Ancylostoma duodenalis Necator americanus
advertisement

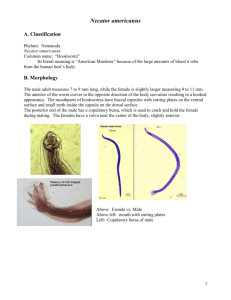
+ Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus Kallie McGettigan + Hookworms http://animal.discovery.com/videos/monsters-inside-meflesh-eating-hookworm.html + Facts: Commonly known as the hookworm 576-740 million people in the world are infected Necator americanus was widespread in the Southeastern United States until 20th century and was known as the “American killer” Second most common human helminthic infection + Taxonomy: Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Chromadorea Order: Rhabditida Family: Ancylostomidae Genus: Ancylostoma Necator Species: duodenale americanus + Geographic Range Worldwide, most common in areas with warm, moist climates and soil N. americanus commonly found in the Americas, Africa, India, Southeast Asia, China and the Pacific Islands A. duodenale commonly found in Southeastern Europe, Northern Africa, India, China, and Southeast Asia, also in small areas of the U.S., Caribbean Islands, and South America + Hosts Definitive Host: Humans Intermediate Host: None + Morphology Necator americanus The anterior end is curved dorsally giving them their “hook” appearance Has a pair of dorsal and a pair of ventral cutting plates surrounding the anterior margin of the buccal capsule. Also has a pair of subdorsal and subventral teeth near the rear of the buccal capsule Males: 7 to 9 mm long have a copulatory bursa that’s diagnostic for the genus The needle like spicules have minute barbs at their tips and are fused distally Females: 9 to 11 mm long Vulva is located in middle of their body Produce 5,000 to 10,000 eggs a day Live for 3 to 5 years + Morphology Ancylostoma duodenale The anterior end is curved dorsally giving them their “hook” appearance Has two ventral plates on the anterior margin of the buccal capsule that each have two large teeth. They also have a pair of smaller teeth further back in the capsule Males: 8 to 11 mm long Have a copulatory bursa characteristic to the species Needle like spicules have simple tips and are not fused distally Females: 10 to 13 mm long Vulva is located about a third of the body length from the posterior end Can lay 10,000 to 30,000 eggs a day Can live up to a year + Life Cycle + Life Cycle Eggs are passed in the stool, and hatch in 1 to 2 days when in warm moist conditions. The released rhabditiform larvae grow in the feces and soil. After 5 to 10 days and two molts they become filariform larvae that are infective. The infective larvae can survive 3 to 4 weeks in favorable environmental conditions. When contact occurs with a human host, the larvae penetrate the skin and are carried through the blood vessels to the heart and then to the lungs. Then they penetrate into the pulmonary alveoli, up the bronchial trees to the pharynx and then are swallowed. They end up in the small intestine, where they attach to the intestinal wall, where they ingest blood. Most adult worms are eliminated in 1 to 2 years, but can survive for several years. Adult females release eggs which are then excreted in the feces. + Pathology Small infections typically asymptomatic, less than 25 worms Localized skin manifestations (“ground itch”) can occur during penetration of the L3 larvae Severe infections Anemia due to blood loss, can eventually lead to cardiac complications In children, the lack of iron and protein can lead to growth and developmental problems Gastrointestinal and nutritional symptoms can occur Respiratory symptoms can occur during the migration of the larvae through the pulmonary system + Diagnosis Identification of eggs in a fecal sample In light infections, a more concentrated sample is used by performing a formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation technique Use larvae to distinguish between the two worms, cannot tell them apart by the eggs + Treatment In countries where the infection is common and reinfection is high, light infections are not treated In the U.S. mebendazole and albendazole are typically used Pyrantel pamoate is also used Iron supplements are also given if infected person has anemia + Control and Prevention Avoid walking barefoot in areas where infection is common and where night soil is used Avoid ingesting soil from these areas Effective prevention includes not defecating outdoors and using effective sewage disposal systems + References http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/hookworm/ http://dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/HTML/Hookworm.htm http://animal.discovery.com/videos/monsters-insideme-flesh-eating-hookworm.html Roberts, L. Janovy, J. Foundations of Parasitology, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009. + Quiz: Which of these is a host? + Which hookworm is able to cause more damage with a few number of worms present ? Necator americanus Ancylostoma duodenale + Which order does the hookworm belong to? Piroplasmida Trichurida Rhabditida Cyclophylidea + Where do you find the adult hookworms? + Which stage of the life cycle is infective? Rhabditiform Adult Worm Larvae Eggs Filariform Larvae