/ORA Bioresearch Monitoring FDA: Compliance Program Guidance Manual (CPGM) (Chapter 48) FDA Guidance: Computerized Systems Used in Clinical Investigations FDA Guidance: FDA Inspections of Clinical Investigators FDA: Form 483 Frequently Asked Questions Sheet: Guidance for IRBs, Clinical Investigators, and Sponsors: FDA ICH: International Committee on Harmonization (ICH) E: 6 Good Clinical FDA: Investigations Operations Manual FDA Guidance: Investigator Responsibilities — Protecting the Rights, Safety, and Welfare of Study Subjects FDA Guidance: Part 11, Electronic Records, Electronic Signatures – Scope and FDA: Preparing for a Clinical Investigator Inspection FDA: Regulatory Procedures Manual (RPM)